Omeprazole and famotidine are two commonly prescribed medications used to treat various gastrointestinal disorders, including gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcers, and dyspepsia. While both medications are effective in reducing stomach acid production, they belong to different classes of drugs and have distinct mechanisms of action, indications, and side effect profiles. In this article, we will delve into the differences between omeprazole and famotidine, exploring their pharmacology, clinical uses, and potential interactions.
Pharmacological Comparison
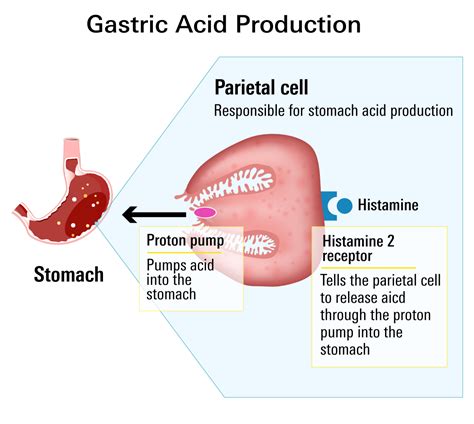
Omeprazole is a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) that works by irreversibly inhibiting the H+/K+ ATPase enzyme system at the secretory surface of gastric parietal cells. This action blocks the final step of acid production, resulting in a significant reduction in gastric acid secretion. Famotidine, on the other hand, is a histamine-2 (H2) receptor antagonist that competes with histamine for binding sites on the H2 receptors of gastric parietal cells, thereby reducing acid secretion.
Onset and Duration of Action
The onset of action for omeprazole is approximately 1-3 hours, with a duration of action lasting up to 72 hours due to its irreversible inhibition of the proton pump. In contrast, famotidine has a faster onset of action, typically within 1-2 hours, with a shorter duration of action, lasting around 8-12 hours. This difference in duration of action may impact dosing regimens and patient compliance.
Key Points
- Omeprazole is a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) that irreversibly inhibits gastric acid production.
- Famotidine is a histamine-2 (H2) receptor antagonist that competitively inhibits acid secretion.
- Omeprazole has a slower onset but longer duration of action compared to famotidine.
- Both medications are effective in treating GERD, peptic ulcers, and dyspepsia, but omeprazole may be more effective in severe cases.
- Patient-specific factors, such as age, renal function, and potential interactions, should guide medication selection.
Clinical Uses and Efficacy

Both omeprazole and famotidine are indicated for the treatment of GERD, peptic ulcers, and dyspepsia. However, omeprazole may be more effective in severe cases of GERD and peptic ulcers due to its potent and long-lasting inhibition of acid production. Famotidine, on the other hand, may be preferred for patients with mild to moderate symptoms or those who require a shorter duration of therapy.
Side Effects and Interactions
Common side effects of omeprazole include headache, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting, while famotidine is often associated with headache, dizziness, and constipation. Omeprazole may interact with other medications, such as warfarin, diazepam, and phenytoin, due to its inhibition of the cytochrome P450 enzyme system. Famotidine, being a H2 receptor antagonist, has a lower potential for interactions, but may still interact with medications like warfarin and theophylline.
| Medication | Common Side Effects | Potential Interactions |
|---|---|---|
| Omeprazole | Headache, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting | Warfarin, diazepam, phenytoin |
| Famotidine | Headache, dizziness, constipation | Warfarin, theophylline |

Special Considerations and Future Directions
In recent years, concerns have been raised regarding the long-term use of PPIs, such as omeprazole, and their potential association with increased risks of osteoporosis, Clostridioides difficile infection, and magnesium deficiency. As a result, healthcare providers should carefully weigh the benefits and risks of PPI therapy and consider alternative treatment options, such as H2 receptor antagonists like famotidine, for patients requiring long-term acid suppression.
Emerging Therapies and Treatment Strategies
Research into new therapeutic agents and treatment strategies for gastrointestinal disorders is ongoing. For example, the development of potassium-competitive acid blockers (P-CABs) and the exploration of non-pharmacological interventions, such as lifestyle modifications and alternative therapies, may offer promising alternatives for patients with GERD, peptic ulcers, and dyspepsia.
What is the primary difference between omeprazole and famotidine?
+Omeprazole is a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) that irreversibly inhibits gastric acid production, while famotidine is a histamine-2 (H2) receptor antagonist that competitively inhibits acid secretion.
Which medication is more effective for severe cases of GERD?
+Omeprazole may be more effective in severe cases of GERD due to its potent and long-lasting inhibition of acid production.
What are the potential interactions between omeprazole and other medications?
+Omeprazole may interact with medications like warfarin, diazepam, and phenytoin due to its inhibition of the cytochrome P450 enzyme system.
Meta description suggestion: “Discover the differences between omeprazole and famotidine, including their mechanisms of action, clinical uses, and potential interactions, to inform treatment decisions for gastrointestinal disorders.” (149 characters)