Understanding fractions is a fundamental aspect of mathematics, and there are several ways to approach this concept. Fractions represent a part of a whole, and mastering them is crucial for more advanced mathematical operations. In this article, we will explore five distinct methods to work with fractions, each with its own set of applications and benefits. These methods include simplifying fractions, adding and subtracting fractions, multiplying fractions, dividing fractions, and comparing fractions. By grasping these techniques, individuals can enhance their mathematical proficiency and tackle a wide range of problems with confidence.
Simplifying Fractions
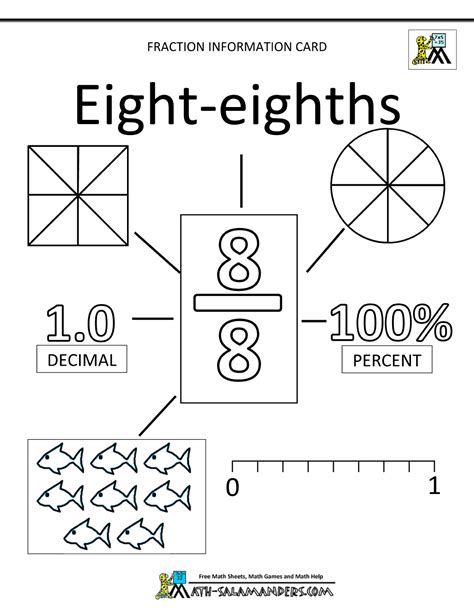
Simplifying fractions involves reducing them to their lowest terms, which means finding the equivalent fraction with the smallest possible numerator and denominator. This process is essential for making fractions easier to work with and understand. To simplify a fraction, one must find the greatest common divisor (GCD) of the numerator and the denominator and then divide both numbers by this GCD. For instance, to simplify the fraction 6⁄8, we find that the GCD of 6 and 8 is 2. Dividing both the numerator and the denominator by 2 gives us 3⁄4, which is the simplified form of 6⁄8.
Step-by-Step Simplification
The step-by-step process of simplifying fractions is straightforward. First, identify the numerator and the denominator of the fraction you want to simplify. Next, determine the greatest common divisor of these two numbers. Finally, divide both the numerator and the denominator by the GCD to obtain the simplified fraction. This method not only makes fractions more manageable but also helps in reducing errors when performing operations with fractions.
| Original Fraction | Simplified Fraction |
|---|---|
| 6/8 | 3/4 |
| 12/16 | 3/4 |
| 9/12 | 3/4 |

Adding and Subtracting Fractions
Adding and subtracting fractions require a common denominator. If the fractions already have a common denominator, you can directly add or subtract the numerators while keeping the denominator the same. However, if the denominators are different, you must first find a common denominator. The least common multiple (LCM) of the denominators can serve as the common denominator. Once you have a common denominator, you can add or subtract the numerators as needed.
Common Denominator
Finding a common denominator is crucial for adding and subtracting fractions. To do this, identify the denominators of the fractions involved and calculate their least common multiple. The LCM becomes the common denominator. Then, adjust the numerators of each fraction so that when divided by their original denominator and multiplied by the necessary factor to achieve the LCM, the fractions are equivalent to the originals but with the common denominator.
Key Points
- Identify the need for a common denominator when adding or subtracting fractions.
- Calculate the least common multiple (LCM) of the denominators to find the common denominator.
- Adjust the numerators accordingly to maintain the fractions' values.
- Perform the addition or subtraction of the numerators once a common denominator is established.
- Always simplify the resulting fraction, if possible.
Multiplying Fractions
Multiplying fractions is a straightforward process. To multiply two fractions, you multiply the numerators together to get the new numerator and multiply the denominators together to get the new denominator. The resulting fraction can then be simplified if necessary. For example, to multiply 1⁄2 and 3⁄4, you multiply the numerators (1*3 = 3) and the denominators (2*4 = 8), resulting in 3⁄8.
Step-by-Step Multiplication
The process of multiplying fractions involves multiplying the numerators and denominators separately and then simplifying the resulting fraction. This method applies to multiplying fractions by whole numbers as well, where the whole number is considered as a fraction with a denominator of 1.
| First Fraction | Second Fraction | Product |
|---|---|---|
| 1/2 | 3/4 | 3/8 |
| 2/3 | 4/5 | 8/15 |
Dividing Fractions
Dividing fractions involves inverting the second fraction (i.e., flipping the numerator and denominator) and then multiplying. For instance, to divide 1⁄2 by 3⁄4, you invert the second fraction to get 4⁄3 and then multiply: (1⁄2) * (4⁄3) = 4⁄6, which simplifies to 2⁄3.
Understanding Division
Division of fractions can be understood as the inverse operation of multiplication. By inverting the second fraction and multiplying, you are essentially asking how many times the second fraction fits into the first, which is the essence of division.
Comparing Fractions
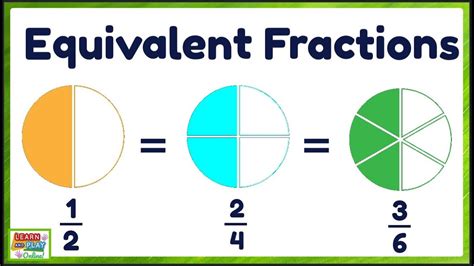
Comparing fractions involves determining which fraction is larger or smaller. This can be done by converting the fractions to equivalent decimals or by comparing their sizes visually on a number line. Another method is to find a common denominator and compare the numerators directly. For fractions with different denominators, finding a common denominator can help in making a direct comparison.
Visual Comparison
Using a number line or visual representations can be an effective way to compare fractions, especially for those who are visually inclined. By plotting the fractions on a number line, one can directly see which fraction is larger or smaller. This method can also help in understanding the concept of fractions as parts of a whole.
What is the simplest way to compare fractions?
+One of the simplest ways to compare fractions is by converting them to equivalent decimals or finding a common denominator to compare the numerators directly.
How do you simplify a fraction?
+To simplify a fraction, divide both the numerator and the denominator by their greatest common divisor (GCD).
What is the rule for dividing fractions?
+To divide fractions, invert the second fraction (i.e., flip the numerator and denominator) and then multiply.
In conclusion, mastering the five ways to work with fractions—simplifying, adding and subtracting, multiplying, dividing, and comparing—lays a strong foundation for advanced mathematical concepts. By understanding and applying these methods, individuals can improve their mathematical literacy and solve problems with precision and confidence. Whether in academics, professional settings, or everyday life, the ability to work with fractions is an indispensable skill that opens doors to a deeper understanding of quantitative relationships and problem-solving strategies.