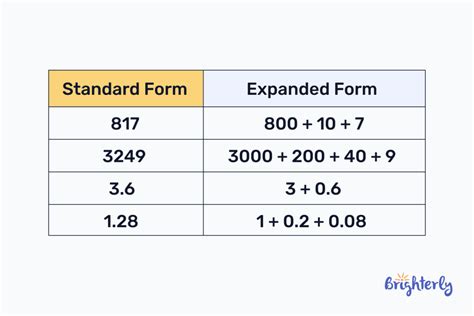
The concept of expanded form in mathematics refers to the representation of a number in a way that shows the value of each digit in the number, based on its position. This concept is fundamental in understanding the place value system, which is a crucial aspect of arithmetic. In the expanded form, each digit of a number is multiplied by its corresponding place value, such as ones, tens, hundreds, and so on, and the results are added together to get the original number. This method of representation helps in simplifying complex arithmetic operations and provides a clear understanding of the structure of numbers.
For instance, consider the number 456. In its expanded form, it can be represented as (4 * 100) + (5 * 10) + (6 * 1), which simplifies to 400 + 50 + 6, and equals 456. This example illustrates how the expanded form helps in breaking down a number into its constituent parts, based on the place value of each digit. This concept is not only essential for basic arithmetic operations but also forms the basis for more advanced mathematical concepts, such as algebra and number theory.
Key Points
- The expanded form of a number represents its value in terms of the place value of each digit.
- This form helps in simplifying arithmetic operations by breaking down numbers into their constituent parts.
- The expanded form is based on the place value system, where each digit's value is determined by its position in the number.
- Understanding the expanded form is crucial for grasping more advanced mathematical concepts, such as algebra and number theory.
- This concept applies to all types of numbers, including integers, decimals, and fractions, though the application may vary.
Naturally Worded Primary Topic Section with Semantic Relevance
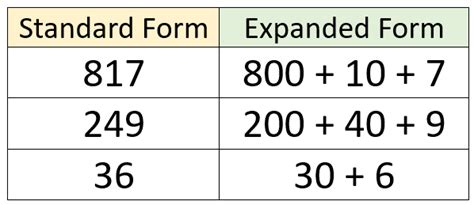
The application of expanded form is not limited to integers; it can also be applied to decimals and fractions. For decimals, the place value system extends to the right of the decimal point, with each position representing a power of 10, such as tenths, hundredths, thousandths, and so on. For fractions, the concept of expanded form can be applied to both the numerator and the denominator, helping in simplifying complex fraction operations. The versatility of the expanded form in representing different types of numbers makes it a powerful tool in mathematics.
Specific Subtopic with Natural Language Phrasing
One of the significant advantages of using the expanded form is its ability to simplify complex arithmetic operations. For example, when adding or subtracting numbers, representing them in their expanded form can help in aligning the numbers correctly, based on their place values. This alignment ensures that the operation is performed accurately, reducing the chance of errors. Furthermore, the expanded form facilitates the multiplication and division of numbers, especially when dealing with large or complex numbers, by allowing for a more systematic and step-by-step approach to these operations.
| Arithmetic Operation | Expanded Form Application |
|---|---|
| Addition/Subtraction | Aligns numbers based on place value, ensuring accurate operations |
| Multiplication | Facilitates step-by-step multiplication, especially with large numbers |
| Division | Helps in systematic division, reducing errors and improving accuracy |
Advanced Applications of Expanded Form
Beyond basic arithmetic, the expanded form has significant applications in algebra and number theory. In algebra, the expanded form can be used to simplify and solve equations, especially those involving polynomials. By representing the variables and constants in their expanded form, it becomes easier to manipulate and solve the equations. In number theory, the expanded form is crucial for understanding properties of numbers, such as divisibility, primality, and congruences. The ability to represent numbers in their expanded form facilitates the proof of theorems and the derivation of formulas in number theory.
Technical Specifications and Contextual Explanation
From a technical standpoint, the expanded form relies heavily on the concept of place value, which is a positional notation system. In this system, each position in a number represents a power of the base (usually 10 for decimal numbers), and the digit in that position is multiplied by this power of the base. The choice of base is arbitrary, and different bases can be used, such as binary (base 2) for computer applications or hexadecimal (base 16) for programming. Understanding the technical aspects of the place value system and how it applies to different number systems is essential for appreciating the universality and flexibility of the expanded form concept.
The application of the expanded form in real-world scenarios is vast, ranging from financial calculations to scientific research. In finance, the expanded form can be used to calculate interest rates, investments, and loans, providing a clear breakdown of how these calculations are performed. In scientific research, the expanded form is essential for precise measurements and calculations, especially in fields like physics and chemistry, where small discrepancies can lead to significant errors in results.
What is the primary purpose of the expanded form in mathematics?
+The primary purpose of the expanded form is to represent a number in a way that shows the value of each digit based on its position, facilitating a deeper understanding of arithmetic operations and number properties.
How does the expanded form apply to decimals and fractions?
+The expanded form applies to decimals by extending the place value system to the right of the decimal point, and to fractions by applying the concept to both the numerator and the denominator, aiding in simplification and operation.
What are the advanced applications of the expanded form in mathematics?
+The expanded form has significant applications in algebra for simplifying and solving equations and in number theory for understanding number properties, proving theorems, and deriving formulas.
In conclusion, the expanded form is a fundamental concept in mathematics that provides a detailed representation of numbers, facilitating a deeper understanding of arithmetic operations, number properties, and advanced mathematical concepts. Its applications are diverse, ranging from basic arithmetic to advanced algebra and number theory, and its importance in real-world calculations and scientific research cannot be overstated. As such, mastering the expanded form is essential for anyone seeking to develop a strong foundation in mathematics and to appreciate the intricacies and beauty of numerical representation and manipulation.