Linear interpolation is a fundamental concept in mathematics and computer science, used to estimate the value of a function between two known points. The linear interpolation equation formula is a straightforward and efficient method for calculating these estimates. In this article, we will delve into the world of linear interpolation, exploring its definition, formula, and applications, as well as providing examples and explanations to help solidify understanding.
Definition and Formula of Linear Interpolation
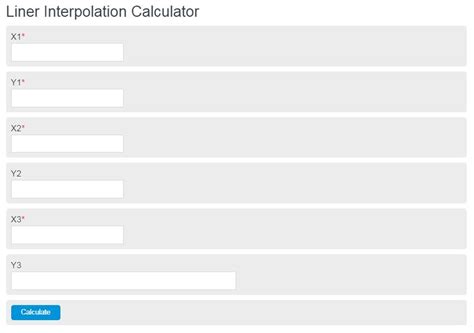
Linear interpolation is a technique used to approximate the value of a function at an unknown point, given two known points. The linear interpolation equation formula is given by:
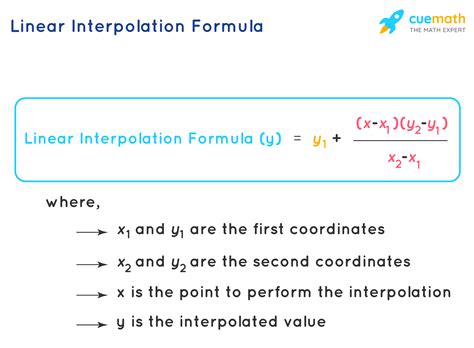
y = y1 + (x - x1) * (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)
where (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) are the known points, and (x, y) is the point at which we want to estimate the value of the function. This formula calculates the value of y at point x, based on the linear relationship between the two known points.
Key Points
- The linear interpolation equation formula is used to estimate the value of a function between two known points.
- The formula is given by y = y1 + (x - x1) * (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1), where (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) are the known points.
- Linear interpolation is a fundamental concept in mathematics and computer science, with applications in various fields, including data analysis, computer graphics, and engineering.
- The formula is based on the linear relationship between the two known points, and it calculates the value of y at point x.
- Linear interpolation is a simple and efficient method for estimating the value of a function, but it may not be accurate for all types of functions or data sets.
How Linear Interpolation Works
Linear interpolation works by creating a linear equation that passes through the two known points. This equation is then used to estimate the value of the function at the unknown point. The linear interpolation equation formula is derived from the slope-intercept form of a linear equation, which is given by:
y = mx + b
where m is the slope of the line, and b is the y-intercept. The slope of the line is calculated using the formula:
m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)
The y-intercept is then calculated using one of the known points, for example:
b = y1 - m * x1
Once the slope and y-intercept are calculated, the linear equation can be used to estimate the value of the function at the unknown point.
| Known Points | Linear Interpolation Formula | Estimated Value |
|---|---|---|
| (x1, y1) = (2, 3) | y = 3 + (x - 2) * (5 - 3) / (4 - 2) | y = 3 + (x - 2) * 1 |
| (x2, y2) = (4, 5) | y = 3 + (x - 2) * 1 | y = 3 + x - 2 |
Applications of Linear Interpolation
Linear interpolation has numerous applications in various fields, including:
Data analysis: Linear interpolation is used to estimate missing values in a data set, creating a continuous function that can be used for analysis and visualization.
Computer graphics: Linear interpolation is used to create smooth animations and transitions between images, by estimating the position and color of pixels at intermediate points.
Engineering: Linear interpolation is used to model the behavior of physical systems, such as the motion of objects, and to estimate the response of systems to different inputs.
Signal processing: Linear interpolation is used to reconstruct signals from sampled data, creating a continuous signal that can be used for analysis and processing.
Advantages and Limitations of Linear Interpolation
Linear interpolation has several advantages, including:
Simplitude: Linear interpolation is a simple and efficient method for estimating the value of a function.
Accuracy: Linear interpolation can provide accurate results for functions that are approximately linear over the interpolation interval.
Computational efficiency: Linear interpolation requires minimal computational resources, making it suitable for real-time applications.
However, linear interpolation also has some limitations, including:
Assumes linearity: Linear interpolation assumes a linear relationship between the points, which may not always be the case.
Lack of smoothness: Linear interpolation can produce discontinuities in the estimated function, particularly when the interpolation interval is large.
Sensitivity to noise: Linear interpolation can be sensitive to noise in the data, particularly when the noise is large compared to the signal.
What is linear interpolation used for?
+Linear interpolation is used to estimate the value of a function between two known points. It has numerous applications in various fields, including data analysis, computer graphics, engineering, and signal processing.
What are the advantages of linear interpolation?
+Linear interpolation has several advantages, including simplicity, accuracy, and computational efficiency. It is a simple and efficient method for estimating the value of a function, and it can provide accurate results for functions that are approximately linear over the interpolation interval.
What are the limitations of linear interpolation?
+Linear interpolation has several limitations, including the assumption of linearity, lack of smoothness, and sensitivity to noise. It assumes a linear relationship between the points, which may not always be the case, and it can produce discontinuities in the estimated function. Additionally, linear interpolation can be sensitive to noise in the data, particularly when the noise is large compared to the signal.
In conclusion, linear interpolation is a powerful tool for estimating the value of a function between two known points. Its simplicity, accuracy, and computational efficiency make it a popular choice for various applications. However, it’s essential to be aware of its limitations, including the assumption of linearity, lack of smoothness, and sensitivity to noise. By understanding these limitations and using linear interpolation judiciously, we can unlock its full potential and achieve accurate and reliable results in a wide range of fields.



