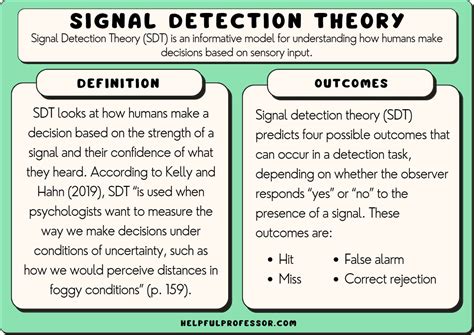
Signal detection is a critical process in various fields, including engineering, biology, and finance, where identifying meaningful signals amidst noise is essential for making informed decisions. The complexity of signal detection arises from the inherent variability in both the signals of interest and the background noise. Effective signal detection strategies can significantly enhance the accuracy of signal identification, leading to better outcomes in fields such as medical diagnosis, quality control, and financial analysis. This article will delve into the nuances of signal detection, providing five pivotal tips to improve the efficacy of signal detection processes.
Key Points
- Understanding the nature of the signal and noise is crucial for effective detection.
- Setting appropriate thresholds can significantly affect the accuracy of signal detection.
- Utilizing statistical methods can enhance the reliability of signal detection processes.
- Filtering techniques can be employed to reduce noise and improve signal clarity.
- Continuous monitoring and adaptation are necessary for maintaining optimal signal detection performance.
Tip 1: Understand the Signal and Noise Characteristics
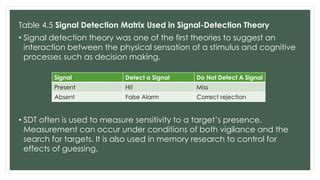
Effective signal detection begins with a comprehensive understanding of both the signal of interest and the background noise. This understanding involves characterizing the amplitude, frequency, and duration of the signals, as well as the statistical properties of the noise. For instance, in medical imaging, understanding the signal characteristics of different tissues and the noise patterns introduced by the imaging equipment is vital for accurate image reconstruction and diagnosis. By grasping these fundamentals, professionals can tailor their detection strategies to maximize the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), thereby enhancing detection accuracy.
The Role of Signal Processing in Characterization
Signal processing techniques play a pivotal role in characterizing signals and noise. These techniques can range from simple filtering methods to complex spectral analysis. For example, in audio signal processing, filters can be designed to remove background hiss (noise) and emphasize the voice or music (signal), improving the overall quality of the audio. Understanding and applying these signal processing methods are essential skills for anyone involved in signal detection.
| Signal Processing Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Filtering | Method to remove unwanted frequencies from a signal. |
| Spectral Analysis | Technique to decompose a signal into its component frequencies. |

Tip 2: Optimize Threshold Settings
The threshold setting is a critical parameter in signal detection systems, as it determines the minimum amplitude or intensity a signal must have to be considered a valid detection. Setting the threshold too low can lead to false positives (detecting noise as signal), while setting it too high can result in false negatives (missing actual signals). The optimal threshold setting often involves a trade-off between these two types of errors, known as the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis. By analyzing the ROC curve, professionals can identify the threshold that balances the rates of false positives and false negatives according to their specific requirements.
Threshold Optimization Strategies
Several strategies can be employed to optimize threshold settings. One common approach is to use adaptive thresholding techniques, which adjust the threshold based on the local characteristics of the signal and noise. Another strategy involves using machine learning algorithms to learn the optimal threshold from a dataset of labeled examples. The choice of strategy depends on the application, the nature of the signal and noise, and the available computational resources.
Tip 3: Leverage Statistical Methods
Statistical methods are invaluable in signal detection, offering tools to analyze and understand the behavior of signals and noise. Techniques such as hypothesis testing and confidence interval estimation can be used to determine whether a detected signal is statistically significant. Additionally, statistical models like Bayesian inference provide a framework for updating beliefs about the presence of a signal based on new data, incorporating prior knowledge and uncertainty in a principled way.
Bayesian Inference in Signal Detection
Bayesian inference is particularly useful in signal detection scenarios where prior information is available. By combining this prior information with the likelihood of observing the data given the presence or absence of a signal, Bayesian methods can provide posterior probabilities that reflect the updated belief in the signal’s presence. This approach can be especially powerful in applications where the cost of false positives or false negatives is high, such as in medical diagnosis or financial forecasting.
Tip 4: Apply Filtering Techniques
Filtering is a fundamental technique in signal processing that can significantly enhance signal detection by reducing noise. Filters can be designed to pass signals of interest while attenuating noise, based on their frequency characteristics. For example, a low-pass filter can remove high-frequency noise from an audio signal, improving its quality. There are various types of filters, including analog and digital filters, each with its own applications and design considerations.
Filter Design Considerations
The design of a filter involves several considerations, including the cutoff frequency, roll-off rate, and filter order. These parameters determine how effectively the filter can separate the signal from the noise. Additionally, the choice between analog and digital filters depends on the application, with digital filters offering greater flexibility and precision but potentially introducing latency.
| Filter Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Analog Filter | Filters signals in the continuous-time domain. |
| Digital Filter | Filters signals in the discrete-time domain, offering programmability and precision. |
Tip 5: Implement Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation
Signal detection is not a one-time process but rather an ongoing activity that requires continuous monitoring and adaptation. The characteristics of both the signal and the noise can change over time, necessitating adjustments to the detection strategy. This might involve periodically retraining machine learning models on new data, updating statistical models to reflect changing conditions, or adjusting filter parameters to maintain optimal performance.
Adaptive Signal Detection Systems
Adaptive systems that can learn from experience and adjust their parameters accordingly are particularly valuable in dynamic environments. These systems can incorporate feedback from previous detections, allowing them to refine their detection criteria and improve performance over time. The development of such adaptive signal detection systems requires a deep understanding of both the application domain and the signal processing techniques involved.
What is the primary challenge in signal detection?
+The primary challenge in signal detection is distinguishing the signal of interest from the background noise, which can lead to false positives or false negatives if not addressed properly.
How can signal detection be improved?
+Signal detection can be improved by understanding the characteristics of the signal and noise, optimizing threshold settings, leveraging statistical methods, applying filtering techniques, and implementing continuous monitoring and adaptation.
What role does filtering play in signal detection?
+Filtering plays a crucial role in signal detection by reducing noise and enhancing the signal-to-noise ratio, thereby improving the accuracy of signal detection.
In conclusion, effective signal detection is a multifaceted process that requires a deep understanding of the signal and noise characteristics, optimal threshold settings, the application of statistical methods, the use of filtering techniques, and continuous adaptation. By mastering these aspects and staying abreast of the latest developments in signal processing and detection, professionals can significantly enhance the efficacy of their signal detection systems, leading to improved outcomes in a wide range of applications.