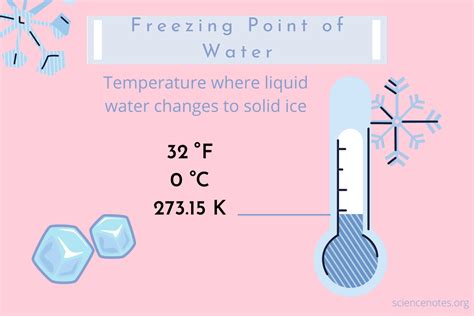
Freezing temperature, also known as the freezing point, is the temperature at which a liquid transforms into a solid. This phenomenon occurs when the molecules of a substance slow down to the point where they come together in a crystalline structure, resulting in a solid state. The freezing temperature of a substance is a fundamental physical property that is influenced by various factors, including the type of substance, pressure, and the presence of impurities. In the context of everyday life, freezing temperatures play a crucial role in various aspects, such as food preservation, climate, and industrial processes.
Key Points
- The freezing temperature of water is 0 degrees Celsius (°C) or 32 degrees Fahrenheit (°F) at standard atmospheric pressure.
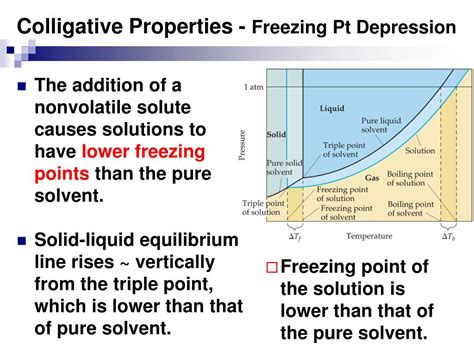
- The freezing point of a substance can be affected by the presence of impurities, which can lower the freezing point.
- Freezing temperatures are essential in various industries, such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and cryogenics.
- The concept of freezing temperature is closely related to the concept of melting point, which is the temperature at which a solid transforms into a liquid.
- Understanding freezing temperatures is crucial in understanding various natural phenomena, such as the formation of ice and snow, and the behavior of liquids in extreme cold conditions.
Scientific Explanation of Freezing Temperature
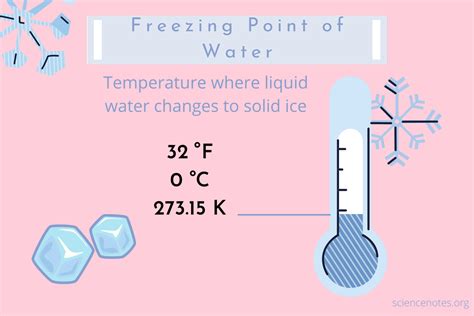
From a scientific perspective, the freezing temperature of a substance is determined by the intermolecular forces between its molecules. As the temperature of a liquid decreases, the kinetic energy of its molecules decreases, allowing them to come closer together and form a crystalline structure. The freezing point of a substance is the temperature at which the liquid and solid phases are in equilibrium, meaning that the rate of freezing is equal to the rate of melting. The freezing temperature of a substance can be affected by various factors, such as pressure, the presence of impurities, and the surface tension of the liquid.
Factors Affecting Freezing Temperature
There are several factors that can affect the freezing temperature of a substance. One of the most significant factors is the presence of impurities, which can lower the freezing point of a substance. This phenomenon is known as freezing-point depression. Another factor that can affect the freezing temperature is pressure. An increase in pressure can raise the freezing point of a substance, while a decrease in pressure can lower it. The surface tension of a liquid can also affect its freezing temperature, as it can influence the rate of nucleation and crystal growth.
| Substance | Freezing Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|
| Water | 0 |
| Mercury | -38.83 |
| Aluminum | 660.32 |
| Copper | 1,085 |
| Silver | 961.93 |
Applications of Freezing Temperature
Freezing temperatures have numerous applications in various industries, including food processing, pharmaceuticals, and cryogenics. In food processing, freezing temperatures are used to preserve food by preventing the growth of microorganisms and slowing down chemical reactions. In pharmaceuticals, freezing temperatures are used to preserve biological samples and to create vaccines. In cryogenics, freezing temperatures are used to preserve human tissues and organs for transplantation.
Food Preservation
Freezing temperatures play a crucial role in food preservation. By freezing food, the growth of microorganisms is prevented, and the chemical reactions that cause spoilage are slowed down. This method of preservation is widely used in the food industry to preserve fruits, vegetables, meats, and other perishable items. The freezing temperature of food can affect its quality and texture, and therefore, it is essential to control the freezing temperature carefully.
What is the freezing temperature of water?
+The freezing temperature of water is 0 degrees Celsius (°C) or 32 degrees Fahrenheit (°F) at standard atmospheric pressure.
What factors can affect the freezing temperature of a substance?
+The freezing temperature of a substance can be affected by various factors, including the presence of impurities, pressure, and the surface tension of the liquid.
What are the applications of freezing temperatures?
+Freezing temperatures have numerous applications in various industries, including food processing, pharmaceuticals, and cryogenics.
In conclusion, freezing temperature is a fundamental physical property that plays a crucial role in various aspects of our lives, from food preservation to industrial processes. Understanding the concept of freezing temperature and its applications can help us appreciate the complexities of the physical world and the importance of temperature control in various industries. By controlling the freezing temperature, we can preserve food, create vaccines, and even preserve human tissues and organs for transplantation.