The terms LLM (Large Language Model) and JD (Job Description) may seem unrelated at first glance, but they intersect in the realm of artificial intelligence, natural language processing, and workforce management. A Large Language Model is a type of artificial intelligence designed to process and understand human language, generating text that is often indistinguishable from that written by humans. On the other hand, a Job Description is a document that outlines the responsibilities, duties, required skills, and outcomes for a specific role within an organization. Understanding the differences between these two concepts can provide insights into how AI is changing the way we approach job roles and descriptions.
Introduction to LLM and JD: Context and Purpose

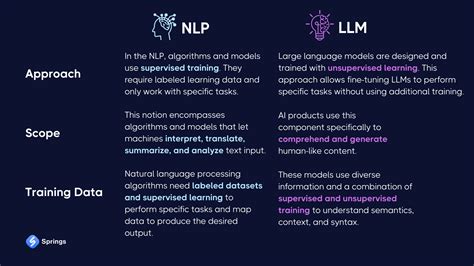
Large Language Models are built to learn the patterns and structures of language from vast datasets, enabling them to generate coherent and contextually relevant text. Their applications range from content creation and translation to chatbots and virtual assistants. Job Descriptions, however, are foundational documents in human resources, serving as the basis for hiring, performance evaluation, and career development. The purpose of a JD is to clearly communicate the expectations and requirements of a job, helping both employers and employees understand their roles and responsibilities.
Key Points
- LLMs are AI models designed for natural language processing and generation.
- JDs are documents outlining job responsibilities, skills, and outcomes.
- LLMs can automate certain aspects of job description creation and analysis.
- JDs require human judgment and understanding of organizational needs.
- The integration of LLMs in HR can enhance efficiency but also raises ethical considerations.
1. Purpose and Functionality
The primary purpose of a Large Language Model is to understand and generate human-like text based on the input it receives. This can range from simple queries to complex content creation tasks. In contrast, the purpose of a Job Description is to define and communicate the role of a position within an organization, including its responsibilities, required skills, and performance metrics. While an LLM can assist in generating or analyzing job descriptions, its functionality is fundamentally different from the purpose and use of a JD.
2. Creation and Development
Large Language Models are developed through complex algorithms and machine learning processes, involving the analysis of vast amounts of text data. This process allows LLMs to learn patterns and relationships within language, enabling them to generate text. Job Descriptions, on the other hand, are typically created by human resources professionals or hiring managers, who use their understanding of the organization’s needs and the role’s requirements to craft a document that accurately reflects the position’s responsibilities and expectations.
| Aspect | LLM | JD |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Natural Language Processing and Generation | Define and Communicate Job Responsibilities |
| Creation | Machine Learning and Algorithmic Processes | Human Resources and Hiring Managers |
| Application | Content Creation, Translation, Chatbots | Hiring, Performance Evaluation, Career Development |
3. Application and Impact
The applications of Large Language Models are diverse and expanding, from customer service and content creation to language translation and research assistance. In the context of Job Descriptions, LLMs can be used to automate the process of generating job postings, analyzing resumes, and even predicting job fit based on candidate profiles. However, Job Descriptions have a direct impact on organizational structure, workforce planning, and individual career paths, influencing how roles are defined, how employees are evaluated, and how organizations attract and retain talent.
4. Ethical Considerations
Both Large Language Models and Job Descriptions raise important ethical considerations. For LLMs, concerns include the potential for biased outputs, privacy issues related to data collection, and the impact of automation on employment. Job Descriptions, while more traditional, must also be crafted with care to avoid bias, ensure fairness in hiring practices, and comply with legal requirements. The use of LLMs in generating or analyzing JDs introduces additional ethical layers, such as ensuring that AI-driven processes do not inadvertently discriminate against certain groups of candidates.
5. Future Development and Integration
As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see further integration of Large Language Models into various aspects of human resources, including the creation, analysis, and application of Job Descriptions. This integration has the potential to revolutionize how organizations approach talent acquisition, employee development, and performance management. However, it also requires ongoing evaluation and adaptation to address the ethical, legal, and societal implications of relying on AI in these critical processes.
How can LLMs be used to improve Job Descriptions?
+LLMs can assist in generating job descriptions, analyzing resumes, and predicting job fit, thereby enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of hiring processes.
What are the ethical considerations of using LLMs in HR processes?
+Key ethical considerations include avoiding bias in AI decision-making, ensuring privacy and data protection, and addressing the potential impact of automation on employment and workforce dynamics.
How can organizations ensure the effective integration of LLMs and JDs?
+Organizations should approach the integration of LLMs and JDs with a focus on transparency, ongoing evaluation, and a commitment to addressing ethical and societal implications. This includes regularly updating AI systems, training personnel, and maintaining a human-centric approach to decision-making processes.
In conclusion, while Large Language Models and Job Descriptions serve distinct purposes and have different functionalities, their intersection highlights the evolving landscape of work and technology. As we move forward, it will be crucial to balance the benefits of technological advancement with the need for ethical consideration, human judgment, and societal responsibility.



