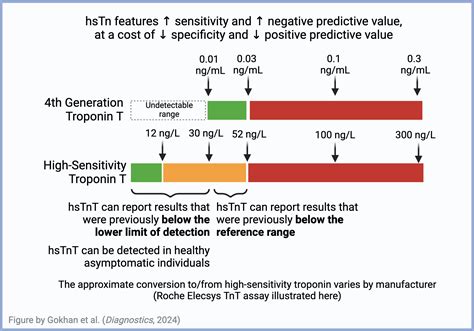
Troponin high sensitivity assays have revolutionized the field of cardiovascular diagnostics, enabling healthcare professionals to detect even minor myocardial damage with unparalleled precision. The introduction of high-sensitivity troponin (hs-TnT) assays has significantly enhanced the diagnostic accuracy of acute myocardial infarction (AMI), allowing for earlier intervention and improved patient outcomes. With a detection limit of 0.001 ng/mL, hs-TnT assays can identify troponin elevations that were previously undetectable, thereby expanding the scope of cardiac damage assessment.
Principles of Troponin High Sensitivity Assays
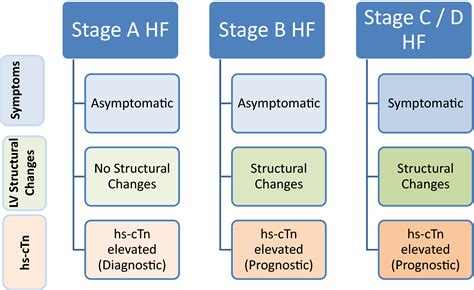
The hs-TnT assay is based on a sandwich immunoassay principle, where two highly specific antibodies bind to the troponin T molecule, facilitating its detection. The high sensitivity of these assays stems from the use of advanced antibody technologies and optimized assay designs, which enable the detection of troponin concentrations as low as 1-2 ng/L. This heightened sensitivity allows for the identification of subtle myocardial damage, even in the absence of overt clinical symptoms.
Clinical Applications of Troponin High Sensitivity Assays
The clinical applications of hs-TnT assays are multifaceted, with a primary focus on the diagnosis and management of acute coronary syndromes (ACS). By detecting minor elevations in troponin levels, healthcare professionals can identify patients at high risk of adverse cardiac events, enabling timely initiation of evidence-based therapies. Furthermore, hs-TnT assays have been shown to be valuable in the assessment of cardiac damage in patients with chronic kidney disease, heart failure, and pulmonary embolism.
| Assay Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Detection Limit | 0.001 ng/mL |
| Upper Reference Limit | 14 ng/L |
| Coefficient of Variation | <10% |
Key Points
- High-sensitivity troponin assays can detect minor myocardial damage with unparalleled precision, enabling earlier intervention and improved patient outcomes.
- The clinical applications of hs-TnT assays extend beyond the diagnosis of acute coronary syndromes, including the assessment of cardiac damage in patients with chronic kidney disease, heart failure, and pulmonary embolism.
- Interpretation of hs-TnT results requires careful consideration of the individual patient's clinical presentation and medical history, as troponin elevations can occur in non-ACS conditions.
- The upper reference limit for hs-TnT assays is 14 ng/L, with a coefficient of variation of <10%.
- Healthcare professionals should be aware of the potential for false-positive results, particularly in patients with chronic kidney disease or other conditions that may affect troponin levels.
Diagnostic Criteria and Interpretation of Troponin High Sensitivity Assays
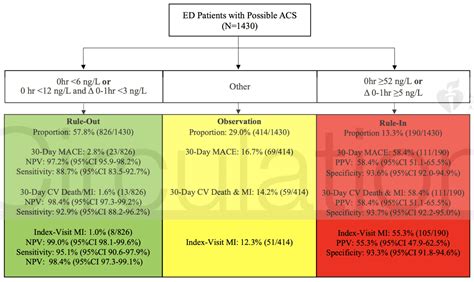
The diagnostic criteria for AMI using hs-TnT assays are based on the detection of a rise and/or fall in troponin levels, with at least one value exceeding the 99th percentile upper reference limit. The interpretation of hs-TnT results requires careful consideration of the individual patient’s clinical presentation, medical history, and electrocardiographic findings. A nuanced understanding of the assay’s limitations, including the potential for false-positive results, is essential to ensure accurate diagnosis and effective management of patients with suspected ACS.
Technical Specifications and Analytical Performance of Troponin High Sensitivity Assays
The technical specifications of hs-TnT assays vary depending on the manufacturer and the specific assay design. However, most commercial hs-TnT assays exhibit excellent analytical performance, with high sensitivity, specificity, and precision. The coefficient of variation for hs-TnT assays is typically <10%, ensuring reliable and reproducible results. Furthermore, the assays are often calibrated to the international troponin standard, facilitating comparisons across different laboratories and studies.
The development of hs-TnT assays has been a significant advancement in the field of cardiovascular diagnostics, offering unprecedented sensitivity and precision in the detection of myocardial damage. As the field continues to evolve, it is likely that hs-TnT assays will play an increasingly important role in the diagnosis and management of cardiovascular disease, enabling healthcare professionals to provide more effective and personalized care for their patients.
What is the detection limit of high-sensitivity troponin assays?
+The detection limit of high-sensitivity troponin assays is 0.001 ng/mL.
What are the clinical applications of troponin high sensitivity assays?
+The clinical applications of troponin high sensitivity assays include the diagnosis and management of acute coronary syndromes, assessment of cardiac damage in patients with chronic kidney disease, heart failure, and pulmonary embolism, and detection of myocardial damage in patients with non-ACS conditions.
How should healthcare professionals interpret troponin high sensitivity assay results?
+Healthcare professionals should interpret troponin high sensitivity assay results within the context of the individual patient’s clinical presentation, medical history, and electrocardiographic findings, taking into account the potential for false-positive results and the assay’s limitations.