The concept of zero exponent rules is a fundamental aspect of algebra and mathematics, playing a crucial role in simplifying expressions and solving equations. At its core, the zero exponent rule states that any number raised to the power of zero is equal to 1. This principle, often represented as $a^0 = 1$, applies to all non-zero values of $a$. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the zero exponent rule, exploring its underlying principles, applications, and significance in various mathematical contexts.
Key Points
- The zero exponent rule asserts that any non-zero number raised to the power of zero equals 1.
- This principle is foundational in algebra and mathematics, facilitating the simplification of expressions and the solution of equations.
- The rule applies universally to all non-zero values, with the exception of zero itself, which is undefined when raised to the power of zero.
- Understanding the zero exponent rule is essential for manipulating algebraic expressions, solving polynomial equations, and grasping more advanced mathematical concepts.
- The rule's implications extend beyond basic algebra, influencing fields such as calculus, geometry, and mathematical analysis.
Understanding the Zero Exponent Rule

The zero exponent rule is based on the concept of exponents, which represent the operation of repeated multiplication. For instance, a^3 means a \times a \times a. However, when we encounter a^0, it signifies a scenario where a is not multiplied by itself at all, suggesting a “neutral” or “identity” element in terms of multiplication. This element, in the context of multiplication, is 1, as any number multiplied by 1 remains unchanged.
Mathematical Justification
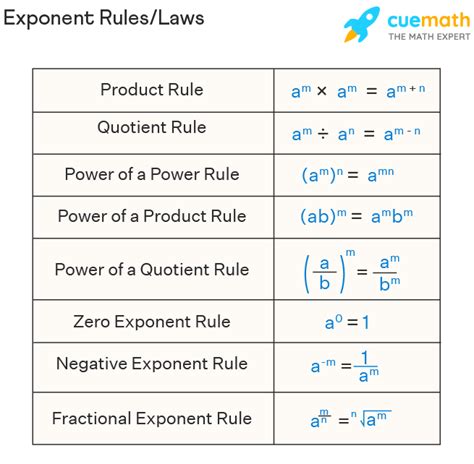
One way to justify the zero exponent rule is through the use of the laws of exponents, specifically the rule that a^m \times a^n = a^{m+n}. By considering a^m \times a^{-m}, we can see that this product must equal a^{m-m} = a^0. Since a^m \times a^{-m} = 1 (because a^{-m} is the reciprocal of a^m, and their product is 1), it follows that a^0 = 1. This reasoning underscores the consistency and coherence of the zero exponent rule within the broader framework of algebraic operations.
| Exponent Rule | Mathematical Representation |
|---|---|
| Zero Exponent Rule | $a^0 = 1$ |
| Product of Powers Rule | $a^m \times a^n = a^{m+n}$ |
| Power of a Power Rule | $(a^m)^n = a^{m \times n}$ |
Applications of the Zero Exponent Rule

The zero exponent rule has far-reaching implications in mathematics, extending beyond the realm of basic algebra. It plays a crucial role in calculus, particularly in the study of limits and the differentiation of functions. In geometry, understanding the zero exponent rule can aid in comprehending the properties of shapes and figures, especially when dealing with scaling factors and dimensional analysis.
Calculus and Limits
In calculus, the concept of limits is fundamental, and the zero exponent rule can be instrumental in evaluating certain types of limits. For instance, when considering the limit of f(x) = x^0 as x approaches any non-zero value, the function evaluates to 1, illustrating the rule’s applicability in this context.
Moreover, the rule is essential in the application of L'Hôpital's rule, where it helps in simplifying expressions and resolving indeterminate forms. The ability to recognize and apply the zero exponent rule in these scenarios underscores its importance in calculus and mathematical analysis.
What is the significance of the zero exponent rule in algebra?
+The zero exponent rule is significant in algebra as it provides a foundational principle for simplifying expressions and solving equations. It ensures consistency and coherence in algebraic operations, particularly when dealing with exponents.
How does the zero exponent rule apply to calculus and limits?
+In calculus, the zero exponent rule is crucial for evaluating certain types of limits and for applying L'Hôpital's rule. It helps in simplifying expressions and resolving indeterminate forms, demonstrating its utility in advanced mathematical contexts.
What are the implications of the zero exponent rule for geometric and dimensional analysis?
+The zero exponent rule has implications for geometric and dimensional analysis, particularly in understanding scaling factors and the properties of shapes and figures. It aids in comprehending how dimensions interact and influence the characteristics of geometric entities.
In conclusion, the zero exponent rule is a fundamental principle in mathematics, underpinning various algebraic operations and extending its influence into calculus, geometry, and beyond. Its significance lies not only in its simplicity but also in its profound implications for understanding and manipulating mathematical expressions. By grasping the zero exponent rule, individuals can develop a deeper appreciation for the coherence and beauty of mathematical structures, ultimately enhancing their ability to navigate and contribute to the vast expanse of mathematical knowledge.