Itching in the clitoral area, also known as pruritus, can be a frustrating and sensitive issue for many individuals. The clitoris is a highly sensitive and nerve-rich area, making it prone to irritation and discomfort. In this article, we will delve into the possible causes of clitoral itching, discuss the importance of proper hygiene and self-care, and provide guidance on when to seek medical attention.
Understanding the Causes of Clitoral Itching
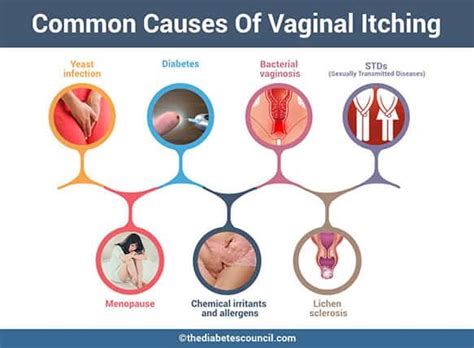
There are several potential causes of clitoral itching, ranging from innocuous to more serious conditions. Some common causes include:
- Yeast infections: Also known as candidiasis, yeast infections can cause intense itching, redness, and swelling in the genital area.
- Bacterial vaginosis: An imbalance of bacteria in the vagina can lead to itching, burning, and abnormal discharge.
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs): Certain STIs, such as herpes, gonorrhea, and chlamydia, can cause itching, burning, and discomfort in the genital area.
- Irritation from soaps or laundry detergents: Harsh chemicals in soaps, bubble baths, or laundry detergents can irritate the skin and cause itching.
- Tight clothing or synthetic fabrics: Wearing tight clothing or underwear made from synthetic materials can trap moisture and irritate the skin, leading to itching.
- Hormonal changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels during menstruation, menopause, or pregnancy can affect the pH balance of the vagina, leading to itching and discomfort.
Diagnosing the Cause of Clitoral Itching
To determine the underlying cause of clitoral itching, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider. They will perform a physical examination, take a medical history, and may order laboratory tests to rule out any underlying infections or conditions. A proper diagnosis is crucial to receiving effective treatment and preventing further complications.
| Common Causes | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Yeast infections | Itching, redness, swelling, and abnormal discharge | Antifungal medications, such as clotrimazole or fluconazole |
| Bacterial vaginosis | Itching, burning, and abnormal discharge | Antibiotics, such as metronidazole or clindamycin |
| STIs | Itching, burning, and discomfort in the genital area | Antiviral or antibiotic medications, depending on the specific STI |

Key Points
- Clitoral itching can be caused by a range of factors, including yeast infections, bacterial vaginosis, STIs, and irritation from soaps or laundry detergents.
- Proper hygiene and self-care, such as wearing breathable clothing and avoiding harsh chemicals, can help prevent clitoral itching.
- A healthcare provider can help diagnose the underlying cause of clitoral itching and provide effective treatment.
- Hormonal changes during menstruation, menopause, or pregnancy can affect the pH balance of the vagina, leading to itching and discomfort.
- Seeking medical attention is crucial to preventing further complications and ensuring proper treatment.
In conclusion, clitoral itching can be a distressing and uncomfortable issue, but by understanding the possible causes and seeking medical attention, individuals can receive effective treatment and prevent further complications. By prioritizing proper hygiene, self-care, and comprehensive medical care, we can promote healthy and comfortable genital health.
What are the most common causes of clitoral itching?
+The most common causes of clitoral itching include yeast infections, bacterial vaginosis, STIs, and irritation from soaps or laundry detergents.
How can I prevent clitoral itching?
+To prevent clitoral itching, it is essential to practice proper hygiene, wear breathable clothing, and avoid harsh chemicals. Additionally, getting regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help identify any underlying conditions early on.
When should I seek medical attention for clitoral itching?
+It is essential to seek medical attention if the itching persists, worsens, or is accompanied by other symptoms such as abnormal discharge, burning, or pain. A healthcare provider can help diagnose the underlying cause and provide effective treatment.