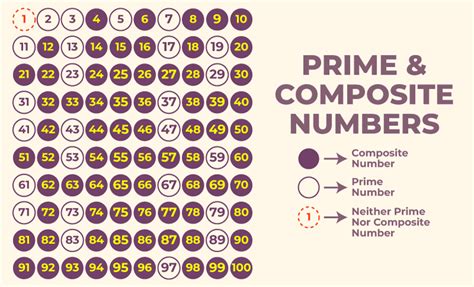
When it comes to prime numbers, there are several key facts that are essential to understanding these unique numerical entities. Prime numbers, defined as numbers greater than 1 that have no positive divisors other than 1 and themselves, play a critical role in number theory and have numerous applications in mathematics, computer science, and cryptography. Here are five prime facts about prime numbers that highlight their importance and intriguing properties.
Definition and Basic Properties

The definition of a prime number is straightforward: a prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. This means that the only factors of a prime number are 1 and the number itself. For example, 5 is a prime number because its only factors are 1 and 5. This basic property of prime numbers underlies their role in mathematics and makes them fundamental building blocks of all other numbers, as every positive integer can be expressed as a product of prime numbers in a unique way, known as the prime factorization.
Prime Factorization
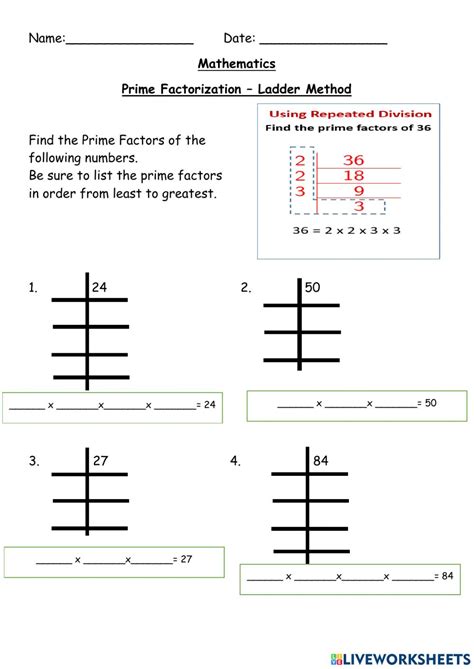
Prime factorization is the process of finding the prime numbers that multiply together to create a given number. This concept is crucial because it demonstrates how prime numbers are the foundation of the numerical system. For instance, the number 12 can be factored into its prime factors as 2^2 * 3, showing that 12 is composed of the primes 2 and 3. The uniqueness of prime factorization, as stated by the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic, ensures that every integer greater than 1 is either prime itself or can be factorized as a product of prime numbers in a unique way, except for the order in which these prime numbers are listed.
| Prime Number | Example of Prime Factorization |
|---|---|
| 2 | 2 = 2 (prime itself) |
| 3 | 3 = 3 (prime itself) |
| 4 | 4 = 2 * 2 |
| 5 | 5 = 5 (prime itself) |
| 6 | 6 = 2 * 3 |
Key Points
- Prime numbers are numbers greater than 1 that have no divisors other than 1 and themselves.
- Every positive integer can be uniquely expressed as a product of prime numbers, a concept known as prime factorization.
- Prime numbers are the building blocks of all other numbers, playing a critical role in mathematics and computer science.
- The study of prime numbers has significant implications for cryptography, where the difficulty of factorizing large numbers is exploited to create secure encryption methods.
- Understanding prime numbers and their properties is essential for advancing in various fields of mathematics and computer science.
Distribution of Prime Numbers

The distribution of prime numbers among the integers is a fascinating area of study. While prime numbers become less frequent as numbers get larger, there is no largest prime number. In fact, Euclid’s proof of the infinitude of primes demonstrates that there are infinitely many prime numbers. This has significant implications for many areas of mathematics and computer science, particularly in cryptography, where large prime numbers are used to create unbreakable codes.
Applications of Prime Numbers
Prime numbers have numerous applications beyond pure mathematics. In computer science, prime numbers are used in algorithms for cryptography, such as RSA and elliptic curve cryptography, which rely on the difficulty of factoring large composite numbers into their prime factors. This difficulty is what makes these cryptographic systems secure, as factorizing large numbers into their primes is computationally infeasible with current technology. Additionally, prime numbers are used in pseudorandom number generators, hash functions, and in the study of cyclic codes, further highlighting their importance in digital communication and data security.
What is the significance of prime numbers in cryptography?
+Prime numbers are crucial in cryptography because the difficulty of factorizing large composite numbers into their prime factors is used to create secure encryption algorithms. This is particularly true for RSA encryption, which relies on the product of two large prime numbers to ensure the security of data transmission over the internet.
Are there infinitely many prime numbers?
+Yes, there are infinitely many prime numbers. This was proven by Euclid, who showed that if you assume there are only finitely many prime numbers, you can always construct a new number that is not divisible by any of the assumed finite list of primes, thus proving that there must be infinitely many primes.
What is prime factorization, and why is it important?
+Prime factorization is the process of finding the prime numbers that multiply together to create a given number. It's important because it shows that every positive integer can be expressed uniquely as a product of prime numbers, making prime numbers the fundamental building blocks of all other numbers.
In conclusion, prime numbers are not just a curiosity in the realm of mathematics but are fundamental to our understanding of numbers and have significant practical applications. Their unique properties and the difficulty of certain operations related to them, such as factorization, underpin the security of our digital communications and transactions. As mathematics and computer science continue to evolve, the study of prime numbers remains a vibrant and critical area of research, promising new insights and applications that can shape the future of technology and security.