Biochemistry, the study of the chemical processes that occur within living organisms, is a vast and intricate field that underlies all aspects of life. From the simplest bacteria to the most complex human beings, biochemistry plays a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of life. At its core, biochemistry involves the study of the structure, function, and interactions of biological molecules such as DNA, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. In this article, we will delve into five ways biochemistry works, exploring its fundamental principles, mechanisms, and applications.
Key Points
- Biochemistry is the foundation of life, governing the chemical processes that occur within living organisms.
- The structure and function of biological molecules, such as DNA and proteins, are crucial to understanding biochemical processes.
- Metabolic pathways, including glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, are essential for energy production and conversion in living organisms.
- Enzymes, biological catalysts, play a vital role in facilitating biochemical reactions and maintaining the balance of life.
- Biochemical principles have numerous applications in fields such as medicine, agriculture, and biotechnology, improving our daily lives and contributing to scientific advancements.
Understanding Biological Molecules
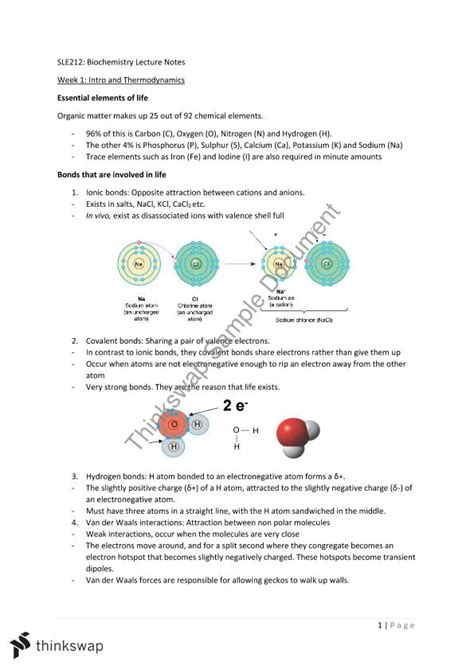
The foundation of biochemistry lies in the understanding of biological molecules, including nucleic acids (DNA and RNA), proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. Each of these molecules has a unique structure and function that contributes to the overall biochemical processes within living organisms. For instance, DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) contains the genetic instructions used in the development and function of all living organisms, while proteins are complex molecules that perform a wide array of functions, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, replicating DNA, and responding to stimuli.
The Role of Enzymes in Biochemical Reactions
Enzymes, biological catalysts, are proteins that speed up chemical reactions in the body, allowing them to occur at a faster rate and with less energy. They are highly specific, meaning each enzyme only catalyzes one particular reaction or a small group of related reactions. The activity of enzymes is crucial for life, as they facilitate the breakdown of nutrients, the synthesis of new molecules, and the regulation of metabolic pathways. For example, the enzyme lactase breaks down lactose, a sugar found in milk, into glucose and galactose, which can then be absorbed and utilized by the body.
| Enzyme | Substrate | Product |
|---|---|---|
| Lactase | Lactose | Glucose + Galactose |
| Amylase | Starch | Maltose |
| Lipase | Triglycerides | Fatty Acids + Glycerol |

Metabolic Pathways and Energy Production
Metabolic pathways are series of chemical reactions that occur within cells, facilitating the breakdown of nutrients to produce energy and the synthesis of new molecules necessary for growth and maintenance. Two of the most critical metabolic pathways are glycolysis and the citric acid cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle). Glycolysis is the first step in cellular respiration, where glucose is converted into pyruvate, generating a small amount of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADH. The citric acid cycle, on the other hand, takes place in the mitochondria and is a key process by which cells generate energy, producing ATP, NADH, and FADH2 as byproducts.
Regulation of Biochemical Processes
The regulation of biochemical processes is essential for maintaining homeostasis within living organisms. This is achieved through various mechanisms, including feedback inhibition, where the end product of a metabolic pathway inhibits an earlier step in the pathway, and allosteric control, where the binding of an effector molecule to an enzyme changes its shape, thereby affecting its activity. These regulatory mechanisms ensure that biochemical reactions occur at the appropriate rate and time, preventing the overproduction or underproduction of critical molecules.
What is the primary function of enzymes in biochemical reactions?
+Enzymes act as biological catalysts, speeding up chemical reactions in the body and allowing them to occur at a faster rate and with less energy.
How do metabolic pathways contribute to energy production in cells?
+Metabolic pathways, such as glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, facilitate the breakdown of nutrients to produce energy in the form of ATP, which is essential for various cellular functions.
What role do biological molecules play in maintaining the balance of life?
+Biological molecules, including DNA, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids, have unique structures and functions that contribute to the overall biochemical processes within living organisms, maintaining the delicate balance necessary for life.
In conclusion, biochemistry works through the intricate interplay of biological molecules, enzymes, metabolic pathways, and regulatory mechanisms. Understanding these components and their interactions is crucial for appreciating the complexity and beauty of life. As research in biochemistry continues to advance, it not only deepens our understanding of the biological world but also opens up new avenues for medical, agricultural, and biotechnological innovations, ultimately improving human life and contributing to scientific progress.