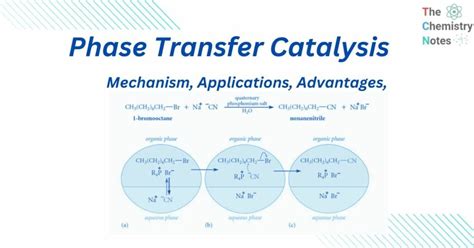
Phase transfer catalysis is a versatile and efficient technique used in organic synthesis to facilitate the reaction between two or more reactants that are insoluble in each other. This method has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential to enhance reaction rates, yields, and selectivity, while minimizing the formation of by-products. In this article, we will delve into the concept of phase transfer catalysis, its underlying principles, and its applications in various fields.
Key Points
- Phase transfer catalysis is a technique used to facilitate reactions between insoluble reactants.
- It involves the use of a phase transfer catalyst to transport reactants from one phase to another.
- The technique has been applied in various fields, including organic synthesis, materials science, and pharmaceuticals.
- Phase transfer catalysis offers several advantages, including enhanced reaction rates, yields, and selectivity.
- The choice of phase transfer catalyst is crucial in determining the outcome of the reaction.
Principles of Phase Transfer Catalysis

Phase transfer catalysis is based on the principle of transporting reactants from one phase to another using a phase transfer catalyst. The catalyst acts as a shuttle, carrying the reactant from the donor phase to the acceptor phase, where the reaction occurs. This process allows the reactants to interact with each other, even if they are insoluble in the same solvent. The phase transfer catalyst can be a quaternary ammonium salt, a crown ether, or a cryptand, among others.
Types of Phase Transfer Catalysts
There are several types of phase transfer catalysts, each with its own unique properties and applications. Quaternary ammonium salts, such as tetra-n-butylammonium bromide (TBAB), are commonly used as phase transfer catalysts due to their high solubility in organic solvents and their ability to form stable complexes with anions. Crown ethers, on the other hand, are used to transport cations from one phase to another. Cryptands are a type of phase transfer catalyst that can form stable complexes with both cations and anions.
| Type of Catalyst | Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Quaternary Ammonium Salts | High solubility in organic solvents, forms stable complexes with anions | Organic synthesis, materials science |
| Crown Ethers | Forms stable complexes with cations | Organic synthesis, pharmaceuticals |
| Cryptands | Forms stable complexes with both cations and anions | Organic synthesis, materials science |
Applications of Phase Transfer Catalysis

Phase transfer catalysis has been applied in various fields, including organic synthesis, materials science, and pharmaceuticals. In organic synthesis, phase transfer catalysis is used to facilitate reactions between insoluble reactants, such as the synthesis of alkyl halides and the preparation of Grignard reagents. In materials science, phase transfer catalysis is used to synthesize nanoparticles and other materials with unique properties. In pharmaceuticals, phase transfer catalysis is used to synthesize active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and intermediates.
Advantages of Phase Transfer Catalysis
Phase transfer catalysis offers several advantages, including enhanced reaction rates, yields, and selectivity. The technique also allows for the use of mild reaction conditions, which can help to minimize the formation of by-products and reduce the environmental impact of the reaction. Additionally, phase transfer catalysis can be used to synthesize complex molecules that are difficult to prepare using traditional methods.
However, phase transfer catalysis also has some limitations. The technique requires the use of a phase transfer catalyst, which can be expensive and difficult to remove from the reaction mixture. Additionally, the choice of phase transfer catalyst can be crucial in determining the outcome of the reaction, and the wrong choice of catalyst can lead to reduced yields and selectivity.
What is phase transfer catalysis?
+Phase transfer catalysis is a technique used to facilitate reactions between insoluble reactants by transporting them from one phase to another using a phase transfer catalyst.
What are the advantages of phase transfer catalysis?
+The advantages of phase transfer catalysis include enhanced reaction rates, yields, and selectivity, as well as the ability to use mild reaction conditions and minimize the formation of by-products.
What are the limitations of phase transfer catalysis?
+The limitations of phase transfer catalysis include the requirement for a phase transfer catalyst, which can be expensive and difficult to remove from the reaction mixture, and the need for careful selection of the catalyst to achieve optimal results.
In conclusion, phase transfer catalysis is a powerful technique that has been used to facilitate reactions between insoluble reactants in various fields. The technique offers several advantages, including enhanced reaction rates, yields, and selectivity, and has been used to synthesize complex molecules that are difficult to prepare using traditional methods. However, the technique also has some limitations, and the choice of phase transfer catalyst can be crucial in determining the outcome of the reaction. Further research is needed to fully explore the potential of phase transfer catalysis and to develop new phase transfer catalysts with improved properties.