Access to clean drinking water is a fundamental human right, and its importance cannot be overstated. With the global population projected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050, according to the United Nations, the demand for water is increasing exponentially. However, many communities around the world still struggle to access this basic necessity. The good news is that there are several innovative methods to produce water easily, which can help alleviate this crisis. In this article, we will explore some of these methods, including their technical specifications, advantages, and limitations.
Atmospheric Water Generation
Atmospheric water generation (AWG) is a technology that extracts water from the air, even in arid environments. This method uses a combination of cooling and condensation to capture water vapor, which is then filtered and purified to produce clean drinking water. AWG systems can be powered by solar energy, making them a sustainable and eco-friendly option. For instance, the FogQuest system, which uses a mesh to capture fog droplets, has been successfully implemented in various countries, including Chile and South Africa. According to a study published in the Journal of Water Resources Management, AWG systems can produce up to 1,000 liters of water per day, depending on the humidity and temperature of the air.
Advantages and Limitations of AWG
One of the primary advantages of AWG is its ability to provide clean drinking water in areas where traditional water sources are scarce. Additionally, AWG systems are relatively low-maintenance and can be powered by renewable energy sources. However, the high initial investment cost and energy requirements are significant limitations. Furthermore, AWG systems may not be effective in extremely dry environments, where the air humidity is very low. To overcome these limitations, researchers are exploring new technologies, such as nanotechnology-based AWG systems, which can improve the efficiency and affordability of water production.
| AWG System | Water Production Capacity | Energy Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| FogQuest | Up to 1,000 liters per day | 2-5 kW |
| Atmoswater | Up to 500 liters per day | 1-3 kW |

Desalination
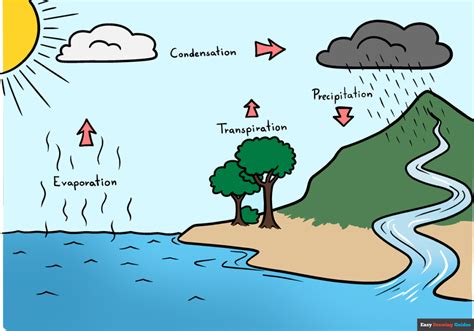
Desalination is the process of removing salt and other minerals from seawater or brackish water to produce fresh water. There are several desalination methods, including reverse osmosis, distillation, and electrodialysis. Desalination plants can be powered by fossil fuels or renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power. According to the International Desalination Association, there are over 20,000 desalination plants worldwide, producing more than 100 million cubic meters of fresh water per day. However, desalination has several drawbacks, including high energy consumption, environmental impacts, and high costs. For example, a study published in the Journal of Environmental Science and Health found that desalination plants can harm marine ecosystems by releasing toxic chemicals and excess salt into the ocean.
Technical Specifications of Desalination
The technical specifications of desalination plants vary depending on the method used. Reverse osmosis, for instance, requires a semi-permeable membrane to separate salt and other minerals from water. Distillation, on the other hand, involves heating the water to produce steam, which is then condensed to produce fresh water. Electrodialysis uses an electrical current to remove salt and other minerals from water. Understanding these technical specifications is crucial for effective implementation and maintenance of desalination plants.
Key Points
- AWS systems can produce up to 1,000 liters of water per day, depending on the humidity and temperature of the air.
- Desalination plants can be powered by fossil fuels or renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power.
- The technical specifications of desalination plants vary depending on the method used.
- AWG systems have the potential to revolutionize the way we access clean drinking water, but their high initial investment cost and energy requirements are significant limitations.
- Understanding the technical specifications, advantages, and limitations of each water production method is crucial for effective implementation and maintenance.
Rainwater Harvesting
Rainwater harvesting is a simple and effective method of collecting and storing rainwater for non-potable uses, such as irrigation, toilet flushing, and washing machines. This method can help reduce the demand on municipal water supplies and decrease stormwater runoff. According to the United States Environmental Protection Agency, rainwater harvesting can reduce stormwater runoff by up to 70%. However, rainwater harvesting requires adequate storage facilities and treatment systems to ensure water quality. For example, a study published in the Journal of Water Resources Management found that rainwater harvesting systems can reduce the risk of waterborne diseases by up to 50%.
Advantages and Limitations of Rainwater Harvesting
One of the primary advantages of rainwater harvesting is its ability to provide a free and sustainable source of water. Additionally, rainwater harvesting can help reduce the demand on municipal water supplies and decrease stormwater runoff. However, the high initial investment cost and maintenance requirements are significant limitations. Furthermore, rainwater harvesting may not be effective in areas with low rainfall or inadequate storage facilities. To overcome these limitations, researchers are exploring new technologies, such as rainwater harvesting systems with built-in treatment facilities, which can improve the efficiency and affordability of water production.
What is the difference between AWG and desalination?
+AWG extracts water from the air, while desalination removes salt and other minerals from seawater or brackish water. AWG is a more sustainable and eco-friendly option, while desalination has higher energy consumption and environmental impacts.
How can I implement a rainwater harvesting system?
+You can implement a rainwater harvesting system by installing a roof catchment, gutter, and downspout system, and connecting it to a storage tank. You may also need to install a treatment system to ensure water quality.
What are the benefits of using AWG systems?
+AWG systems can provide clean drinking water in areas where traditional water sources are scarce, and they are relatively low-maintenance and can be powered by renewable energy sources.
Meta description: Learn about innovative methods to produce water easily, including atmospheric water generation, desalination, and rainwater harvesting, and discover their technical specifications, advantages, and limitations. (150 characters)