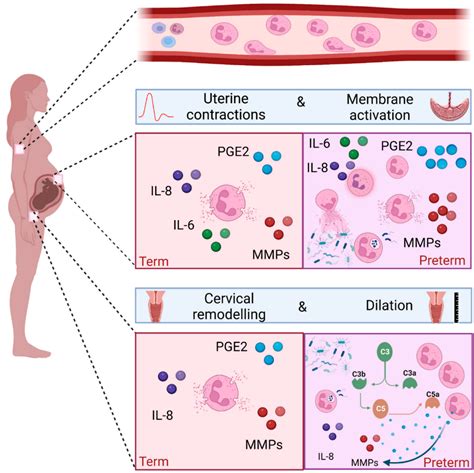
During pregnancy, the body undergoes numerous physiological changes to support the growth and development of the fetus. One of these changes involves the hematological system, where alterations in blood cell counts are observed. A notable change is the increase in white blood cell count, particularly neutrophils, which are a type of granulocyte that plays a crucial role in the innate immune response. Neutrophils absolute high pregnancy is a condition where the absolute neutrophil count (ANC) is elevated beyond the normal range, and it is essential to understand the implications of this condition for both the mother and the fetus.
Physiological Changes in Pregnancy
Pregnancy is associated with significant changes in the maternal immune system. The immune response is modulated to prevent rejection of the fetus, which is genetically distinct from the mother. This modulation involves a shift from a pro-inflammatory to an anti-inflammatory state, allowing the fetus to develop without being attacked by the maternal immune system. However, this shift also increases the susceptibility of pregnant women to infections, making the monitoring of white blood cell counts, including neutrophils, critical during pregnancy.
Neutrophil Count in Pregnancy
The normal range for the absolute neutrophil count (ANC) in non-pregnant women is approximately 1,500 to 8,000 cells per microliter (µL) of blood. During pregnancy, the ANC can increase, with some studies suggesting that an ANC of up to 15,000 cells/µL can be considered normal due to the physiological changes associated with pregnancy. However, an ANC above this range may indicate an underlying infection or inflammatory condition, which requires immediate medical attention.
| Trimester | Normal ANC Range |
|---|---|
| First Trimester | 6,000 - 12,000 cells/µL |
| Second Trimester | 7,000 - 14,000 cells/µL |
| Third Trimester | 8,000 - 15,000 cells/µL |
Clinical Implications of High Neutrophil Count in Pregnancy
A high neutrophil count during pregnancy can be indicative of several conditions, including infections, inflammatory diseases, and in some cases, pregnancy-related complications such as preeclampsia or placental abruption. It is essential to investigate the cause of an elevated ANC to provide appropriate management and prevent potential adverse outcomes for both the mother and the fetus.
Diagnosis and Management
The diagnosis of an elevated ANC involves a comprehensive clinical evaluation, including a detailed medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests to identify any underlying infection or inflammatory condition. Management strategies may include antibiotic therapy for infections, anti-inflammatory medications for inflammatory conditions, and close monitoring of the pregnancy to prevent complications.
Key Points
- Physiological changes during pregnancy can lead to an increase in neutrophil count.
- An ANC above 15,000 cells/µL may indicate an underlying condition requiring medical attention.
- Consideration of gestational age and individual baseline ANC is crucial for accurate interpretation.
- High neutrophil count can be associated with infections, inflammatory diseases, and pregnancy-related complications.
- Appropriate management, including diagnostic evaluation and treatment, is essential to prevent adverse outcomes.
In conclusion, while an increase in neutrophil count is a normal physiological change during pregnancy, an excessively high count can signal an underlying condition that requires prompt medical evaluation and management. Healthcare providers must be vigilant in monitoring white blood cell counts and interpreting these values within the context of the individual's overall health and gestational age to ensure the best possible outcomes for both mother and fetus.
What is considered a high neutrophil count during pregnancy?
+A neutrophil count above 15,000 cells/µL is generally considered high during pregnancy and may indicate an underlying infection or inflammatory condition.
Why do neutrophil counts increase during pregnancy?
+The increase in neutrophil count during pregnancy is part of the body’s physiological response to support the growth of the fetus and prepare the mother’s body for childbirth.
How is a high neutrophil count during pregnancy managed?
+Management of a high neutrophil count during pregnancy involves identifying and treating any underlying infection or inflammatory condition, as well as close monitoring of the pregnancy to prevent complications.