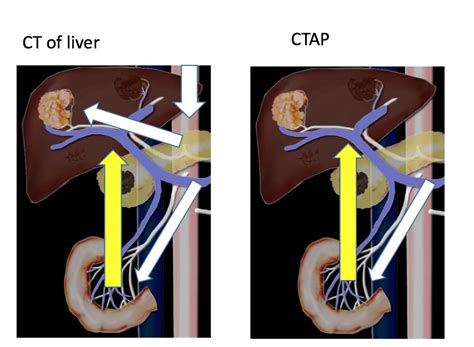
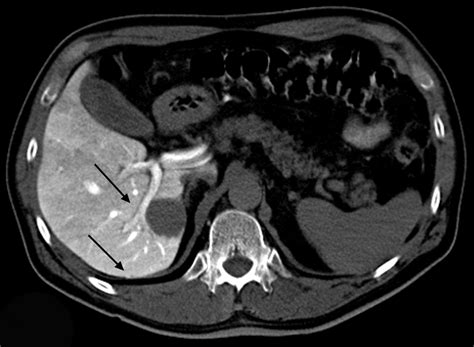
The CTAP medical abbreviation is a term that is commonly used in the medical field, particularly in the context of medical imaging and diagnostics. CTAP stands for Computed Tomography Angiography with Pigtail, which is a type of medical imaging procedure that combines computed tomography (CT) scans with angiography to produce detailed images of blood vessels and other vascular structures.
In the CTAP procedure, a pigtail catheter is inserted into an artery, typically in the leg, and guided to the area of interest using fluoroscopy. Once in place, a contrast agent is injected through the catheter, which highlights the blood vessels and allows them to be visualized on the CT scans. The resulting images provide valuable information about the structure and function of the blood vessels, which can be used to diagnose and treat a range of vascular conditions, including aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations, and vascular stenosis.
Key Points
- CTAP is a medical imaging procedure that combines CT scans with angiography to produce detailed images of blood vessels.
- The procedure involves the insertion of a pigtail catheter into an artery, which is guided to the area of interest using fluoroscopy.
- A contrast agent is injected through the catheter to highlight the blood vessels and allow them to be visualized on the CT scans.
- CTAP is used to diagnose and treat a range of vascular conditions, including aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations, and vascular stenosis.
- The procedure provides valuable information about the structure and function of blood vessels, which can be used to guide treatment decisions.
Technical Specifications and Procedure

The CTAP procedure typically involves the following technical specifications and steps:
1. Patient preparation: The patient is prepared for the procedure by removing any clothing or jewelry that may interfere with the imaging process. They are also asked to remove any metal objects, such as glasses or dentures, and to change into a hospital gown.
2. Catheter insertion: The pigtail catheter is inserted into an artery, typically in the leg, using a needle and guidewire. The catheter is then guided to the area of interest using fluoroscopy.
3. Contrast agent injection: A contrast agent is injected through the catheter to highlight the blood vessels and allow them to be visualized on the CT scans.
4. CT scanning: The patient is then placed in the CT scanner, which takes detailed images of the blood vessels and surrounding tissues.
5. Image interpretation: The resulting images are interpreted by a radiologist, who looks for any signs of vascular disease or other conditions that may require treatment.
Advantages and Limitations
The CTAP procedure has several advantages, including:
High-resolution images: The CTAP procedure produces high-resolution images of blood vessels and surrounding tissues, which can be used to diagnose and treat a range of vascular conditions.
Minimally invasive: The procedure is minimally invasive, which reduces the risk of complications and allows patients to recover quickly.
However, the CTAP procedure also has some limitations, including:
Radiation exposure: The CTAP procedure involves exposure to radiation, which can increase the risk of cancer and other health problems.
Contrast agent reactions: Some patients may experience an allergic reaction to the contrast agent, which can cause symptoms such as hives, itching, and difficulty breathing.
| CTAP Procedure Metrics | Values |
|---|---|
| Resolution | 0.5-1.0 mm |
| Radiation dose | 10-20 mSv |
| Contrast agent volume | 100-200 mL |
FAQ Section
What is the purpose of the CTAP procedure?
+The CTAP procedure is used to diagnose and treat vascular conditions, such as aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations, and vascular stenosis.
What are the risks and limitations of the CTAP procedure?
+The CTAP procedure involves exposure to radiation and may cause an allergic reaction to the contrast agent. Additionally, the procedure may not be suitable for patients with certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease or allergies to contrast agents.
How long does the CTAP procedure take?
+The CTAP procedure typically takes 30-60 minutes to complete, depending on the complexity of the procedure and the number of images required.
In conclusion, the CTAP medical abbreviation refers to a type of medical imaging procedure that combines CT scans with angiography to produce detailed images of blood vessels and surrounding tissues. The procedure has several advantages, including high-resolution images and minimal invasiveness, but also has some limitations, including radiation exposure and potential contrast agent reactions. By understanding the technical specifications and procedure, as well as the advantages and limitations, healthcare professionals can use the CTAP procedure to diagnose and treat a range of vascular conditions.