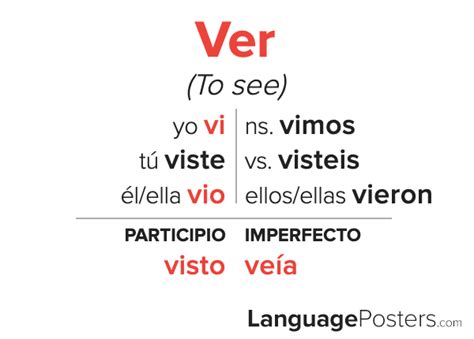
The Spanish language is renowned for its complex conjugation system, with verbs being the core of sentence structure. Among the various tenses, the preterite tense stands out as a fundamental aspect of expressing completed actions in the past. One of the most commonly used verbs in Spanish is "ver," which translates to "to see" in English. Mastering the conjugation of "ver" in the preterite tense is essential for effective communication in Spanish, allowing speakers to describe past events with precision and clarity.
Key Points
- The verb "ver" is a regular -er verb in the present tense but has irregular conjugations in other tenses, including the preterite.
- Understanding the preterite conjugation of "ver" is crucial for describing past events and completed actions.
- The preterite tense of "ver" follows a specific conjugation pattern that differs from its present tense form.
- Practice and contextual examples are key to mastering the preterite conjugation of "ver" and using it correctly in sentences.
- Recognizing the differences between the preterite and imperfect tenses is essential for accurate expression of past actions.
Conjugation of Ver in Preterite Tense
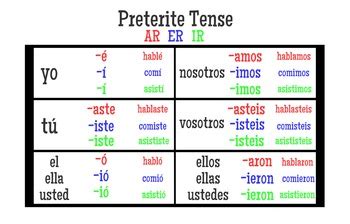
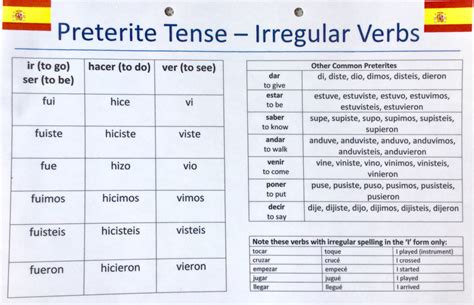
The conjugation of “ver” in the preterite tense is as follows: vi, viste, vio, vimos, visteis, and vieron. This conjugation pattern is used to describe actions that started and ended in the past. For instance, “Yo vi la película anoche” means “I saw the movie last night,” indicating a completed action in the past.
Using Ver in Preterite Tense
To use “ver” in the preterite tense effectively, it’s essential to understand the context in which the action is taking place. The preterite tense is used for actions that are seen as completed and have a specific start and end point in the past. In contrast, the imperfect tense is used for ongoing or repeated actions in the past. For example, “Yo veía la televisión todos los días” means “I used to watch TV every day,” describing a habitual action.
| Subject | Preterite Conjugation of Ver |
|---|---|
| Yo | vi |
| Tú | viste |
| Él/Ella/Usted | vio |
| Nosotros/Nosotras | vimus |
| Vosotros/Vosotras | visteis |
| Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes | vieron |
Practical Applications and Examples

Mastering the preterite conjugation of “ver” opens up a wide range of expressive possibilities. For instance, describing a visit to a museum: “Vi muchas pinturas famosas en el museo,” or talking about watching a sports game: “Vimos el partido de fútbol ayer por la noche.” These examples illustrate how the preterite tense of “ver” is used to convey completed actions in the past.
Common Mistakes and Clarifications
A common mistake among learners is confusing the preterite tense with the imperfect tense. While the preterite is used for completed actions, the imperfect tense describes ongoing or habitual actions. For example, “Yo veía una película cuando sonó el teléfono” (I was watching a movie when the phone rang) versus “Yo vi la película anoche” (I saw the movie last night). Recognizing these differences is key to accurate communication.
In conclusion, the conjugation of "ver" in the preterite tense is a fundamental aspect of Spanish grammar that allows speakers to express completed actions in the past with clarity. By understanding the conjugation pattern and practicing its use in context, learners can improve their ability to communicate effectively in Spanish. Whether describing past events, actions, or experiences, mastering the preterite tense of "ver" is an essential skill for any Spanish language learner.
What is the preterite tense used for in Spanish?
+The preterite tense in Spanish is used to describe actions that started and ended in the past, indicating completed actions.
How does the conjugation of “ver” in the preterite tense differ from its present tense form?
+The preterite conjugation of “ver” follows a specific pattern (vi, viste, vio, vimos, visteis, vieron) that differs significantly from its present tense conjugation.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when using the preterite tense of “ver”?
+A common mistake is confusing the preterite tense with the imperfect tense. It’s essential to recognize the differences between these two tenses to use “ver” correctly in the preterite.