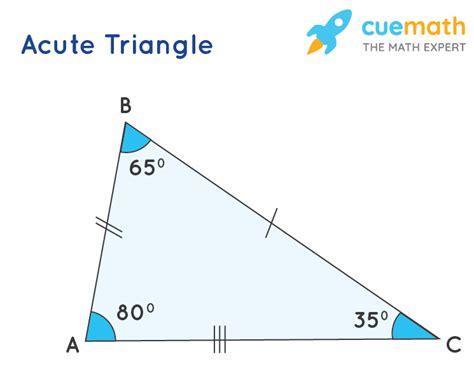
An acute triangle is a type of triangle where all three angles are less than 90 degrees. This means that each angle in the triangle is acute, or sharp, and none of them are right angles (90 degrees) or obtuse angles (greater than 90 degrees). The sum of the interior angles of any triangle is always 180 degrees, and in an acute triangle, the sum of the three acute angles will also equal 180 degrees.
The properties of an acute triangle are quite distinct from those of right triangles or obtuse triangles. For instance, in an acute triangle, the longest side is opposite the largest angle, and the shortest side is opposite the smallest angle. This property can be useful in solving problems related to acute triangles. Furthermore, acute triangles have a unique characteristic where the altitude of the triangle (the line from a vertex perpendicular to the opposite side) will always lie inside the triangle, unlike in obtuse triangles where it can lie outside.
Key Points
- All three angles of an acute triangle are less than 90 degrees.
- The sum of the interior angles of an acute triangle is 180 degrees.
- The longest side of an acute triangle is opposite the largest angle.
- The altitude of an acute triangle always lies inside the triangle.
- Acute triangles can be classified into different types based on their side lengths, such as equilateral, isosceles, or scalene acute triangles.
Properties of Acute Triangles
Acute triangles exhibit several key properties that distinguish them from other types of triangles. One of the most important properties is that the circumcenter of the triangle (the point where the perpendicular bisectors of the sides intersect) lies inside the triangle. This is because all three angles are acute, allowing the circumcenter to be enclosed within the triangle’s boundaries. Additionally, the incenter of the triangle (the point where the angle bisectors intersect) also lies inside the triangle, which is a characteristic shared by all triangles but is particularly notable in acute triangles due to their angular properties.
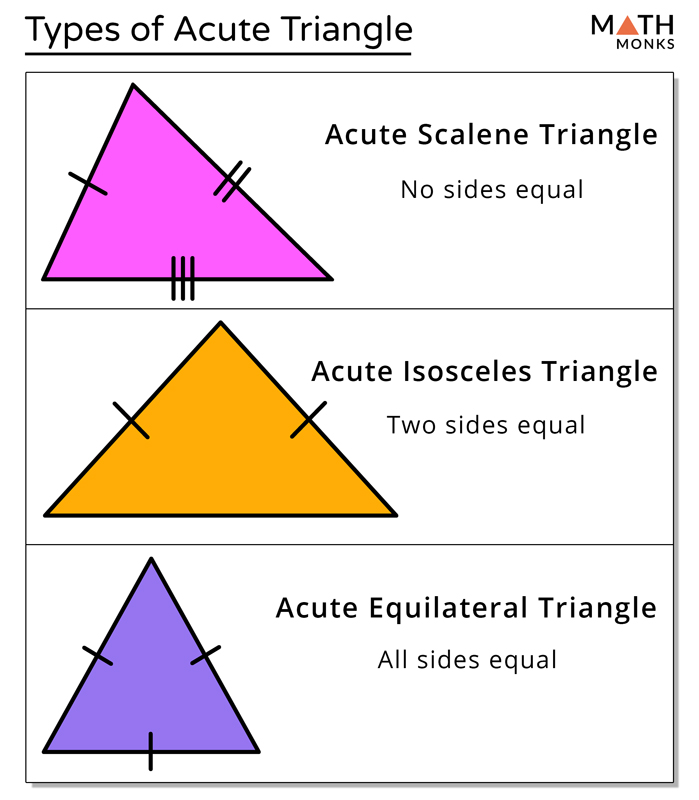
Types of Acute Triangles
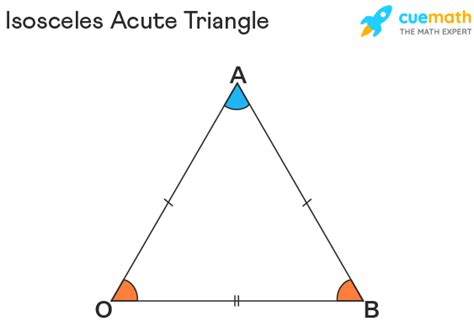
Acute triangles can be further classified based on the lengths of their sides. An equilateral acute triangle has all sides of equal length and all angles equal to 60 degrees, making it a special case of an acute triangle. An isosceles acute triangle has two sides of equal length, with the third side being either longer or shorter. A scalene acute triangle has all sides of different lengths, offering a wide range of possible acute angles. Each type of acute triangle has its unique properties and applications in geometry and real-world problems.
| Type of Acute Triangle | Properties |
|---|---|
| Equilateral Acute Triangle | All sides equal, all angles 60 degrees. |
| Isosceles Acute Triangle | Two sides equal, third side variable. |
| Scalene Acute Triangle | All sides of different lengths. |
Applications of Acute Triangles
Acute triangles have numerous applications across various fields. In architecture, the design of buildings, bridges, and other structures often involves the use of acute triangles to ensure stability and aesthetic appeal. In engineering, acute triangles are used in the design of mechanical components, such as gears and levers, where the angular properties of acute triangles provide specific mechanical advantages. Additionally, in computer graphics and game development, understanding acute triangles is essential for creating realistic models and simulations.
The study of acute triangles also has historical significance, with ancient civilizations recognizing the importance of these geometric figures in their architectural and artistic achievements. The pyramid of Giza, for example, is a masterpiece of ancient engineering that incorporates acute triangles in its design to achieve remarkable stability and durability.
Real-World Examples
Acute triangles are not just theoretical concepts; they are omnipresent in our daily lives. From the shape of roof structures to the design of furniture, acute triangles play a crucial role in ensuring both form and function. In nature, the branching patterns of trees and the structure of molecular compounds also exhibit acute triangular geometries, demonstrating the ubiquity and importance of these geometric figures.
What is the sum of the interior angles of an acute triangle?
+The sum of the interior angles of any triangle, including an acute triangle, is always 180 degrees.
Can an acute triangle be equilateral?
+Yes, an equilateral triangle is a special case of an acute triangle where all sides are equal and all angles are 60 degrees.
What are some real-world applications of acute triangles?
+Acute triangles have applications in architecture, engineering, design, and computer graphics, among other fields, due to their unique properties and stability.