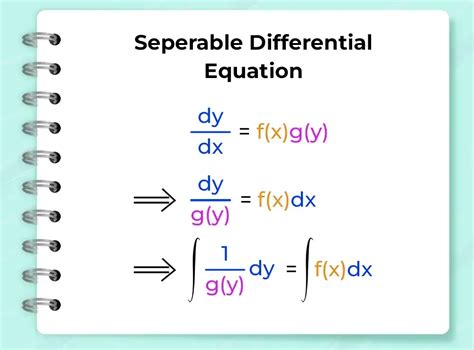
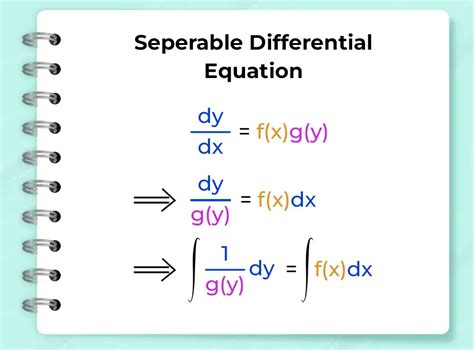
Solving separable differential equations is a fundamental concept in calculus and differential equations, as it allows us to find the solution to a wide range of problems in physics, engineering, and other fields. A separable differential equation is one in which the variables can be separated, meaning that the equation can be written in the form dy/dx = f(x)g(y), where f(x) is a function of x only and g(y) is a function of y only. In this article, we will explore the method for solving separable differential equations, including the key concepts, techniques, and examples.
Key Points
- A separable differential equation can be written in the form dy/dx = f(x)g(y), where f(x) and g(y) are functions of x and y only, respectively.
- The method for solving separable differential equations involves separating the variables, integrating both sides, and then solving for y.
- Solving separable differential equations requires a good understanding of integration, including substitution, integration by parts, and integration by partial fractions.
- Separable differential equations have many applications in physics, engineering, and other fields, including population growth, chemical reactions, and electrical circuits.
- The solution to a separable differential equation can be expressed in either implicit or explicit form, depending on the specific equation and the desired outcome.
Separating the Variables
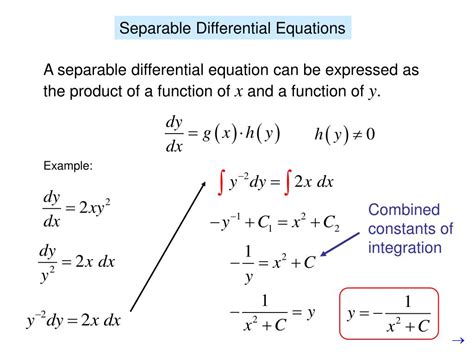
The first step in solving a separable differential equation is to separate the variables. This involves rearranging the equation so that all the terms involving y are on one side, and all the terms involving x are on the other side. For example, consider the differential equation dy/dx = (2x)/(y + 1). To separate the variables, we can multiply both sides by (y + 1) and divide both sides by 2x, giving us (y + 1)dy = 2xdx. This equation is now in a form that can be integrated.
Integrating Both Sides
Once the variables have been separated, the next step is to integrate both sides of the equation. This involves finding the antiderivative of each side, which can be done using a variety of techniques, including substitution, integration by parts, and integration by partial fractions. For example, to integrate the equation (y + 1)dy = 2xdx, we can use the power rule of integration, which gives us (y^2)/2 + y = x^2 + C, where C is the constant of integration.
| Integral | Antiderivative |
|---|---|
| (y + 1)dy | (y^2)/2 + y |
| 2xdx | x^2 |
Solving for y
Once the equation has been integrated, the final step is to solve for y. This can involve rearranging the equation to isolate y on one side, which can be done using algebraic manipulations such as expanding, factoring, and canceling. For example, to solve the equation (y^2)/2 + y = x^2 + C for y, we can first expand the left-hand side, giving us y^2⁄2 + y - x^2 - C = 0. We can then factor the left-hand side, giving us (y - x)(y + x + 2) = 0. Finally, we can solve for y by setting each factor equal to zero, giving us y = x or y = -x - 2.
Implicit and Explicit Solutions
The solution to a separable differential equation can be expressed in either implicit or explicit form, depending on the specific equation and the desired outcome. An implicit solution is one in which the solution is expressed as a relationship between x and y, without explicitly solving for y. An explicit solution, on the other hand, is one in which the solution is expressed as a function of x only, with y explicitly solved for. For example, the equation (y^2)/2 + y = x^2 + C is an implicit solution, while the equation y = x or y = -x - 2 is an explicit solution.
What is a separable differential equation?
+A separable differential equation is one in which the variables can be separated, meaning that the equation can be written in the form dy/dx = f(x)g(y), where f(x) is a function of x only and g(y) is a function of y only.
How do you solve a separable differential equation?
+To solve a separable differential equation, you need to separate the variables, integrate both sides, and then solve for y. This involves rearranging the equation so that all the terms involving y are on one side, and all the terms involving x are on the other side, and then integrating both sides using a variety of techniques such as substitution, integration by parts, and integration by partial fractions.
What are some common applications of separable differential equations?
+Separable differential equations have many applications in physics, engineering, and other fields, including population growth, chemical reactions, and electrical circuits. They are used to model a wide range of phenomena, from the growth of bacteria to the motion of objects in space.