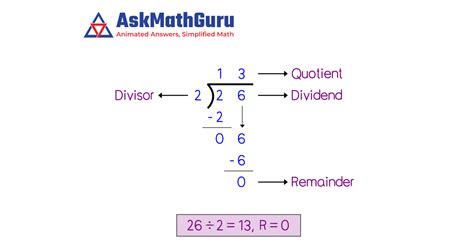
Calculating simple division problems such as 26 divided by 2 can be approached in various ways, making it accessible and understandable for individuals with different learning styles or preferences. Whether you're looking for a straightforward mathematical calculation or exploring alternative methods to reinforce understanding, there are multiple strategies available. Below, we'll explore five distinct ways to calculate 26 divided by 2, ensuring a comprehensive grasp of the concept.
Natural Division Method
The most straightforward way to calculate 26 divided by 2 is through natural division, where you simply divide the numerator (26) by the denominator (2). This method involves basic arithmetic operations that most are familiar with from an early age. To perform this calculation, you would take 26 and find how many times 2 fits into it. This can be done through mental math, a calculator, or by using physical objects to represent the numbers involved. The calculation is as follows: 26 ÷ 2 = 13.
Visual Representation Method
A visual or representational approach can be particularly helpful for those who learn better through seeing or manipulating objects. This method involves dividing a set of objects, in this case, 26, into groups of 2. Imagine having 26 blocks, marbles, or any other objects, and then grouping them into pairs. Each pair represents one group of 2. By counting the number of pairs, you’ll find that you have 13 groups of 2 objects each. This method not only calculates the division but also provides a tangible understanding of what division means in real-world terms.
| Method | Description | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Natural Division | 26 ÷ 2 | 13 |
| Visual Representation | Grouping 26 objects into pairs | 13 pairs |
Repeated Subtraction Method
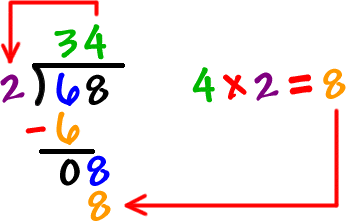
Another approach to calculating 26 divided by 2 is through repeated subtraction. This involves subtracting the divisor (2) from the dividend (26) repeatedly until you reach 0, counting how many times you perform the subtraction. Starting with 26, subtract 2: 26 - 2 = 24. Repeat the process: 24 - 2 = 22, and continue until you reach 0. The number of times you subtract 2 from 26 to reach 0 is the quotient, which is 13.
Multiplication Inverse Method
Understanding that multiplication and division are inverse operations can provide another pathway to solving division problems. If you know your multiplication tables, you can use the fact that 2 times 13 equals 26 to find that 26 divided by 2 equals 13. This method leverages the relationship between these two fundamental arithmetic operations, offering a quick mental math solution for those familiar with their multiplication facts.
Key Points
- Natural division provides a straightforward arithmetic solution.
- Visual representation helps in understanding the concept of division in real terms.
- Repeated subtraction offers an alternative method based on the definition of division.
- The inverse relationship between multiplication and division can be used for quick mental calculations.
- Algebraic representation can be utilized for more complex problems or to reinforce understanding through symbols.
Algebraic Representation Method
Lastly, for those with a background in algebra, representing the problem symbolically can offer another method of calculation. The equation for division can be represented as 26 / 2 = x, where x is the unknown quotient. Solving for x involves finding the value that, when multiplied by 2, gives 26. Thus, x = 26 / 2, which simplifies to x = 13. This algebraic method, while more abstract, reinforces the mathematical principles underlying division and can be particularly useful for solving more complex division problems or equations.
In conclusion, calculating 26 divided by 2 can be accomplished through various methods, each offering a unique perspective on the operation of division. Whether through natural division, visual representation, repeated subtraction, multiplication inverse, or algebraic representation, understanding and calculating division problems can be approached in a way that best suits the learner's style or the context of the problem.
What is the most straightforward way to calculate division problems like 26 divided by 2?
+The most straightforward way is through natural division, where you divide the numerator by the denominator, yielding 26 ÷ 2 = 13.
How can visual representation help in understanding division?
+Visual representation involves grouping objects into sets, making the concept of division tangible and easier to grasp, especially for those who are visual learners.
What is the relationship between multiplication and division, and how can it be used to solve division problems?
+Multiplication and division are inverse operations. Knowing that 2 times 13 equals 26 can help you quickly determine that 26 divided by 2 equals 13, utilizing the inverse relationship for mental math solutions.