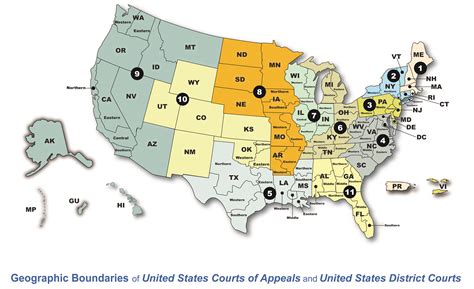
The United States is divided into 94 federal judicial districts, with at least one district in each state. These districts are further subdivided into divisions, and each district has a federal district court, also known as a United States District Court. The federal district courts have jurisdiction over cases involving federal laws, the Constitution, and disputes between citizens of different states. Understanding the federal district court map is essential for navigating the U.S. judicial system, as each district has its unique characteristics, judges, and procedural rules.
Key Points
- The United States is divided into 94 federal judicial districts.
- Each district has a federal district court, also known as a United States District Court.
- The federal district courts have jurisdiction over cases involving federal laws and the Constitution.
- Each district is presided over by a judge or a panel of judges appointed by the President and confirmed by the Senate.
- The federal district court map is crucial for understanding the U.S. judicial system and navigating its complexities.
Federal District Court Jurisdictions and Divisions
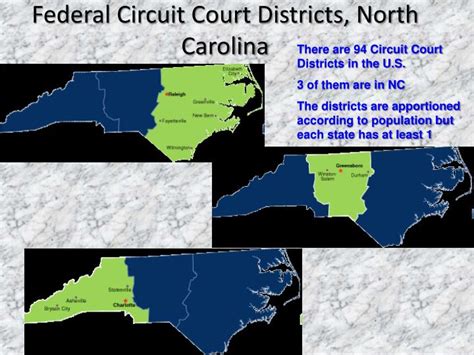
The federal district courts are the trial courts of the federal system, and they have the authority to hear a wide range of cases, including civil rights cases, contract disputes, and criminal prosecutions. The courts are divided into districts based on geographical areas, with some states having only one district, while others, like California and New York, have multiple districts due to their large populations and diverse legal needs. For example, the Central District of California, which includes Los Angeles, is one of the busiest federal courts in the country, handling a high volume of intellectual property and entertainment law cases.
District Courts and Their Roles
Each federal district court plays a critical role in the administration of justice within its jurisdiction. The courts are responsible for ensuring that the rights of all parties are protected and that the law is applied fairly and impartially. The judges who preside over these courts are appointed for life, subject to good behavior, and are expected to remain impartial and avoid conflicts of interest. This lifetime appointment is designed to ensure the independence of the judiciary and prevent political interference in the judicial process.
| District Court | Jurisdiction | Divisions |
|---|---|---|
| United States District Court for the District of Massachusetts | Massachusetts | Boston, Springfield, Worcester |
| United States District Court for the Southern District of New York | Southern part of New York State | New York City, White Plains |
| United States District Court for the Northern District of California | Northern part of California | San Francisco, Oakland, San Jose |

Importance of Federal District Courts in the Judicial System

Federal district courts are vital components of the U.S. judicial system, serving as the first point of contact for most federal cases. They handle a vast array of legal issues, from patent disputes to federal criminal cases, and their decisions can have significant impacts on both individuals and society as a whole. The diversity of cases heard in these courts, ranging from civil rights violations to complex financial fraud, underscores the importance of a fair, impartial, and knowledgeable judiciary.
Challenges Facing Federal District Courts
Despite their importance, federal district courts face numerous challenges, including caseload pressures, budget constraints, and the need for technological upgrades to improve efficiency and access to justice. Additionally, the courts must navigate complex legal issues, such as privacy rights in the digital age and the application of federal law to emerging technologies. The ability of these courts to adapt to changing societal needs and legal landscapes is crucial for maintaining public trust and ensuring that justice is served.
What is the role of a federal district court in the U.S. judicial system?
+Federal district courts are the trial courts of the federal system, responsible for hearing cases involving federal laws, the Constitution, and disputes between citizens of different states.
How are federal district courts divided?
+Federal district courts are divided based on geographical areas, with 94 districts across the United States. Each district has its own court, and some districts are further subdivided into divisions.
What kinds of cases do federal district courts hear?
+Federal district courts have jurisdiction over a wide range of cases, including civil rights cases, contract disputes, criminal prosecutions, and cases involving federal laws and the Constitution.
In conclusion, the federal district court map of the USA is a complex and dynamic system, reflecting the country’s legal, historical, and geographical diversity. Each district court plays a vital role in the administration of justice, ensuring that the rights of all individuals are protected and that the law is applied fairly and impartially. As the legal landscape continues to evolve, the adaptability and resilience of these courts will remain crucial for upholding the principles of justice and equality that underpin American society.