Abductor hallucis pain, a condition affecting the foot, is a common complaint among individuals who engage in activities that involve repetitive foot movements or those who have anatomical abnormalities. The abductor hallucis muscle, located on the medial side of the foot, plays a crucial role in foot mechanics, contributing to balance, propulsion, and the maintenance of the medial longitudinal arch. Pain in this area can significantly affect an individual's quality of life, impairing their ability to perform daily activities or participate in sports. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for abductor hallucis pain is essential for effective management and prevention of this condition.
Key Points
- Abductor hallucis pain often results from overuse, biomechanical issues, or direct trauma, highlighting the importance of proper footwear and training techniques.
- Symptoms can include localized pain, swelling, and restricted mobility, necessitating a comprehensive diagnostic approach.
- Conservative management strategies, such as physical therapy, orthotics, and pain management, are typically the first line of treatment.
- In severe cases, surgical intervention may be required to address underlying anatomical issues or to repair damaged tissues.
- Prevention strategies, including strengthening exercises, flexibility routines, and the use of appropriate footwear, can significantly reduce the risk of developing abductor hallucis pain.
Causes and Risk Factors of Abductor Hallucis Pain
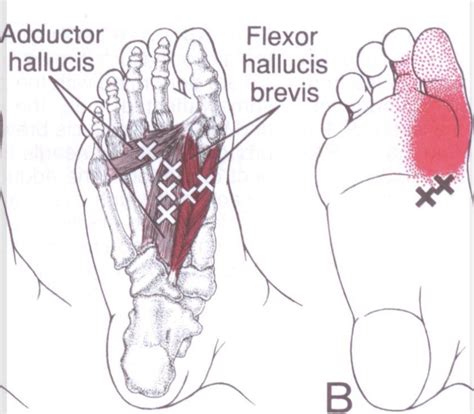
The etiology of abductor hallucis pain is multifactorial, involving a combination of intrinsic and extrinsic factors. Intrinsic factors include anatomical abnormalities, such as flat feet or high arches, which can alter the normal biomechanics of the foot, placing additional stress on the abductor hallucis muscle. Extrinsic factors, such as overuse or repetitive strain injuries from running, dancing, or other high-impact activities, can also contribute to the development of pain in this area. Furthermore, direct trauma to the foot, poorly fitting shoes, and training errors can precipitate the onset of symptoms.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The symptoms of abductor hallucis pain can vary but typically include localized pain on the medial aspect of the foot, which may be exacerbated by activity and relieved by rest. Swelling, redness, and warmth over the affected area may also be present, especially in cases of acute injury. The diagnosis is primarily clinical, based on a thorough history and physical examination. Imaging studies, such as X-rays or MRI, may be used to rule out other conditions, such as fractures or tendinopathies, and to assess the integrity of the soft tissues.
| Diagnostic Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Clinical Examination | To assess pain location, tenderness, and swelling, as well as to evaluate foot biomechanics. |
| Imaging Studies | To rule out fractures, assess soft tissue integrity, and evaluate the presence of any anatomical abnormalities. |
| Biomechanical Analysis | To identify any gait or foot mechanics abnormalities that may be contributing to the pain. |
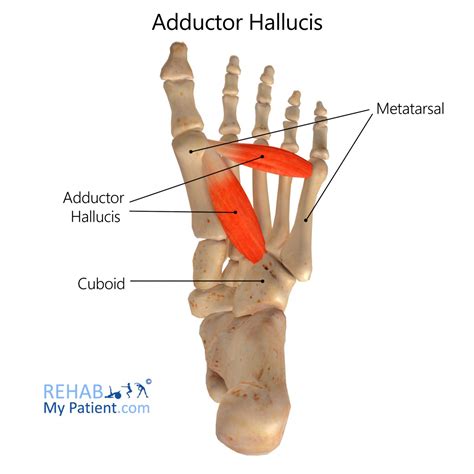
Treatment and Management Strategies
The management of abductor hallucis pain typically involves a multi-disciplinary approach, incorporating elements of physical therapy, orthotics, pain management, and, in some cases, surgical intervention. Conservative management is usually the first line of treatment and includes rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) to reduce inflammation, as well as physical therapy to improve flexibility, strengthen the foot muscles, and correct any biomechanical abnormalities. Orthotic devices can be particularly beneficial in redistributing pressure and alleviating stress on the abductor hallucis muscle.
Surgical Intervention
Surgical intervention may be considered in cases where conservative management has failed to provide adequate relief or when there is an underlying anatomical issue that requires correction. Procedures may include the release of tight structures, the repair of damaged tissues, or the realignment of foot bones to improve biomechanical function. The decision to proceed with surgery should be made after careful consideration and consultation with a specialist.
What are the most common causes of abductor hallucis pain?
+Overuse, biomechanical issues, and direct trauma are among the most common causes of abductor hallucis pain. Proper training, footwear, and foot care can significantly reduce the risk of developing this condition.
How is abductor hallucis pain diagnosed?
+Diagnosis is primarily based on clinical evaluation, including a thorough history and physical examination. Imaging studies may be used to rule out other conditions and assess the integrity of the soft tissues.
What are the treatment options for abductor hallucis pain?
+Treatment options include conservative management with physical therapy, orthotics, and pain management, as well as surgical intervention in severe or chronic cases. The choice of treatment depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition.
In conclusion, abductor hallucis pain is a complex condition that requires a comprehensive and multi-disciplinary approach for effective management. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent this condition and healthcare professionals can provide informed and effective care. The integration of preventive strategies, such as strengthening exercises and the use of appropriate footwear, into daily life can significantly reduce the risk of developing abductor hallucis pain, underscoring the importance of education and awareness in the management of this condition.


