The interior angle formula is a fundamental concept in geometry, essential for calculating the sum of interior angles in a polygon. Understanding this formula is crucial for various geometric calculations, including finding the measure of each interior angle in a regular polygon. In this article, we will delve into the world of interior angles, exploring the formula, its derivation, and practical applications, making the interior angle formula easy to comprehend and apply.
Key Points
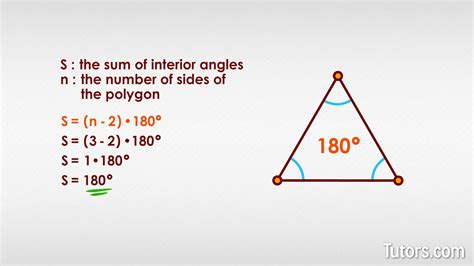
- The interior angle formula states that the sum of the interior angles of a polygon can be calculated using the formula (n-2)*180 degrees, where n is the number of sides of the polygon.
- The formula applies to all types of polygons, including regular and irregular polygons.
- For regular polygons, the measure of each interior angle can be found by dividing the sum of the interior angles by the number of sides.
- Understanding the interior angle formula is essential for various geometric calculations and real-world applications.
- Practical applications of the interior angle formula include architecture, engineering, and design.
Derivation of the Interior Angle Formula
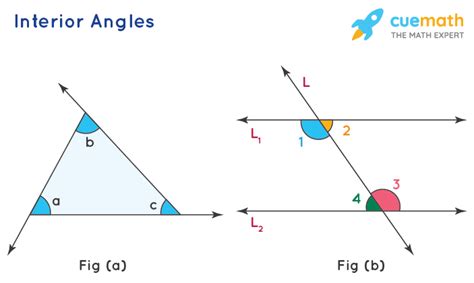
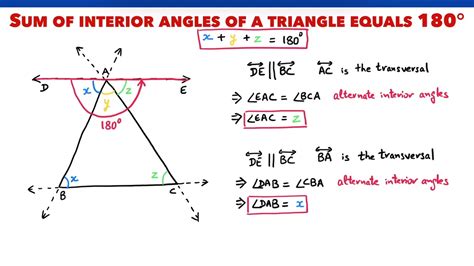
The interior angle formula can be derived by considering the sum of the exterior angles of a polygon. The sum of the exterior angles of any polygon is always 360 degrees. By subtracting the sum of the exterior angles from 360 degrees, we can find the sum of the interior angles. This can be represented as (n-2)*180 degrees, where n is the number of sides of the polygon.
Understanding the Formula
To understand the formula, let’s break it down into its components. The number of sides (n) is a critical component, as it determines the sum of the interior angles. For example, a triangle has 3 sides, so the sum of its interior angles is (3-2)*180 = 180 degrees. A quadrilateral has 4 sides, so the sum of its interior angles is (4-2)*180 = 360 degrees.
| Polygon | Number of Sides (n) | Sum of Interior Angles |
|---|---|---|
| Triangle | 3 | 180 degrees |
| Quadrilateral | 4 | 360 degrees |
| Pentagon | 5 | 540 degrees |
| Hexagon | 6 | 720 degrees |
Practical Applications of the Interior Angle Formula
The interior angle formula has numerous practical applications in various fields, including architecture, engineering, and design. For example, architects use the formula to design buildings with specific interior angles, while engineers use it to calculate the stress and strain on structures. In design, the formula is used to create visually appealing and balanced compositions.
Real-World Examples
One real-world example of the interior angle formula is in the design of bridges. Bridge architects use the formula to calculate the interior angles of the bridge’s support structure, ensuring that it can withstand various loads and stresses. Another example is in the design of buildings, where architects use the formula to create aesthetically pleasing and functional interior spaces.
In conclusion, the interior angle formula is a fundamental concept in geometry, essential for calculating the sum of interior angles in a polygon. By understanding the formula and its derivation, you can apply it to various geometric calculations and real-world applications, making it a valuable tool in your mathematical toolkit.
What is the interior angle formula?
+The interior angle formula states that the sum of the interior angles of a polygon can be calculated using the formula (n-2)*180 degrees, where n is the number of sides of the polygon.
How is the interior angle formula derived?
+The interior angle formula can be derived by considering the sum of the exterior angles of a polygon. The sum of the exterior angles of any polygon is always 360 degrees. By subtracting the sum of the exterior angles from 360 degrees, we can find the sum of the interior angles.
What are some practical applications of the interior angle formula?
+The interior angle formula has numerous practical applications in various fields, including architecture, engineering, and design. For example, architects use the formula to design buildings with specific interior angles, while engineers use it to calculate the stress and strain on structures.