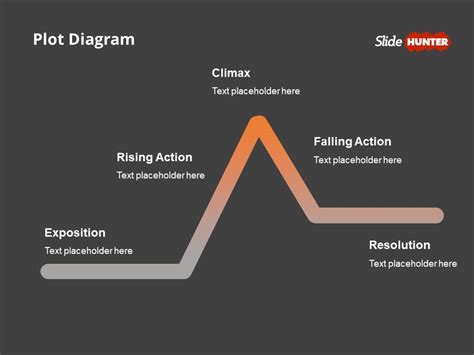
Exposition in storytelling refers to the process of introducing background information, setting, characters, and context to the audience, providing them with a deeper understanding of the narrative. It is a crucial element in storytelling, as it helps to establish the foundation of the story, creates tension, and guides the audience's expectations. Exposition can be presented through various techniques, including dialogue, narration, flashbacks, and description, and is often used to reveal character traits, motivations, and backstory.
Types of Exposition
There are several types of exposition, each with its own unique characteristics and purposes. Direct exposition involves directly telling the audience information about the story, often through narration or dialogue. Indirect exposition, on the other hand, shows the audience the information through action, expression, or other subtle cues. Gradual exposition reveals information slowly over time, while immediate exposition presents it all at once.
Techniques for Effective Exposition
To effectively use exposition in storytelling, writers can employ various techniques. Show, don’t tell is a fundamental principle, where the audience is shown the information rather than being told it directly. Varying pacing can also help to keep the audience engaged, by alternating between fast-paced action and slower, more introspective moments. Using subtext can add depth to the story, by conveying information through underlying emotions and motivations rather than explicit statements.
| Exposition Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Dialogue | Characters discuss background information or reveal their thoughts and feelings through conversation |
| Narration | A narrator provides background information or explains the story's context |
| Flashbacks | Scenes from the past are shown to provide background information or explain character motivations |
| Description | The setting, characters, or objects are described in detail to create a vivid image in the audience's mind |
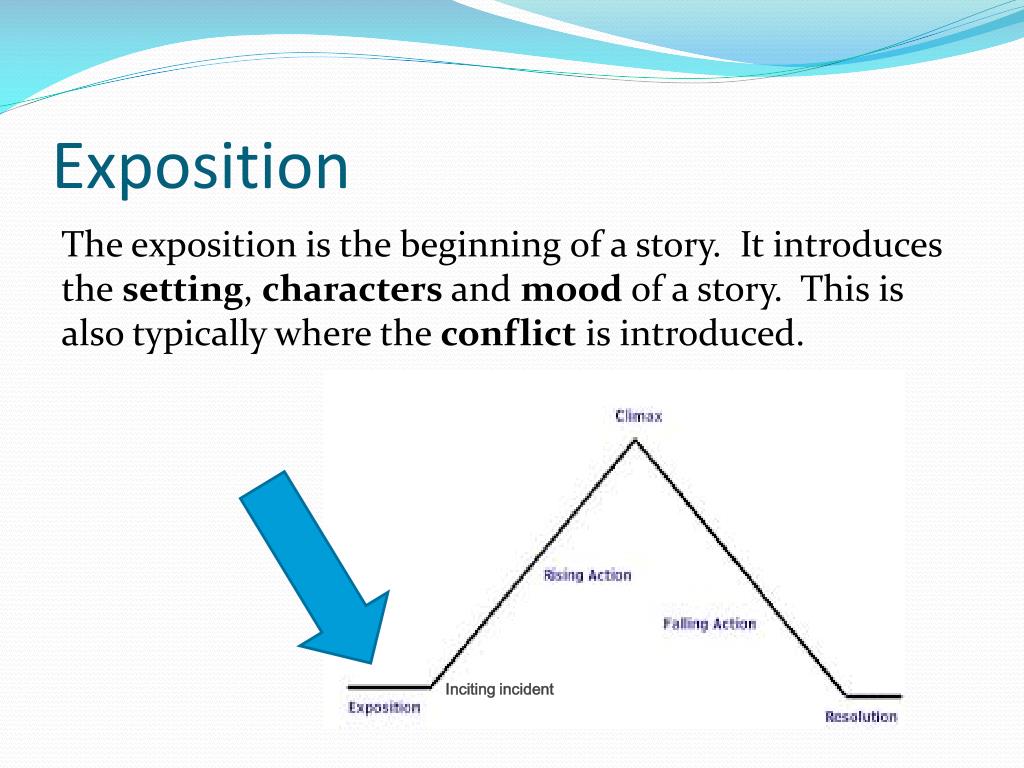
Key Points
- Exposition is the process of introducing background information, setting, characters, and context to the audience
- Effective exposition techniques include showing rather than telling, varying pacing, and using subtext
- Types of exposition include direct, indirect, gradual, and immediate
- Exposition can be presented through dialogue, narration, flashbacks, and description
- A balance between providing necessary information and avoiding info-dumps is crucial to keeping the audience engaged
Challenges of Exposition

One of the significant challenges of exposition is finding the right balance between providing necessary information and overwhelming the audience. Too much exposition can slow down the pace of the story, while too little can leave the audience confused. Info-dumps, where large amounts of information are presented all at once, can be particularly problematic, as they can feel like a convenient way to convey information rather than a natural part of the story.
Best Practices for Exposition
To avoid the pitfalls of exposition, writers can follow some best practices. Integrate exposition naturally into the story, rather than forcing it into awkward or contrived scenes. Use exposition to reveal character, by showing their thoughts, feelings, and motivations through their actions and dialogue. Keep exposition concise, by providing only the necessary information and avoiding unnecessary details.
What is the purpose of exposition in storytelling?
+The purpose of exposition is to introduce background information, setting, characters, and context to the audience, providing them with a deeper understanding of the narrative.
How can writers effectively use exposition in their stories?
+Writers can effectively use exposition by showing rather than telling, varying pacing, and using subtext. They can also integrate exposition naturally into the story, use it to reveal character, and keep it concise.
What are some common challenges of exposition in storytelling?
+Some common challenges of exposition include finding the right balance between providing necessary information and overwhelming the audience, avoiding info-dumps, and integrating exposition naturally into the story.
In conclusion, exposition is a vital element of storytelling, providing the audience with the background information and context necessary to understand the narrative. By using effective exposition techniques, such as showing rather than telling, varying pacing, and using subtext, writers can create a engaging and immersive story that draws the audience in and keeps them invested. By following best practices, such as integrating exposition naturally, using it to reveal character, and keeping it concise, writers can avoid the pitfalls of exposition and create a compelling and memorable story.