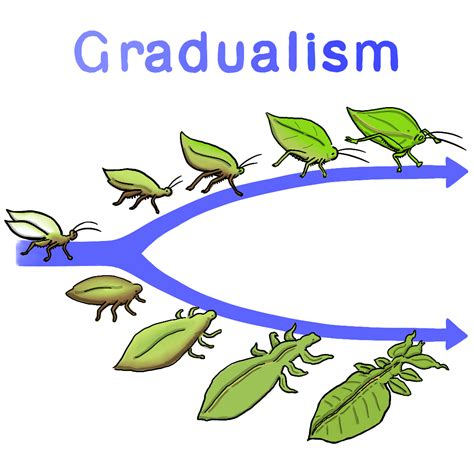
The concept of gradualism has been a cornerstone in the field of biology, particularly in the realm of evolutionary theory. Gradualism, in this context, refers to the idea that species evolve over time through a series of small, incremental changes, rather than through sudden, dramatic transformations. This perspective is rooted in the work of Charles Darwin, who first proposed the concept of gradualism in his seminal book, "On the Origin of Species," published in 1859. According to Darwin, species evolve through the process of natural selection, where individuals with favorable traits are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing those traits on to their offspring.
The gradualist approach to evolution suggests that these changes occur at a relatively constant rate, with species undergoing a series of subtle modifications over millions of years. This concept is often contrasted with the idea of punctuated equilibrium, which proposes that evolution occurs in rapid bursts, followed by long periods of stability. While both theories have their merits, gradualism remains a widely accepted explanation for the diversity of life on Earth. The fossil record, for example, provides evidence of gradual changes in species over time, with transitional forms and intermediate fossils supporting the idea of incremental evolution.
Key Points
- Gradualism refers to the idea that species evolve through small, incremental changes over time.
- This concept is rooted in the work of Charles Darwin and the process of natural selection.
- Gradualism is often contrasted with punctuated equilibrium, which proposes rapid bursts of evolution followed by periods of stability.
- The fossil record provides evidence of gradual changes in species over time, with transitional forms and intermediate fossils.
- Gradualism remains a widely accepted explanation for the diversity of life on Earth, with implications for fields such as conservation biology and evolutionary medicine.
Gradualism and the Fossil Record
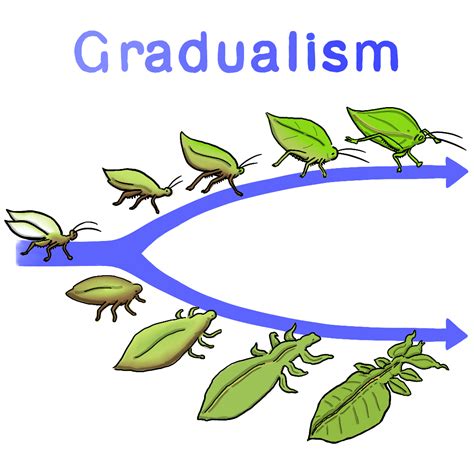
The fossil record provides a critical test of the gradualist hypothesis, as it offers a tangible record of the history of life on Earth. Fossils of transitional forms, such as Tiktaalik and Archaeopteryx, demonstrate the gradual evolution of species over time. These fossils exhibit characteristics of both the ancestral and descendant species, providing strong evidence for the gradualist perspective. Furthermore, the fossil record shows a clear pattern of gradual changes in species over time, with the emergence of new traits and the modification of existing ones.
Gradualism and Speciation
Gradualism also plays a critical role in the process of speciation, where a single species splits into two or more distinct species. According to the gradualist perspective, speciation occurs through the accumulation of small genetic differences between populations over time. As these differences become more pronounced, the populations eventually become reproductively isolated, resulting in the formation of new species. This process can occur through various mechanisms, such as geographic isolation or genetic drift, and is supported by a range of empirical studies.
| Species | Transitional Fossils | Gradual Changes |
|---|---|---|
| Tiktaalik | Fish-like characteristics with limb-like fins | Gradual evolution of tetrapod traits |
| Archaeopteryx | Reptilian characteristics with feathered wings | Gradual evolution of avian traits |
| Homo sapiens | Emergence of bipedalism and brain enlargement | Gradual evolution of human-specific traits |
Criticisms and Controversies

While gradualism remains a widely accepted theory, it is not without its criticisms and controversies. Some scientists have argued that the fossil record is incomplete, and that the absence of transitional fossils is evidence against gradualism. However, this criticism is based on a misunderstanding of the fossil record, which is inherently incomplete due to the processes of fossilization and erosion. Others have proposed alternative theories, such as punctuated equilibrium, which suggest that evolution occurs in rapid bursts rather than through gradual changes.
Reconciling Gradualism with Punctuated Equilibrium
Despite these criticisms, gradualism and punctuated equilibrium are not mutually exclusive theories. In fact, many scientists argue that both perspectives are necessary to explain the complexity of evolutionary history. Gradualism can account for the slow and steady changes that occur over millions of years, while punctuated equilibrium can explain the rapid bursts of evolution that occur in response to changing environmental conditions. By reconciling these two perspectives, we can gain a more nuanced understanding of the evolutionary process and its role in shaping the diversity of life on Earth.
What is the main difference between gradualism and punctuated equilibrium?
+Gradualism proposes that evolution occurs through small, incremental changes over time, while punctuated equilibrium suggests that evolution occurs in rapid bursts followed by periods of stability.
What is the role of the fossil record in supporting gradualism?
+The fossil record provides evidence of gradual changes in species over time, with transitional forms and intermediate fossils supporting the idea of incremental evolution.
How do gradualism and punctuated equilibrium relate to each other?
+Gradualism and punctuated equilibrium are not mutually exclusive theories. Many scientists argue that both perspectives are necessary to explain the complexity of evolutionary history, with gradualism accounting for slow and steady changes and punctuated equilibrium explaining rapid bursts of evolution.
In conclusion, gradualism remains a fundamental concept in the field of biology, providing a framework for understanding the evolution of species over time. While criticisms and controversies exist, the gradualist perspective is supported by a range of empirical evidence, including the fossil record and comparative studies of living organisms. By recognizing the gradual nature of evolutionary change, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complex and dynamic relationships between species and their environments, and better understand the mechanisms that have shaped the diversity of life on Earth.