The Z-transform is a powerful tool used in signal processing and control systems to analyze and manipulate discrete-time signals. It is a mathematical representation of a discrete-time signal in the frequency domain, which allows for the analysis of the signal's frequency content and the design of filters and other signal processing systems. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive reference table for the Z-transform, including the transform of common signals, properties of the Z-transform, and examples of its application.
Introduction to the Z-Transform
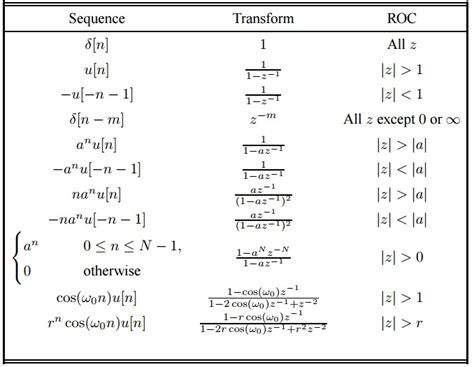
The Z-transform is defined as the sum of the products of the signal samples and the complex exponential function, where the complex exponential function is raised to the power of the sample index. The Z-transform is typically denoted as X(z), where X is the discrete-time signal and z is the complex variable. The Z-transform is defined as:
X(z) = ∑[x(n) * z^(-n)] from n = -∞ to ∞
where x(n) is the nth sample of the signal X, and z is the complex variable.
Properties of the Z-Transform
The Z-transform has several properties that make it a useful tool for signal processing and analysis. Some of the key properties of the Z-transform include:
- Linearity: The Z-transform is a linear transformation, meaning that the Z-transform of a linear combination of signals is equal to the linear combination of the Z-transforms of the individual signals.
- Time shifting: The Z-transform of a time-shifted signal is equal to the Z-transform of the original signal multiplied by the complex exponential function raised to the power of the time shift.
- Frequency shifting: The Z-transform of a frequency-shifted signal is equal to the Z-transform of the original signal with the frequency shift applied to the complex variable.
Z-Transform Table Reference
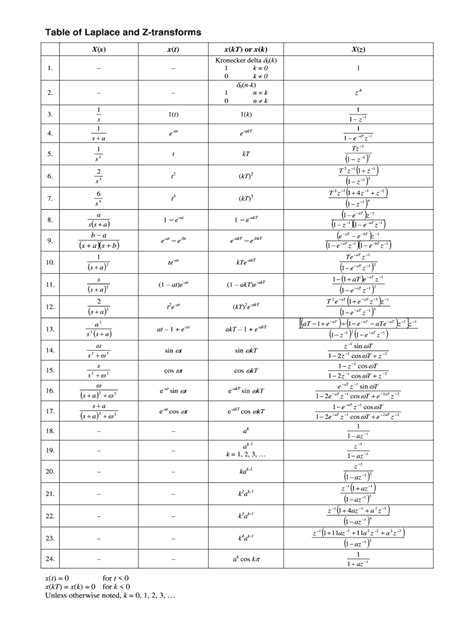
The following table provides a reference for the Z-transform of common signals:
| Signal | Z-Transform |
|---|---|
| Unit impulse | 1 |
| Unit step | 1 / (1 - z^(-1)) |
| Exponential | 1 / (1 - a * z^(-1)) |
| Sinusoidal | (1 - e^(-j * ω * T) * z^(-1)) / (1 - 2 * cos(ω * T) * z^(-1) + z^(-2)) |
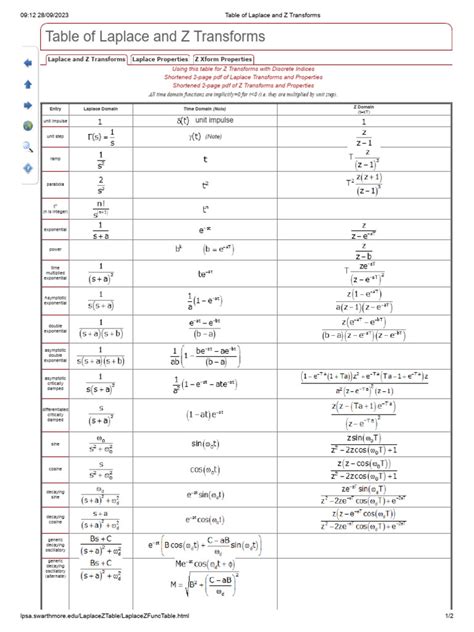
where a is the exponential decay rate, ω is the angular frequency, and T is the sampling period.
Key Points
- The Z-transform is a powerful tool for analyzing and manipulating discrete-time signals.
- The Z-transform has several properties, including linearity, time shifting, and frequency shifting, that make it a useful tool for signal processing and analysis.
- The Z-transform table reference provides a comprehensive list of the Z-transforms of common signals, including the unit impulse, unit step, exponential, and sinusoidal signals.
- The Z-transform can be used to design filters and other signal processing systems, and to analyze the frequency content of discrete-time signals.
- The Z-transform is a fundamental concept in signal processing and control systems, and is widely used in a variety of applications, including audio processing, image processing, and control systems design.
Examples of Z-Transform Application
The Z-transform has a wide range of applications in signal processing and control systems. Some examples of its application include:
- Filter design: The Z-transform can be used to design filters, such as low-pass, high-pass, and band-pass filters, by manipulating the frequency response of the filter.
- Signal analysis: The Z-transform can be used to analyze the frequency content of discrete-time signals, and to identify the presence of specific frequency components.
- Control systems design: The Z-transform can be used to design control systems, such as feedback control systems, by analyzing the frequency response of the system and designing controllers that meet specific performance requirements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Z-transform is a fundamental concept in signal processing and control systems, and has a wide range of applications in fields such as audio processing, image processing, and control systems design. The Z-transform table reference provided in this article provides a comprehensive list of the Z-transforms of common signals, and can be used as a reference for engineers and researchers working in these fields. By understanding the properties and applications of the Z-transform, engineers and researchers can design and analyze complex signal processing systems, and develop new technologies that rely on the manipulation of discrete-time signals.
What is the Z-transform, and how is it used in signal processing?
+The Z-transform is a mathematical representation of a discrete-time signal in the frequency domain, which allows for the analysis of the signal’s frequency content and the design of filters and other signal processing systems. It is used in signal processing to analyze and manipulate discrete-time signals, and to design filters and other signal processing systems.
What are the properties of the Z-transform, and how are they used in signal processing?
+The Z-transform has several properties, including linearity, time shifting, and frequency shifting, that make it a useful tool for signal processing and analysis. These properties are used to design filters and other signal processing systems, and to analyze the frequency content of discrete-time signals.
What are some common applications of the Z-transform in signal processing and control systems?
+The Z-transform has a wide range of applications in signal processing and control systems, including filter design, signal analysis, and control systems design. It is used in fields such as audio processing, image processing, and control systems design to analyze and manipulate discrete-time signals, and to design filters and other signal processing systems.



