Incomplete dominance is a fascinating concept in genetics that explains how certain traits are inherited from parents to offspring. Unlike complete dominance, where one allele completely masks the effect of the other, incomplete dominance results in a blending of the two alleles, creating a new trait that is a combination of the two parental traits. This phenomenon is crucial in understanding the complexity of genetics and how it influences the characteristics of living organisms. In this article, we will delve into the world of incomplete dominance, exploring its mechanisms, examples, and significance in the field of genetics.
What is Incomplete Dominance?
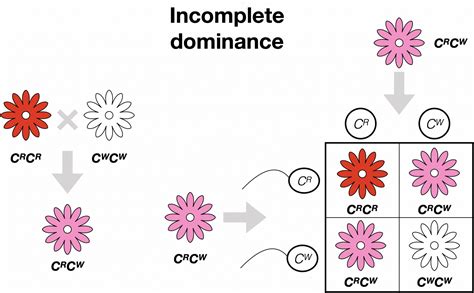
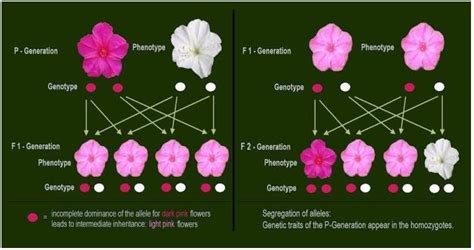
Incomplete dominance occurs when one allele does not completely dominate the other allele, resulting in a phenotype that is a mixture of the two parental phenotypes. This means that the effect of the two alleles is neither completely dominant nor completely recessive, but rather a combination of the two. For example, if we consider the inheritance of flower color in a plant, where one allele ® codes for red flowers and the other allele ® codes for white flowers, incomplete dominance would result in a phenotype with pink flowers, which is a combination of the two parental phenotypes.
Key Points
- Incomplete dominance results in a blending of the two alleles, creating a new trait that is a combination of the two parental traits.
- This phenomenon is crucial in understanding the complexity of genetics and how it influences the characteristics of living organisms.
- Incomplete dominance occurs when one allele does not completely dominate the other allele, resulting in a phenotype that is a mixture of the two parental phenotypes.
- The effect of the two alleles is neither completely dominant nor completely recessive, but rather a combination of the two.
- Incomplete dominance is significant in the field of genetics, as it helps to explain the diversity of traits in living organisms.
Examples of Incomplete Dominance
One of the most well-known examples of incomplete dominance is the inheritance of flower color in snapdragons. In this case, the allele for red flowers ® and the allele for white flowers ® are incompletely dominant, resulting in a phenotype with pink flowers. Another example is the inheritance of hair color in humans, where the allele for black hair (B) and the allele for blond hair (b) are incompletely dominant, resulting in a phenotype with brown hair.
| Characteristic | Allele | Phenotype |
|---|---|---|
| Flower color | R (red) and r (white) | Pink flowers |
| Hair color | B (black) and b (blond) | Brown hair |
Mechanisms of Incomplete Dominance
The mechanisms of incomplete dominance are complex and involve the interaction of multiple genes and environmental factors. In general, incomplete dominance occurs when the two alleles have different effects on the phenotype, but neither allele completely masks the effect of the other. This can result in a range of phenotypes, from a complete blending of the two parental traits to a more complex interaction between the two alleles.
Significance of Incomplete Dominance
Incomplete dominance has significant implications for our understanding of genetics and the inheritance of traits. It helps to explain the diversity of traits in living organisms and the complexity of genetic interactions. Incomplete dominance also has practical applications in fields such as agriculture and medicine, where it can be used to develop new traits and treatments.
In conclusion, incomplete dominance is a fascinating concept that helps to explain the complexity of genetics and the inheritance of traits. By understanding the mechanisms of incomplete dominance, scientists can gain insights into the complex interactions between genes and environmental factors that shape the characteristics of living organisms. This knowledge has significant implications for our understanding of genetics and the development of new traits and treatments.
What is incomplete dominance?
+Incomplete dominance is a phenomenon in genetics where one allele does not completely dominate the other allele, resulting in a phenotype that is a mixture of the two parental phenotypes.
What are some examples of incomplete dominance?
+Examples of incomplete dominance include the inheritance of flower color in snapdragons and the inheritance of hair color in humans.
What are the mechanisms of incomplete dominance?
+The mechanisms of incomplete dominance involve the interaction of multiple genes and environmental factors, resulting in a range of phenotypes.



