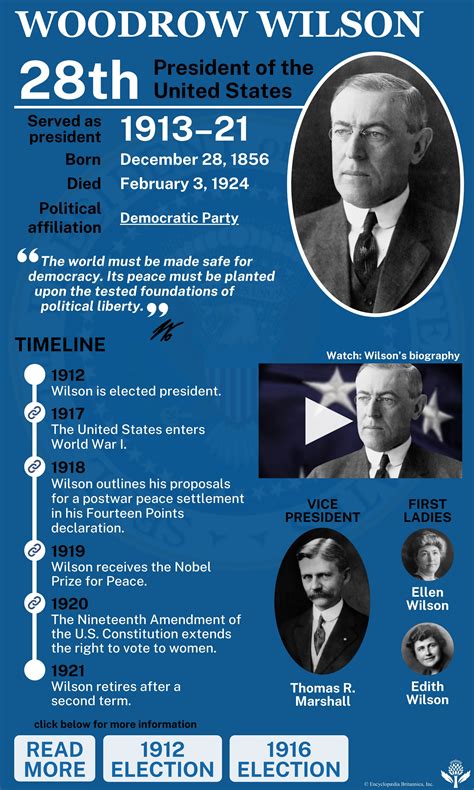
On October 2, 1919, President Woodrow Wilson suffered a severe stroke that would leave him partially paralyzed and significantly impact his ability to perform his presidential duties. The stroke occurred while Wilson was on a national tour, promoting his vision for the League of Nations, a crucial component of the Treaty of Versailles that aimed to prevent future wars. Wilson's stroke was a pivotal event in American history, marking a significant turning point in his presidency and the country's foreign policy trajectory.
The Events Leading Up to the Stroke
In the months preceding the stroke, Wilson had been under immense pressure, both physically and mentally. He had recently returned from the Paris Peace Conference, where he played a key role in shaping the Treaty of Versailles. The conference had been a grueling experience, with Wilson often finding himself at odds with other world leaders, particularly British Prime Minister David Lloyd George and French Prime Minister Georges Clemenceau. Upon his return to the United States, Wilson embarked on a nationwide tour, delivering speeches in support of the League of Nations and the treaty. The tour was highly demanding, with Wilson traveling thousands of miles by train and giving multiple speeches per day.
The Stroke and Its Immediate Aftermath
The stroke occurred in the early morning hours of October 2, 1919, while Wilson was aboard his train, which was stopped in Wichita, Kansas. Wilson’s wife, Edith, was the first to discover him, finding him unconscious and unresponsive in their train car. A team of doctors was quickly summoned, and they diagnosed Wilson with a severe stroke, which had caused significant damage to the left side of his brain. The stroke left Wilson partially paralyzed, with limited mobility on his left side, and significant cognitive impairments. For several weeks, Wilson’s condition was precarious, with his doctors fearing for his life.
| Medical Condition | Description |
|---|---|
| Stroke Type | Ischemic stroke, caused by a blockage in the blood vessels supplying the brain |
| Location | Left side of the brain, affecting motor control and cognitive function |
| Symptoms | Partial paralysis, limited mobility, cognitive impairments, and difficulty with speech and communication |

The Impact on Wilson’s Presidency

The stroke significantly curtailed Wilson’s ability to perform his presidential duties, leading to a period of uncertainty and instability in the White House. Edith Wilson and Dr. Grayson became the de facto decision-makers, with Edith acting as a gatekeeper, controlling access to the president and making decisions on his behalf. This arrangement was not without controversy, with many questioning the constitutionality of Edith’s role and the secrecy surrounding Wilson’s condition. The stroke also marked a significant shift in Wilson’s policy priorities, with his focus on domestic issues, such as the League of Nations, giving way to more pressing concerns, including his own health and the management of the executive branch.
Legacy and Historical Significance
Woodrow Wilson’s stroke had far-reaching consequences, both for his presidency and for the country as a whole. The event marked a turning point in Wilson’s leadership style, with his inability to fully engage with his duties leading to a more autocratic and secretive decision-making process. The stroke also had significant implications for the country’s foreign policy, with the League of Nations ultimately failing to gain Senate approval, in part due to Wilson’s inability to effectively lobby for its passage. Today, Wilson’s stroke is remembered as a pivotal moment in American history, highlighting the importance of transparency and accountability in government, as well as the need for robust systems of governance to ensure continuity and stability in times of crisis.
Key Points
- Woodrow Wilson suffered a severe stroke on October 2, 1919, while on a national tour promoting the League of Nations.
- The stroke left Wilson partially paralyzed and with significant cognitive impairments, affecting his ability to perform his presidential duties.
- Edith Wilson and Dr. Cary Grayson played key roles in managing Wilson's care and making decisions on his behalf, leading to a period of secrecy and controversy.
- The stroke had significant implications for Wilson's presidency, including a shift in policy priorities and a more autocratic decision-making process.
- The event marked a turning point in American history, highlighting the importance of transparency and accountability in government, as well as the need for robust systems of governance to ensure continuity and stability in times of crisis.
In the years following Wilson's stroke, the country would continue to grapple with the consequences of his illness, including the failed ratification of the Treaty of Versailles and the rise of isolationism in American foreign policy. However, the event also spurred important discussions about the role of the president, the importance of transparency and accountability in government, and the need for robust systems of governance to ensure continuity and stability in times of crisis.
What were the immediate effects of Wilson's stroke on his presidency?
+The stroke significantly curtailed Wilson's ability to perform his presidential duties, leading to a period of uncertainty and instability in the White House. Edith Wilson and Dr. Grayson became the de facto decision-makers, with Edith acting as a gatekeeper, controlling access to the president and making decisions on his behalf.
How did Wilson's stroke impact the country's foreign policy?
+The stroke had significant implications for the country's foreign policy, with the League of Nations ultimately failing to gain Senate approval, in part due to Wilson's inability to effectively lobby for its passage. The event marked a turning point in American history, highlighting the importance of transparency and accountability in government, as well as the need for robust systems of governance to ensure continuity and stability in times of crisis.
What lessons can be learned from Wilson's stroke and its impact on his presidency?
+The event highlights the importance of transparency and accountability in government, as well as the need for robust systems of governance to ensure continuity and stability in times of crisis. It also underscores the importance of planning for succession and ensuring that systems are in place to manage the transition of power in the event of a president's incapacitation.
Woodrow Wilson’s stroke serves as a reminder of the importance of transparency, accountability, and robust systems of governance in ensuring the continuity and stability of government, even in times of crisis. As the country continues to grapple with the complexities of modern governance, the lessons of Wilson’s stroke remain relevant, highlighting the need for careful planning, clear communication, and a commitment to the principles of democracy.