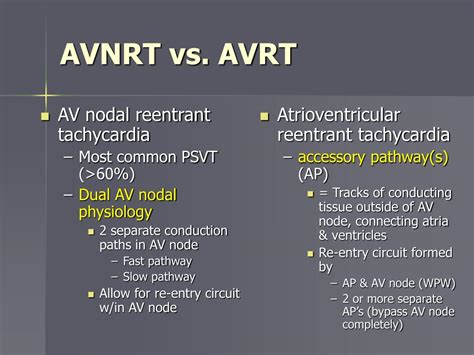
Atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia (AVRT) and atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) are two types of supraventricular tachycardias that originate from the atrioventricular junction. While they share some similarities, these conditions have distinct electrophysiological mechanisms, clinical presentations, and management strategies. Understanding the differences between AVRT and AVNRT is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Key Points
- AVRT involves an accessory electrical pathway between the atria and ventricles, whereas AVNRT involves a reentrant circuit within the atrioventricular node.
- AVRT typically presents with a narrow QRS complex, whereas AVNRT may present with a narrow or wide QRS complex.
- AVRT often requires ablation of the accessory pathway, whereas AVNRT may be managed with catheter ablation or medication.
- Accurate diagnosis of AVRT and AVNRT relies on electrophysiological studies and analysis of the ECG.
- Understanding the differences between AVRT and AVNRT is essential for developing effective treatment strategies.
Electrophysiological Mechanisms
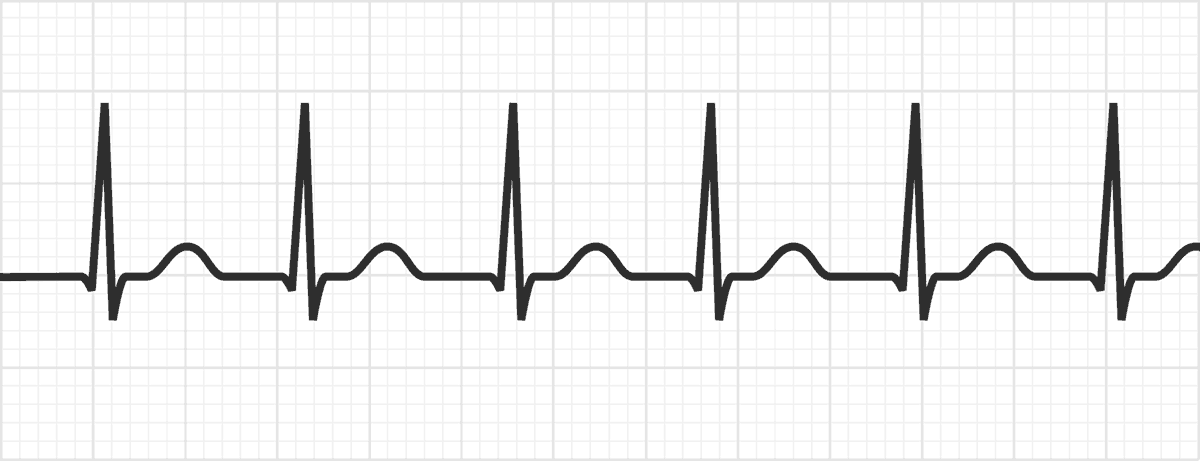
AVRT occurs when an electrical impulse travels from the atria to the ventricles through an accessory pathway, which is an abnormal electrical connection between the atria and ventricles. This accessory pathway can be either orthodromic (antegrade conduction down the AV node and retrograde conduction up the accessory pathway) or antidromic (antegrade conduction down the accessory pathway and retrograde conduction up the AV node). In contrast, AVNRT involves a reentrant circuit within the atrioventricular node, where an electrical impulse travels in a circular pattern, causing rapid activation of the atria and ventricles.
Clinical Presentation
The clinical presentation of AVRT and AVNRT can be similar, with patients often experiencing palpitations, shortness of breath, and chest discomfort. However, AVRT tends to have a more rapid ventricular rate (typically > 180 beats per minute) and may be associated with a higher risk of ventricular fibrillation. AVNRT, on the other hand, typically presents with a slower ventricular rate (typically < 180 beats per minute) and may be more responsive to vagal maneuvers.
| Condition | Electrophysiological Mechanism | Clinical Presentation |
|---|---|---|
| AVRT | Accessory pathway | Rapid ventricular rate, palpitations, shortness of breath |
| AVNRT | Reentrant circuit within AV node | Slower ventricular rate, palpitations, shortness of breath |
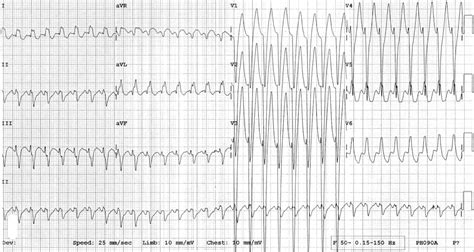
Diagnostic Approaches
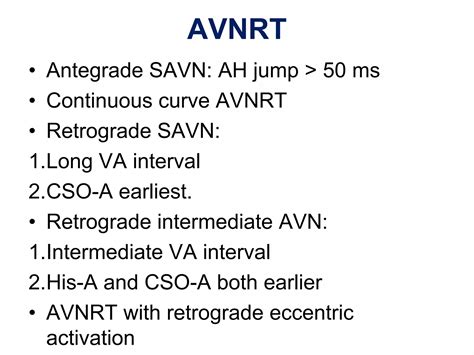
Accurate diagnosis of AVRT and AVNRT relies on a combination of electrocardiographic (ECG) analysis, electrophysiological studies, and clinical evaluation. The ECG may show a narrow QRS complex in AVRT and a narrow or wide QRS complex in AVNRT. Electrophysiological studies, such as intracardiac electrograms and pacing maneuvers, can help identify the presence of an accessory pathway in AVRT and a reentrant circuit within the AV node in AVNRT.
Treatment Strategies
Treatment strategies for AVRT and AVNRT differ significantly. AVRT often requires catheter ablation of the accessory pathway to prevent recurrence. AVNRT, on the other hand, may be managed with medication, such as adenosine or beta-blockers, or catheter ablation of the AV node. In some cases, AVNRT may be treated with pacing maneuvers, such as atrial pacing or ventricular pacing, to interrupt the reentrant circuit.
What is the primary difference between AVRT and AVNRT?
+The primary difference between AVRT and AVNRT is the presence of an accessory electrical pathway in AVRT, whereas AVNRT involves a reentrant circuit within the atrioventricular node.
How are AVRT and AVNRT diagnosed?
+Accurate diagnosis of AVRT and AVNRT relies on a combination of electrocardiographic (ECG) analysis, electrophysiological studies, and clinical evaluation.
What are the treatment options for AVRT and AVNRT?
+Treatment strategies for AVRT and AVNRT differ significantly, with AVRT often requiring catheter ablation of the accessory pathway and AVNRT being managed with medication, catheter ablation, or pacing maneuvers.
Meta Description: Understand the differences between AVRT and AVNRT, including electrophysiological mechanisms, clinical presentations, and treatment strategies. Learn how to diagnose and manage these supraventricular tachycardias effectively. (150 characters)