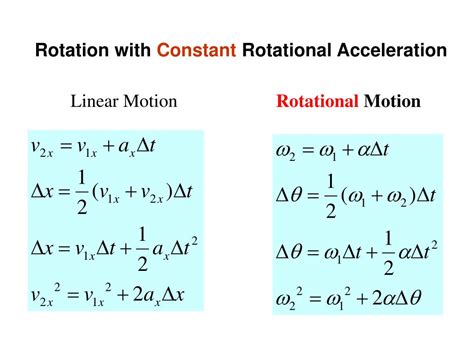
The concept of rotational acceleration is a fundamental aspect of physics and engineering, describing the rate of change of angular velocity of an object. Understanding the rotational acceleration formula is crucial for analyzing and predicting the motion of rotating systems, from simple pendulums to complex machinery. In this article, we will delve into the rotational acceleration formula, its derivation, and its applications, providing a comprehensive overview of this essential concept.
Key Points
- The rotational acceleration formula is given by α = Δω / Δt, where α is the rotational acceleration, Δω is the change in angular velocity, and Δt is the time over which the change occurs.
- The rotational acceleration is a vector quantity, with both magnitude and direction, and is measured in units of radians per second squared (rad/s²).
- The rotational acceleration is related to the torque and moment of inertia of an object, and can be calculated using the formula α = τ / I, where τ is the net torque acting on the object and I is its moment of inertia.
- Understanding rotational acceleration is essential for designing and optimizing rotating systems, such as gears, motors, and turbines.
- Rotational acceleration has numerous applications in various fields, including physics, engineering, and astronomy.
Derivation of the Rotational Acceleration Formula
The rotational acceleration formula can be derived from the definition of angular velocity and the concept of acceleration. Angular velocity (ω) is defined as the rate of change of angular displacement (θ) with respect to time (t), and is measured in units of radians per second (rad/s). The rotational acceleration (α) is the rate of change of angular velocity, and can be calculated using the formula α = Δω / Δt, where Δω is the change in angular velocity and Δt is the time over which the change occurs.
Relationship between Rotational Acceleration and Torque
The rotational acceleration is also related to the torque (τ) and moment of inertia (I) of an object. Torque is a measure of the rotational force that causes an object to rotate, and is measured in units of newton-meters (N·m). The moment of inertia is a measure of an object’s resistance to changes in its rotation, and is measured in units of kilograms per square meter (kg·m²). The rotational acceleration can be calculated using the formula α = τ / I, which shows that the rotational acceleration is directly proportional to the torque and inversely proportional to the moment of inertia.
| Quantity | Symbol | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Rotational Acceleration | α | rad/s² |
| Angular Velocity | ω | rad/s |
| Torque | τ | N·m |
| Moment of Inertia | I | kg·m² |
Applications of Rotational Acceleration

Rotational acceleration has numerous applications in various fields, including physics, engineering, and astronomy. In physics, rotational acceleration is used to describe the motion of rotating objects, such as tops and gyroscopes. In engineering, rotational acceleration is used to design and optimize rotating systems, such as gears, motors, and turbines. In astronomy, rotational acceleration is used to study the motion of celestial objects, such as planets and stars.
Designing Rotating Systems
Understanding rotational acceleration is essential for designing and optimizing rotating systems. By calculating the rotational acceleration of a system, engineers can determine the torque and moment of inertia required to achieve a desired angular velocity. This information can be used to design more efficient and effective rotating systems, such as gears and motors, which are critical components in many industrial and consumer applications.
What is the unit of rotational acceleration?
+The unit of rotational acceleration is radians per second squared (rad/s²).
How is rotational acceleration related to torque and moment of inertia?
+Rotational acceleration is directly proportional to torque and inversely proportional to moment of inertia, as described by the formula α = τ / I.
What are some applications of rotational acceleration?
+Rotational acceleration has numerous applications in physics, engineering, and astronomy, including designing and optimizing rotating systems, studying the motion of celestial objects, and analyzing the motion of rotating objects.
In conclusion, the rotational acceleration formula is a fundamental concept in physics and engineering, describing the rate of change of angular velocity of an object. By understanding the relationship between rotational acceleration, torque, and moment of inertia, engineers and physicists can design and optimize complex rotating systems, from gears and motors to turbines and spacecraft. The applications of rotational acceleration are diverse and numerous, and continue to play a critical role in advancing our understanding of the physical world.