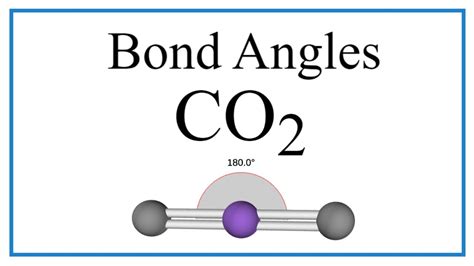
The CO2 bond angle is a fundamental concept in chemistry, particularly in the study of molecular geometry. Carbon dioxide, or CO2, is a molecule composed of one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms. The bond angle between the oxygen atoms and the central carbon atom is a crucial aspect of the molecule's structure, influencing its physical and chemical properties. In this article, we will delve into the CO2 bond angle, exploring its significance, the factors that influence it, and the implications of its value.
Understanding the CO2 Bond Angle
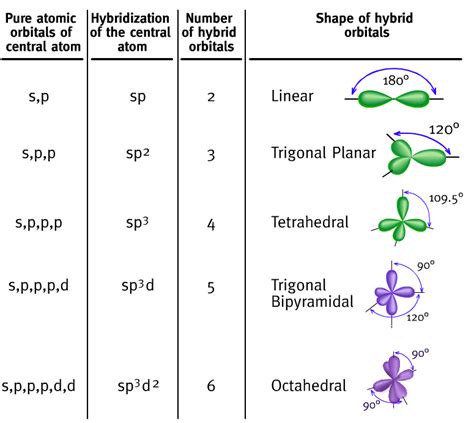
The CO2 bond angle refers to the angle formed between the two oxygen atoms and the central carbon atom in the carbon dioxide molecule. This angle is a result of the molecular geometry of CO2, which is linear. The linear geometry of CO2 is due to the sp hybridization of the carbon atom, which leads to the formation of two sigma bonds between the carbon and oxygen atoms. The bond angle is a critical parameter in determining the molecule’s shape and its reactivity.
Molecular Geometry and Hybridization
The molecular geometry of CO2 is determined by the hybridization of the carbon atom. The carbon atom in CO2 undergoes sp hybridization, resulting in the formation of two sp hybrid orbitals. These orbitals are oriented at an angle of 180 degrees, leading to the linear geometry of the molecule. The sp hybridization also results in the formation of two sigma bonds between the carbon and oxygen atoms, which are responsible for the molecule’s stability.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Bond Angle | 180 degrees |
| Bond Length | 116.3 pm |
| Molecular Geometry | Linear |
Factors Influencing the CO2 Bond Angle
The CO2 bond angle is influenced by several factors, including the molecular geometry, hybridization, and the presence of lone pairs. The linear geometry of CO2 results in a bond angle of 180 degrees, which is a consequence of the sp hybridization of the carbon atom. The presence of lone pairs on the oxygen atoms also plays a crucial role in determining the bond angle, as they occupy space and influence the orientation of the sigma bonds.
Lone Pairs and Bond Angle
The presence of lone pairs on the oxygen atoms in CO2 influences the bond angle by occupying space and affecting the orientation of the sigma bonds. The lone pairs on the oxygen atoms are oriented at an angle of 120 degrees, which results in a slight deviation from the ideal bond angle of 180 degrees. However, the linear geometry of CO2 is maintained due to the sp hybridization of the carbon atom.
Key Points
- The CO2 bond angle is 180 degrees, resulting from the linear geometry of the molecule.
- The sp hybridization of the carbon atom leads to the formation of two sigma bonds between the carbon and oxygen atoms.
- The presence of lone pairs on the oxygen atoms influences the bond angle by occupying space and affecting the orientation of the sigma bonds.
- The molecular geometry of CO2 is crucial in determining its physical and chemical properties.
- The bond angle of CO2 is a fundamental concept in chemistry, with implications for understanding molecular structure and reactivity.
Implications of the CO2 Bond Angle
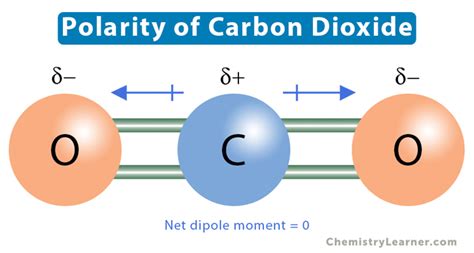
The CO2 bond angle has significant implications for understanding the physical and chemical properties of the molecule. The linear geometry of CO2 results in a molecule with high symmetry, which influences its reactivity and stability. The bond angle also affects the molecule’s polarity, with the linear geometry resulting in a non-polar molecule.
Polarity and Reactivity
The polarity of CO2 is influenced by the bond angle, with the linear geometry resulting in a non-polar molecule. The non-polarity of CO2 is due to the symmetrical distribution of charge within the molecule, resulting from the sp hybridization of the carbon atom. The non-polarity of CO2 affects its reactivity, with the molecule being less reactive than polar molecules.
The CO2 bond angle is a fundamental concept in chemistry, with significant implications for understanding molecular structure and reactivity. The linear geometry of CO2, resulting from the sp hybridization of the carbon atom, leads to a bond angle of 180 degrees. The presence of lone pairs on the oxygen atoms influences the bond angle, while the molecular geometry affects the molecule's polarity and reactivity. Understanding the CO2 bond angle is essential for appreciating the physical and chemical properties of this important molecule.
What is the CO2 bond angle, and why is it important?
+The CO2 bond angle is 180 degrees, resulting from the linear geometry of the molecule. It is important because it influences the molecule's physical and chemical properties, such as its reactivity and stability.
What factors influence the CO2 bond angle?
+The CO2 bond angle is influenced by the molecular geometry, hybridization, and the presence of lone pairs on the oxygen atoms.
How does the CO2 bond angle affect the molecule's polarity and reactivity?
+The linear geometry of CO2, resulting from the sp hybridization of the carbon atom, leads to a non-polar molecule. The non-polarity of CO2 affects its reactivity, with the molecule being less reactive than polar molecules.
Meta description: “Discover the significance of the CO2 bond angle and its influence on the molecule’s physical and chemical properties. Learn about the factors that affect the bond angle and its implications for understanding molecular structure and reactivity.” (150 characters)