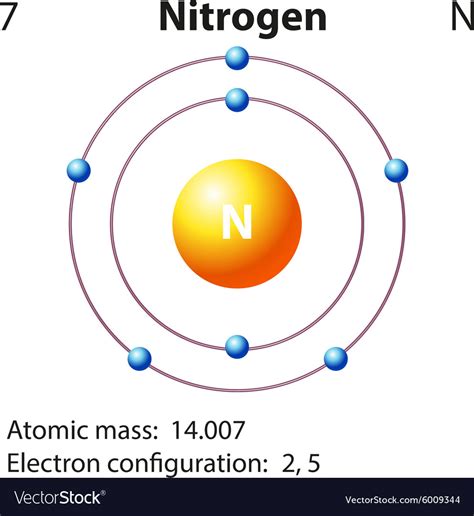
Nitrogen charge, a fundamental concept in chemistry, refers to the overall charge that a nitrogen atom possesses within a molecule or ion. This charge is a result of the nitrogen atom's ability to either gain or lose electrons, thereby altering its electronic configuration. Understanding nitrogen charge is crucial in various fields, including organic chemistry, biochemistry, and materials science, as it influences the chemical properties and reactivity of nitrogen-containing compounds.
The nitrogen atom, with its atomic number of 7, has 7 electrons. In its ground state, the electronic configuration of nitrogen is 1s² 2s² 2p³, indicating that it has 5 valence electrons. The ability of nitrogen to form bonds with other atoms, either by sharing electrons (covalent bonds) or by gaining/losing electrons (ionic bonds), is what leads to the concept of nitrogen charge. In the context of organic chemistry, nitrogen can exhibit a range of charges, from -3 (in ammonium ions, NH₄⁺) to +5 (in nitronium ion, NO₂⁺), depending on the compound it forms.
Key Points
- The nitrogen charge is determined by the number of electrons gained or lost by the nitrogen atom.
- Nitrogen can exhibit various charges, ranging from -3 to +5, depending on the compound it forms.
- Understanding nitrogen charge is essential in predicting the chemical properties and reactivity of nitrogen-containing compounds.
- Nitrogen charge plays a critical role in the stability and reactivity of molecules, influencing their ability to participate in chemical reactions.
- The charge on nitrogen affects its ability to form bonds with other atoms, thereby influencing the structure and properties of the resulting compounds.
Factors Influencing Nitrogen Charge
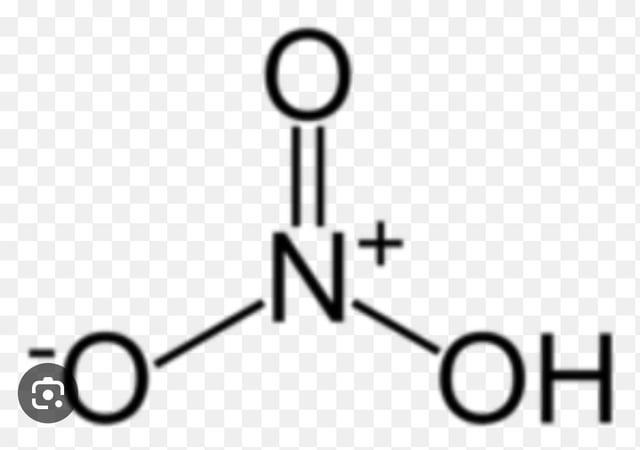
The charge on a nitrogen atom is influenced by several factors, including the type of bonds it forms with other atoms, the electronegativity of the atoms it bonds with, and the molecular structure of the compound. For instance, in the case of ammonia (NH₃), the nitrogen atom has a lone pair of electrons, resulting in a partial negative charge due to the electronegativity difference between nitrogen and hydrogen. Conversely, in the nitrosonium ion (NO⁺), the nitrogen atom has lost an electron, resulting in a positive charge.
Electronegativity and Bonding
Electronegativity, a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons in a covalent bond, plays a significant role in determining the charge on a nitrogen atom. When nitrogen forms bonds with atoms of higher electronegativity, such as oxygen or fluorine, it tends to lose electron density, potentially leading to a positive charge. In contrast, when nitrogen bonds with atoms of lower electronegativity, such as hydrogen or carbon, it may gain electron density, resulting in a negative charge.
| Compound | Nitrogen Charge | Electronegativity Difference |
|---|---|---|
| Ammonia (NH₃) | Partial negative | N (3.04) - H (2.20) = 0.84 |
| Nitrosonium ion (NO⁺) | Positive | N (3.04) - O (3.44) = -0.40 |
Applications and Implications
The understanding of nitrogen charge has far-reaching implications in various fields. In organic synthesis, knowledge of nitrogen charge is essential for predicting the reactivity of nitrogen-containing compounds and designing synthetic routes. In biochemistry, the charge on nitrogen atoms in biomolecules, such as amino acids and nucleotides, influences their interactions and functions within biological systems. Furthermore, in materials science, the manipulation of nitrogen charge can lead to the development of new materials with unique properties.
In conclusion, nitrogen charge is a fundamental concept that underlies the chemical properties and reactivity of nitrogen-containing compounds. By understanding the factors that influence nitrogen charge, including electronegativity and molecular structure, chemists can predict and manipulate the charge on nitrogen atoms, leading to advancements in various fields of science and technology.
What is the range of charges that nitrogen can exhibit?
+Nitrogen can exhibit a range of charges from -3 to +5, depending on the compound it forms and the type of bonds it participates in.
How does electronegativity influence the charge on a nitrogen atom?
+Electronegativity influences the charge on a nitrogen atom by determining the distribution of electrons in a covalent bond. Nitrogen tends to lose electron density when bonded to atoms of higher electronegativity and gain electron density when bonded to atoms of lower electronegativity.
What are the implications of understanding nitrogen charge in various fields of science?
+Understanding nitrogen charge has implications in organic synthesis, biochemistry, and materials science. It allows for the prediction of reactivity, design of synthetic routes, understanding of biomolecular interactions, and development of new materials with unique properties.