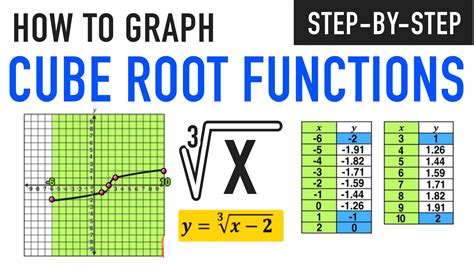
The cube root graph, denoted as $y = \sqrt[3]{x}$, is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in algebra and calculus. It represents a function where the output, $y$, is the cube root of the input, $x$. This graph is essential in understanding various mathematical concepts, including functions, equations, and graphical analysis. In this article, we will delve into the cube root graph, its properties, and its significance in mathematics.
Key Points
- The cube root graph is a representation of the function $y = \sqrt[3]{x}$.
- It has a characteristic shape, with the graph increasing as $x$ increases, but at a decreasing rate.
- The graph passes through the origin, (0,0), and has a point of inflection at this point.
- The cube root graph is symmetric with respect to the origin, meaning that if ($x$, $y$) is on the graph, then ($-x$, $-y$) is also on the graph.
- The graph has numerous applications in mathematics, physics, and engineering, particularly in problems involving volume, surface area, and optimization.
Properties of the Cube Root Graph

The cube root graph exhibits several distinctive properties. Firstly, it is an odd function, meaning that f(-x) = -f(x). This symmetry is evident in the graph, where the function’s values for negative x are the negative of the values for positive x. Additionally, the graph has a single point of inflection at the origin, (0,0), where the function changes from concave down to concave up. The cube root graph also has a vertical asymptote at x = 0, but it does not have any horizontal asymptotes.
Derivative and Integral of the Cube Root Function
The derivative of the cube root function, denoted as y' = \frac{d}{dx} \sqrt[3]{x}, is \frac{1}{3\sqrt[3]{x^2}}. This derivative represents the rate of change of the function with respect to x. On the other hand, the integral of the cube root function, denoted as \int \sqrt[3]{x} dx, is \frac{3}{4} \sqrt[3]{x^4} + C, where C is the constant of integration. These derivative and integral expressions are essential in various mathematical and real-world applications, such as optimization problems and physics.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Domain | All real numbers |
| Range | All real numbers |
| Point of Inflection | (0,0) |
| Vertical Asymptote | |
| Horizontal Asymptote | None |
Applications of the Cube Root Graph

The cube root graph has numerous applications in mathematics, physics, and engineering. One of the primary applications is in problems involving volume and surface area. For instance, the volume of a cube is given by V = s^3, where s is the length of the side of the cube. By taking the cube root of both sides, we can express the side length in terms of the volume: s = \sqrt[3]{V}. This relationship is crucial in designing and optimizing three-dimensional structures, such as buildings, bridges, and electronic components.
Real-World Examples
In physics, the cube root graph is used to model various phenomena, such as the relationship between the volume and pressure of a gas. According to the ideal gas law, PV = nRT, where P is the pressure, V is the volume, n is the number of moles, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature. By rearranging this equation, we can express the volume as a function of pressure: V = \frac{nRT}{P}. Taking the cube root of both sides yields V^{1/3} = \sqrt[3]{\frac{nRT}{P}}, which is a cube root function. This relationship is essential in understanding the behavior of gases and designing systems, such as air conditioning and refrigeration.
What is the cube root graph, and how is it defined?
+The cube root graph is a representation of the function $y = \sqrt[3]{x}$, where $y$ is the cube root of $x$. It is defined as the set of all points ($x$, $y$) such that $y$ is the real number that satisfies the equation $y^3 = x$.
What are some of the key properties of the cube root graph?
+The cube root graph has several key properties, including being an odd function, having a point of inflection at the origin, and being symmetric with respect to the origin. It also has a vertical asymptote at $x = 0$, but no horizontal asymptotes.
What are some real-world applications of the cube root graph?
+The cube root graph has numerous applications in mathematics, physics, and engineering, including problems involving volume and surface area, optimization, and modeling of physical phenomena, such as the behavior of gases.
In conclusion, the cube root graph is a fundamental concept in mathematics, with numerous applications in various fields. Its properties, such as being an odd function and having a point of inflection at the origin, make it a crucial tool in understanding and modeling complex phenomena. By grasping the characteristics and applications of the cube root graph, mathematicians and scientists can develop and apply mathematical models to solve real-world problems and advance our understanding of the world around us.