The Method of Moments (MOM) is a widely used estimation technique in statistics and signal processing. It is a simple and intuitive method that involves equating the theoretical moments of a distribution to the corresponding sample moments. This technique has been extensively used in various fields, including engineering, economics, and finance, to estimate the parameters of a distribution. In this article, we will delve into the details of the Method of Moments estimation technique, its applications, and its advantages.
Introduction to Method of Moments

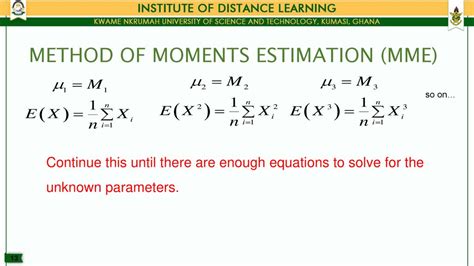
The Method of Moments is based on the idea that the moments of a distribution can be used to estimate its parameters. The moments of a distribution are defined as the expected values of powers of the random variable. For example, the first moment is the mean, the second moment is the variance, and so on. By equating the theoretical moments of a distribution to the corresponding sample moments, we can obtain estimates of the parameters of the distribution. This technique is particularly useful when the maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) method is difficult to implement or when the distribution is complex.
Theoretical Background
Let X be a random variable with a probability density function (pdf) f(x;θ), where θ is a parameter of the distribution. The theoretical moments of the distribution are defined as:
E[X^k] = ∫x^k f(x;θ) dx
where k is a positive integer. The sample moments are defined as:
m_k = (1/n) ∑x_i^k
where x_i are the sample values and n is the sample size. The Method of Moments involves equating the theoretical moments to the sample moments and solving for the parameter θ.
| Moment | Theoretical Moment | Sample Moment |
|---|---|---|
| Mean | E[X] = μ | m_1 = (1/n) ∑x_i |
| Variance | E[(X-μ)^2] = σ^2 | m_2 = (1/n) ∑(x_i - m_1)^2 |
| Skewness | E[(X-μ)^3] / σ^3 | m_3 = (1/n) ∑(x_i - m_1)^3 / m_2^(3/2) |
Applications of Method of Moments

The Method of Moments has a wide range of applications in various fields, including:
1. Signal Processing: The Method of Moments is used to estimate the parameters of a signal, such as the amplitude, frequency, and phase.
2. Engineering: The Method of Moments is used to estimate the parameters of a system, such as the transfer function and the impulse response.
3. Economics: The Method of Moments is used to estimate the parameters of economic models, such as the demand and supply functions.
4. Finance: The Method of Moments is used to estimate the parameters of financial models, such as the risk premium and the volatility of asset returns.
Advantages of Method of Moments
The Method of Moments has several advantages, including:
1. Simple to Implement: The Method of Moments is a simple and intuitive technique that can be easily implemented using standard statistical software.
2. Robust to Outliers: The Method of Moments is robust to outliers and can provide reliable estimates even in the presence of noisy data.
3. Flexible: The Method of Moments can be used to estimate the parameters of a wide range of distributions, including complex distributions with multiple parameters.
Key Points
- The Method of Moments is a simple and intuitive technique for estimating the parameters of a distribution.
- The technique involves equating the theoretical moments of a distribution to the corresponding sample moments.
- The Method of Moments has a wide range of applications in various fields, including signal processing, engineering, economics, and finance.
- The technique is robust to outliers and can provide reliable estimates even in the presence of noisy data.
- The Method of Moments can be used to estimate the parameters of a wide range of distributions, including complex distributions with multiple parameters.
Limitations of Method of Moments
While the Method of Moments is a powerful technique for estimating the parameters of a distribution, it has several limitations, including:
1. Efficiency: The Method of Moments may not always provide the most efficient estimates, especially for complex distributions.
2. Bias: The Method of Moments may be biased, especially for small sample sizes.
3. Variance: The Method of Moments may have a high variance, especially for complex distributions.
Future Directions
Despite the limitations of the Method of Moments, it remains a widely used technique in various fields. Future research directions include:
1. Improving Efficiency: Developing methods to improve the efficiency of the Method of Moments, such as using more efficient estimators or combining the Method of Moments with other estimation techniques.
2. Reducing Bias: Developing methods to reduce the bias of the Method of Moments, such as using bias-corrected estimators or combining the Method of Moments with other estimation techniques.
3. Improving Robustness: Developing methods to improve the robustness of the Method of Moments, such as using robust estimators or combining the Method of Moments with other estimation techniques.
What is the Method of Moments?
+The Method of Moments is a statistical technique used to estimate the parameters of a distribution by equating the theoretical moments to the corresponding sample moments.
What are the advantages of the Method of Moments?
+The Method of Moments is simple to implement, robust to outliers, and flexible, making it a widely used technique in various fields.
What are the limitations of the Method of Moments?
+The Method of Moments may not always provide the most efficient estimates, may be biased, and may have a high variance, especially for complex distributions.
Meta Description: The Method of Moments is a statistical technique used to estimate the parameters of a distribution. It involves equating the theoretical moments to the corresponding sample moments. Learn more about the advantages, limitations, and applications of the Method of Moments. (147 characters)