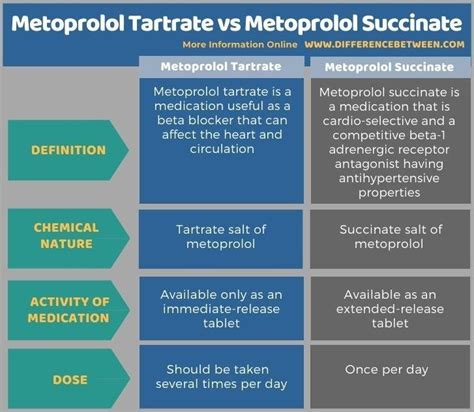
Metoprolol is a widely used beta-blocker medication, primarily prescribed to manage high blood pressure, chest pain (angina), and certain heart-related conditions. It is available in two main formulations: metoprolol tartrate and metoprolol succinate. Understanding the differences between these two formulations is crucial for effective treatment and management of cardiovascular diseases. In this article, we will delve into the details of metoprolol tartrate vs succinate, exploring their pharmacological profiles, clinical applications, and implications for patient care.
Key Points
- Metoprolol tartrate and succinate are two different salt forms of metoprolol, with distinct pharmacokinetic properties.
- Metoprolol tartrate is typically used for immediate-release formulations, while metoprolol succinate is used for extended-release formulations.
- The choice between metoprolol tartrate and succinate depends on the specific clinical condition, patient characteristics, and desired therapeutic effect.
- Both formulations have been shown to be effective in managing hypertension, angina, and heart failure, but with different dosing regimens and potential side effects.
- It is essential to consult a healthcare professional before switching between metoprolol tartrate and succinate, as this may require adjustments in dosage and monitoring.
Pharmacological Profiles

Metoprolol tartrate and metoprolol succinate differ in their salt forms, which affects their pharmacokinetic properties. Metoprolol tartrate is a water-soluble salt, whereas metoprolol succinate is a lipid-soluble salt. This difference influences their absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) profiles. Metoprolol tartrate is absorbed more rapidly, resulting in a faster onset of action, while metoprolol succinate is absorbed more slowly, leading to a longer duration of action.
Immediate-Release vs Extended-Release Formulations
Metoprolol tartrate is commonly used in immediate-release formulations, which are designed to provide a rapid increase in plasma concentrations. This formulation is often used for the treatment of acute conditions, such as hypertension or angina. In contrast, metoprolol succinate is used in extended-release formulations, which provide a sustained release of the medication over a longer period. This formulation is often used for the treatment of chronic conditions, such as heart failure or hypertension.
| Formulation | Pharmacokinetic Properties |
|---|---|
| Metoprolol Tartrate | Rapid absorption, fast onset of action, shorter duration of action |
| Metoprolol Succinate | Slow absorption, slower onset of action, longer duration of action |
Clinical Applications
Both metoprolol tartrate and succinate have been shown to be effective in managing various cardiovascular conditions. Metoprolol tartrate is often used for the treatment of hypertension, angina, and supraventricular tachycardia, while metoprolol succinate is used for the treatment of heart failure, hypertension, and angina. The choice of formulation depends on the specific clinical condition, patient characteristics, and desired therapeutic effect.
Dosing Regimens and Potential Side Effects
The dosing regimens for metoprolol tartrate and succinate differ due to their distinct pharmacokinetic properties. Metoprolol tartrate is typically administered in divided doses, while metoprolol succinate is administered once daily. Potential side effects, such as bradycardia, hypotension, and fatigue, may also differ between the two formulations. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional before initiating or switching between metoprolol tartrate and succinate, as this may require adjustments in dosage and monitoring.
What is the primary difference between metoprolol tartrate and succinate?
+The primary difference between metoprolol tartrate and succinate is their salt form, which affects their pharmacokinetic properties. Metoprolol tartrate is a water-soluble salt, while metoprolol succinate is a lipid-soluble salt.
Which formulation is preferred for the treatment of acute hypertension?
+Metoprolol tartrate is often preferred for the treatment of acute hypertension due to its rapid onset of action.
Can I switch between metoprolol tartrate and succinate without consulting a healthcare professional?
+No, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional before switching between metoprolol tartrate and succinate, as this may require adjustments in dosage and monitoring.
In conclusion, metoprolol tartrate and succinate are two different formulations of metoprolol, each with its own unique pharmacological profile and clinical applications. Understanding the differences between these two formulations is crucial for effective treatment and management of cardiovascular diseases. By consulting a healthcare professional and carefully selecting the appropriate formulation, patients can receive optimal treatment and minimize potential side effects.