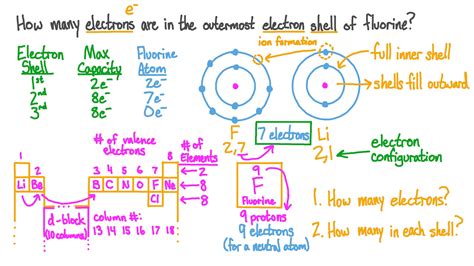
The atomic structure of an element is a complex arrangement of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Understanding the distribution of these particles is essential for comprehending the chemical properties of an element. In this context, finding electrons in an element is a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics. To do this, we need to delve into the atomic structure and the periodic table, which provides a systematic way of organizing elements based on their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties.
The periodic table is divided into rows called periods and columns called groups or families. Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties due to the same number of electrons in their outermost shell. The atomic number of an element, which is the number of protons in the nucleus, determines its position in the periodic table. Electrons, on the other hand, are arranged around the nucleus in energy levels or shells. The number of electrons in a neutral atom is equal to the number of protons, which is the atomic number.
Key Points
- To find electrons in an element, understanding the atomic number and the periodic table is crucial.
- The electron configuration, which describes the distribution of electrons in an atom, can be determined by the periodic table's structure.
- The outermost energy level of an atom, also known as the valence shell, plays a significant role in determining the chemical properties of an element.
- Electrons are arranged in energy levels or shells around the nucleus, with each shell having a specific capacity for electrons.
- The Aufbau principle and the Pauli exclusion principle are essential in predicting the electron configuration of an element.
Understanding Electron Configuration
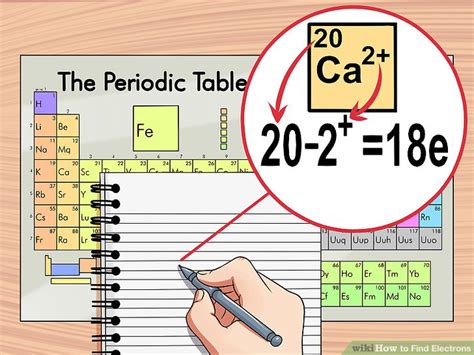
Electron configuration refers to the arrangement of electrons in an atom. It is a crucial concept in understanding the chemical behavior of elements. The electron configuration can be determined by following the Aufbau principle, which states that electrons fill the lowest available energy levels. Additionally, the Pauli exclusion principle, which states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of quantum numbers, helps in understanding how electrons are distributed in an atom.
Determining the Number of Electrons
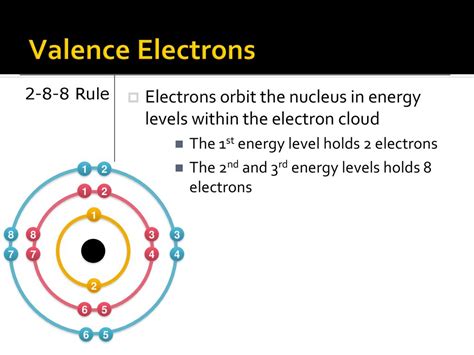
The number of electrons in a neutral atom is equal to the atomic number of the element. For example, carbon has an atomic number of 6, which means a neutral carbon atom has 6 electrons. These electrons are arranged in energy levels or shells around the nucleus. The first energy level can hold up to 2 electrons, the second energy level can hold up to 8 electrons, and so on. Understanding how electrons are distributed in these energy levels is essential for predicting the chemical properties of an element.
| Element | Atomic Number | Number of Electrons |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 1 | 1 |
| Helium | 2 | 2 |
| Carbon | 6 | 6 |
| Oxygen | 8 | 8 |
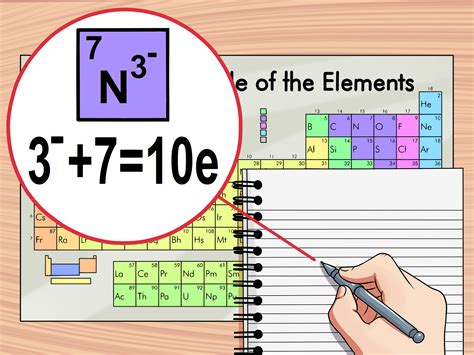
Practical Applications of Electron Configuration
The concept of electron configuration has numerous practical applications in chemistry and physics. It helps in understanding the formation of chemical bonds, the reactivity of elements, and the properties of compounds. For instance, elements in the same group of the periodic table have similar chemical properties because they have the same number of electrons in their outermost shell. This understanding is crucial in predicting how elements will react with each other and in designing new materials and compounds.
Chemical Bonding and Reactivity
Chemical bonding, which involves the sharing or exchange of electrons between atoms, is directly related to the electron configuration of elements. The reactivity of an element, which is its ability to form chemical bonds with other elements, is determined by the number of electrons in its outermost shell. Elements that have a full outer shell are less reactive because they do not tend to gain, lose, or share electrons. On the other hand, elements with incomplete outer shells are more reactive as they seek to achieve a full outer shell configuration.
In conclusion, finding electrons in an element involves understanding the atomic structure, the periodic table, and the principles of electron configuration. By applying these concepts, we can predict the chemical properties and reactivity of elements, which is essential for advancing our knowledge in chemistry and physics.
What determines the chemical properties of an element?
+The chemical properties of an element are determined by the number of electrons in its outermost shell. This is because the outermost electrons are involved in chemical bonding and reactions.
How is the electron configuration of an element determined?
+The electron configuration of an element is determined by following the Aufbau principle and the Pauli exclusion principle. These principles guide how electrons fill the energy levels or shells around the nucleus.
What is the significance of the periodic table in finding electrons in an element?
+The periodic table is significant because it organizes elements in a way that reflects their electron configuration and chemical properties. By understanding the periodic table, one can predict the electron configuration and properties of an element based on its position.