Understanding the relationship between mass, volume, and density is fundamental in physics and engineering. The ability to calculate mass using volume and density is a crucial skill that has numerous applications in various fields, including chemistry, physics, and materials science. In this article, we will delve into the concept of density and how it relates to mass and volume, providing a comprehensive guide on how to find mass with volume and density.
Introduction to Density, Mass, and Volume
Density, mass, and volume are interconnected physical properties of an object. The density of a substance is defined as its mass per unit volume. It is typically denoted by the symbol ρ (rho) and is expressed in units of kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³) in the International System of Units (SI). Mass, on the other hand, is a measure of the amount of matter in an object and is usually measured in kilograms (kg). Volume refers to the amount of three-dimensional space occupied by an object and is measured in cubic meters (m³) in the SI system.
Key Points
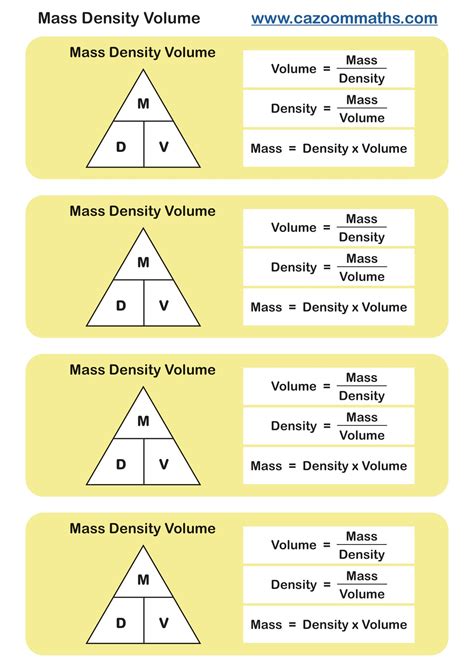
- The formula to calculate density is ρ = m/V, where ρ is density, m is mass, and V is volume.
- Mass can be calculated using the formula m = ρV, given the density and volume of an object.
- Volume can be determined through various methods, including direct measurement, calculation using the dimensions of the object, or by using the formula V = m/ρ.
- Understanding the relationship between mass, volume, and density is crucial for solving problems in physics, chemistry, and engineering.
- Real-world applications of calculating mass with volume and density include designing structures, understanding material properties, and solving problems in fluid dynamics.
Calculating Mass with Volume and Density
To find the mass of an object given its volume and density, we use the formula derived from the definition of density: m = ρV. This formula rearranges the original density formula (ρ = m/V) to solve for mass (m). By multiplying the density of the object (in kg/m³) by its volume (in m³), we obtain the mass of the object in kilograms (kg).
| Property | Symbol | Unit (SI) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | ρ | kg/m³ |
| Mass | m | kg |
| Volume | V | m³ |

Practical Applications and Examples
The ability to calculate mass using volume and density has numerous practical applications. For instance, in construction, knowing the density of building materials allows architects and engineers to calculate the mass of the structure, which is critical for designing foundations, estimating costs, and ensuring structural integrity. In chemistry, understanding the density of substances is vital for calculating the mass of reactants and products in chemical reactions.
Consider an example where we want to find the mass of a block of aluminum given its volume and density. If the volume of the aluminum block is 0.1 m³ and the density of aluminum is approximately 2700 kg/m³, we can calculate the mass as follows: m = ρV = 2700 kg/m³ * 0.1 m³ = 270 kg.
Limitations and Considerations
While the formula m = ρV provides a straightforward method for calculating mass, there are considerations and potential limitations. For instance, the density of a substance can vary with temperature and pressure, especially for gases. Additionally, for objects with complex shapes or non-uniform density, calculating the volume or determining the average density can be challenging.
What is the formula to calculate mass using volume and density?
+The formula to calculate mass (m) using volume (V) and density (ρ) is m = ρV.
Why is it important to ensure unit consistency when calculating mass with volume and density?
+Ensuring unit consistency, preferably using the SI system, helps in avoiding conversion errors and makes calculations more straightforward and accurate.
How does the temperature and pressure affect the density of substances?
+The density of substances, especially gases, can vary with changes in temperature and pressure. It is essential to consider these factors when calculating mass using volume and density, particularly in applications where precise measurements are critical.
In conclusion, understanding how to find mass with volume and density is a fundamental skill that has wide-ranging applications across various scientific and engineering disciplines. By applying the formula m = ρV and considering the factors that can affect density, individuals can accurately calculate the mass of objects, which is essential for problem-solving in physics, chemistry, and beyond.