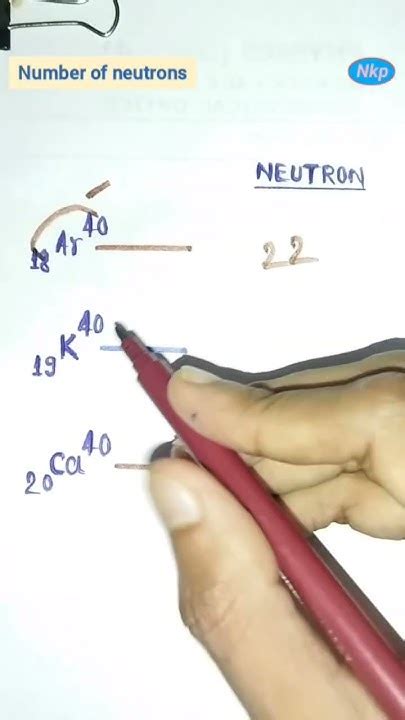
To find the number of neutrons in an atom, we first need to understand the basic structure of an atom. Atoms are composed of three main parts: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus, which is the central part of the atom, while electrons orbit around the nucleus. The number of protons in an atom's nucleus determines the element of an atom, and each element has a unique number of protons in its atoms, known as the atomic number.
Understanding Atomic Number and Mass Number
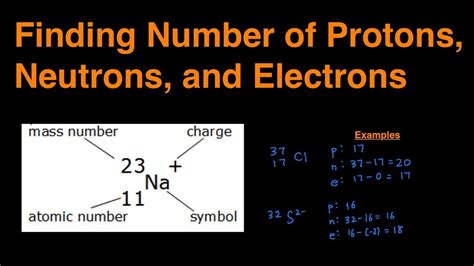
The atomic number (Z) of an element is the number of protons present in the nucleus of an atom. For example, hydrogen has an atomic number of 1, meaning it has 1 proton in its nucleus. The mass number (A) of an atom is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. It is approximated by the atomic mass of the element, which is the average mass of the naturally occurring isotopes of the element. The atomic mass is usually very close to the mass number of the most abundant isotope of the element.
Calculating the Number of Neutrons
To calculate the number of neutrons in an atom, we use the formula: Number of neutrons = Mass number (A) - Atomic number (Z). This formula works because the mass number is the sum of the protons and neutrons, and by subtracting the number of protons (atomic number), we are left with the number of neutrons.
| Element | Atomic Number (Z) | Mass Number (A) | Number of Neutrons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 1 | 1 (for the most common isotope) | 0 |
| Helium | 2 | 4 (for the most common isotope) | 2 |
| Oxygen | 8 | 16 (for the most common isotope) | 8 |
Isotopes and Their Significance
Isotopes are important in chemistry and physics because their different mass numbers can affect the physical properties of an element, such as its density and boiling point, although the chemical properties remain largely unchanged due to the same number of electrons (which is equal to the atomic number in a neutral atom). The variation in the number of neutrons among isotopes of an element leads to different isotopic masses and can influence the element’s nuclear stability and radioactivity.
Practical Applications of Isotopic Variation
The understanding and application of isotopic variations are critical in various fields. In medicine, certain isotopes are used for diagnostic purposes, such as in PET scans, where radioactive isotopes are used to visualize metabolic processes in the body. In environmental science, isotopic analysis can be used to trace the origins of water, pollutants, and nutrients, helping in the understanding of ecological systems and the impact of human activities on the environment.
Key Points
- The number of neutrons in an atom can be found by subtracting the atomic number from the mass number.
- Isotopes of an element have the same atomic number but different mass numbers due to varying numbers of neutrons.
- The existence of isotopes affects the physical properties of an element but not its chemical properties.
- Understanding isotopes and their variations is crucial for applications in medicine, environmental science, and other fields.
- The atomic mass of an element, listed on the periodic table, is a weighted average of the masses of the naturally occurring isotopes of the element.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, finding the number of neutrons in an atom is a straightforward process once the atomic and mass numbers are known. The study of isotopes and their applications continues to evolve, with new techniques and technologies being developed to utilize isotopic variations for the benefit of society. As our understanding of the atomic structure deepens, so does our ability to manipulate and apply this knowledge in innovative ways, promising future breakthroughs in various scientific disciplines.
What is the difference between an atom’s atomic number and mass number?
+The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus, which determines the element of the atom. The mass number is the sum of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus, which can vary among isotopes of the same element.
How do isotopes affect the properties of an element?
+Isotopes primarily affect the physical properties of an element, such as its density and boiling point, due to the differences in mass number. However, the chemical properties, which are determined by the number of electrons (equal to the atomic number in a neutral atom), remain largely unchanged.
What are some practical applications of understanding isotopic variations?
+Practical applications include medical diagnostics, environmental tracing, and industrial processes. For example, radioactive isotopes are used in PET scans for medical imaging, and isotopic analysis can help trace the source of pollutants and understand ecological systems.