The distinction between "has" and "have" is a fundamental aspect of English grammar, often posing challenges for both native and non-native speakers. Understanding the correct usage of these verbs is crucial for effective communication, as they are used in various contexts to express possession, actions, and states of being. In this article, we will delve into the grammar basics of "has" and "have," exploring their differences, usage, and practical applications.
Key Points
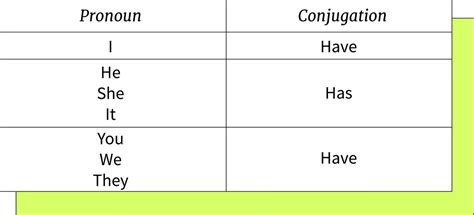
- The verb "has" is used with singular subjects, including the third person singular (he, she, it), to denote possession or action.
- The verb "have" is used with plural subjects, including the first person singular (I) and the second person singular (you), to denote possession or action.
- The correct usage of "has" and "have" is essential for avoiding grammatical errors and ensuring clarity in communication.
- Understanding the differences between "has" and "have" requires a grasp of basic English grammar rules, including subject-verb agreement.
- Practicing the correct usage of "has" and "have" through examples and exercises can help reinforce grammar skills and improve overall language proficiency.
Subject-Verb Agreement: The Foundation of “Has” and “Have” Usage

At the heart of distinguishing between “has” and “have” lies the principle of subject-verb agreement. This grammatical rule dictates that the verb form must agree with the subject in number, either singular or plural. “Has” is used with singular subjects, such as “he,” “she,” and “it,” whereas “have” is used with plural subjects, including “I,” “you,” “we,” and “they.” For instance, “He has a car” illustrates the use of “has” with a singular subject, while “They have cars” demonstrates the use of “have” with a plural subject.
Examples and Exceptions: Understanding the Nuances
While the basic rule of subject-verb agreement provides a solid foundation, there are instances where the choice between “has” and “have” may seem less straightforward. For example, with collective nouns like “team” or “family,” the verb form can depend on whether the noun is considered as a single unit (singular) or as individual members (plural). Thus, “The team has won the championship” treats the team as a singular entity, whereas “The team have different opinions” considers the individual members, leading to the use of “have.” Such nuances highlight the importance of context in determining the correct verb form.
| Subject Type | Verb Form |
|---|---|
| Singular (he, she, it) | Has |
| Plural (I, you, we, they) | Have |
| Collective Nouns | Depends on Context (Has or Have) |
Practical Applications and Exercises

To solidify the understanding of “has” and “have,” practicing with exercises and real-world examples is indispensable. This practical application helps in internalizing the rules and developing a sense of when to use each verb form. For instance, completing sentences like “If I _______ (have/has) more time, I would travel” or “By the time she _______ (have/has) finished her homework, it was late” with the correct verb form based on the subject can serve as an effective learning tool.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
A common mistake in using “has” and “have” incorrectly often stems from a lack of attention to the subject-verb agreement. To avoid such errors, it is essential to identify the subject of the sentence and apply the appropriate verb form accordingly. Additionally, reading and listening to English materials can help in developing an ear for the correct usage, making it easier to recognize and apply the rules in practice.
What is the basic rule for choosing between "has" and "have"?
+The basic rule is based on subject-verb agreement, where "has" is used with singular subjects (he, she, it) and "have" is used with plural subjects (I, you, we, they).
How do collective nouns affect the choice between "has" and "have"?
+With collective nouns, the choice between "has" and "have" can depend on whether the noun is considered as a single unit (using "has") or as individual members (using "have"), depending on the context.
What is the best way to practice and improve the correct usage of "has" and "have"?
+Practicing with exercises, completing sentences with the correct verb form, and engaging with real-world examples and contexts can help in improving the correct usage of "has" and "have."
In conclusion, mastering the distinction between “has” and “have” is a critical aspect of English grammar, essential for clear and effective communication. By understanding the principles of subject-verb agreement, recognizing the nuances in collective nouns, and practicing with various exercises, individuals can improve their grammar skills and enhance their overall language proficiency. As with any aspect of language, continuous practice and exposure to correct usage are key to internalizing the rules and applying them confidently in everyday communication.