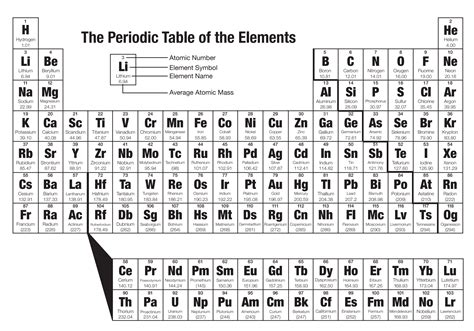
The periodic table is a fundamental tool in chemistry, providing a systematic way to organize and understand the properties of elements. To fully grasp the concepts and applications of the periodic table, practicing problems is essential. This article will guide you through a series of practice problems designed to test your understanding of the periodic table, from basic identification of elements to more complex analyses of their properties and behaviors.
Key Points
- Understanding the structure and organization of the periodic table
- Identifying elements by their symbols, atomic numbers, and atomic masses
- Recognizing periodic trends in atomic radius, electronegativity, and ionization energy
- Applying the periodic table to predict chemical properties and reactions
- Practicing problem-solving strategies for complex periodic table questions
Basic Identification of Elements

To begin with, it’s crucial to be able to identify elements based on the information given in the periodic table. This includes knowing the symbols, atomic numbers, and atomic masses of elements. For example, if you’re given the symbol “Ca,” you should recognize it as calcium, with an atomic number of 20 and an atomic mass of approximately 40.08 u (unified atomic mass units).
Problem 1: Element Identification
Identify the element with the symbol “Ne” and describe its position in the periodic table.
Solution: The element with the symbol “Ne” is neon. It is located in period 2, group 18 (noble gases) of the periodic table, with an atomic number of 10 and an atomic mass of approximately 20.18 u.
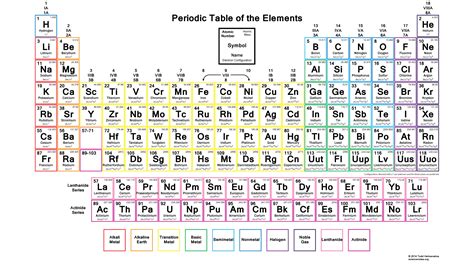
Periodic Trends
One of the powerful aspects of the periodic table is its ability to predict trends in the properties of elements. Key trends include atomic radius, electronegativity, and ionization energy. Generally, atomic radius decreases from left to right across a period and increases down a group. Electronegativity tends to increase from left to right across a period and decrease down a group. Ionization energy usually increases from left to right across a period and decreases down a group.
Problem 2: Analyzing Periodic Trends
Compare the atomic radius and electronegativity of carbon © and oxygen (O), and explain the reasoning behind your observations.
Solution: Carbon has an atomic radius of about 67 pm and an electronegativity of 2.55 on the Pauling scale. Oxygen has an atomic radius of about 48 pm and an electronegativity of 3.44. The smaller atomic radius and higher electronegativity of oxygen compared to carbon are due to its position to the right of carbon in the same period, where atomic radius decreases and electronegativity increases.
Chemical Properties and Reactions
The periodic table can also be used to predict the chemical properties of elements and how they react with other elements. For instance, elements in the same group (vertical column) tend to exhibit similar chemical properties due to the same number of electrons in their outermost shell. This similarity in chemical behavior is why elements in the same group are often used to predict the reactivity of an unknown element.
Problem 3: Predicting Chemical Properties
Predict the chemical properties of astatine (At) based on its position in the periodic table.
Solution: Astatine is in group 17 (halogens) of the periodic table. Like other halogens, it is expected to be highly reactive, readily forming ions with a -1 charge and exhibiting similar chemical properties to other halogens like chlorine (Cl) and iodine (I), such as reacting with metals to form salts.
Practice Problems with Solutions
Practicing a variety of problems will help solidify your understanding of the periodic table and its applications. Here are a few more problems to work through:
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Identify the element in group 1, period 3, and describe its likely chemical behavior. | The element is sodium (Na). Given its position in group 1 (alkali metals), it is expected to be highly reactive, readily losing one electron to form a +1 ion, and reacting vigorously with water and acids. |
| Compare the ionization energy of beryllium (Be) and magnesium (Mg), and explain the trend. | Beryllium has a higher ionization energy than magnesium due to its smaller atomic radius, resulting in a stronger attraction between the nucleus and the outer electrons, making it harder to remove an electron. |
| Predict the electronegativity of an element in group 16, period 5, relative to an element in group 16, period 2. | The element in period 5 (tellurium, Te) would have a lower electronegativity than the element in period 2 (oxygen, O) due to the increase in atomic radius down a group, which results in a weaker attraction between the nucleus and the electrons in the outer shell. |
Conclusion and Future Directions
Mastering the periodic table and its applications is a cornerstone of chemistry. By understanding the periodic trends, the properties of elements, and how to predict chemical behaviors, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle complex chemistry problems. Remember, practice is key, and working through a variety of problems will help reinforce your knowledge and improve your ability to apply the concepts of the periodic table to real-world scenarios.
What is the primary purpose of the periodic table in chemistry?
+The primary purpose of the periodic table is to organize elements in a way that their properties and relationships can be understood and predicted. It allows chemists to classify elements based on their atomic structure and predict their chemical properties and behaviors.
How do I identify an element using the periodic table if I only know its atomic mass?
+If you know the atomic mass of an element, you can approximate its position in the periodic table. However, for an exact identification, knowing the atomic number is more precise, as atomic mass can sometimes be close between different elements. Using a detailed periodic table that includes atomic masses can help narrow down the possibilities.
What is the difference between electronegativity and electron affinity?
+Electronegativity is a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons in a covalent bond, while electron affinity is the energy change associated with the addition of an electron to a neutral atom in its ground state. Both are related to the tendency of an atom to attract electrons, but they are defined and measured differently.