A medical insurance premium is a crucial aspect of health insurance that often sparks curiosity among individuals seeking to understand the intricacies of their coverage. In essence, a medical insurance premium refers to the amount of money that an individual or family must pay to an insurance provider in exchange for health insurance coverage. This payment is typically made on a monthly or annual basis, and it serves as the primary source of revenue for insurance companies. The premium amount is calculated based on various factors, including the policyholder's age, health status, location, and the type of coverage they select.
Understanding medical insurance premiums is vital for making informed decisions about one's health insurance coverage. It is essential to recognize that premiums are not the only cost associated with health insurance. Other expenses, such as deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance, also play a significant role in determining the overall cost of healthcare. Nevertheless, the premium remains a fundamental component of health insurance, and its calculation involves a complex interplay of factors, including actuarial assessments, regulatory requirements, and market forces.
Key Points
- A medical insurance premium is the amount paid to an insurance provider for health coverage.
- Premiums are calculated based on factors such as age, health status, location, and coverage type.
- Understanding premiums is crucial for making informed health insurance decisions.
- Premiums are not the only cost associated with health insurance; other expenses include deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance.
- The calculation of premiums involves actuarial assessments, regulatory requirements, and market forces.
Factors Influencing Medical Insurance Premiums
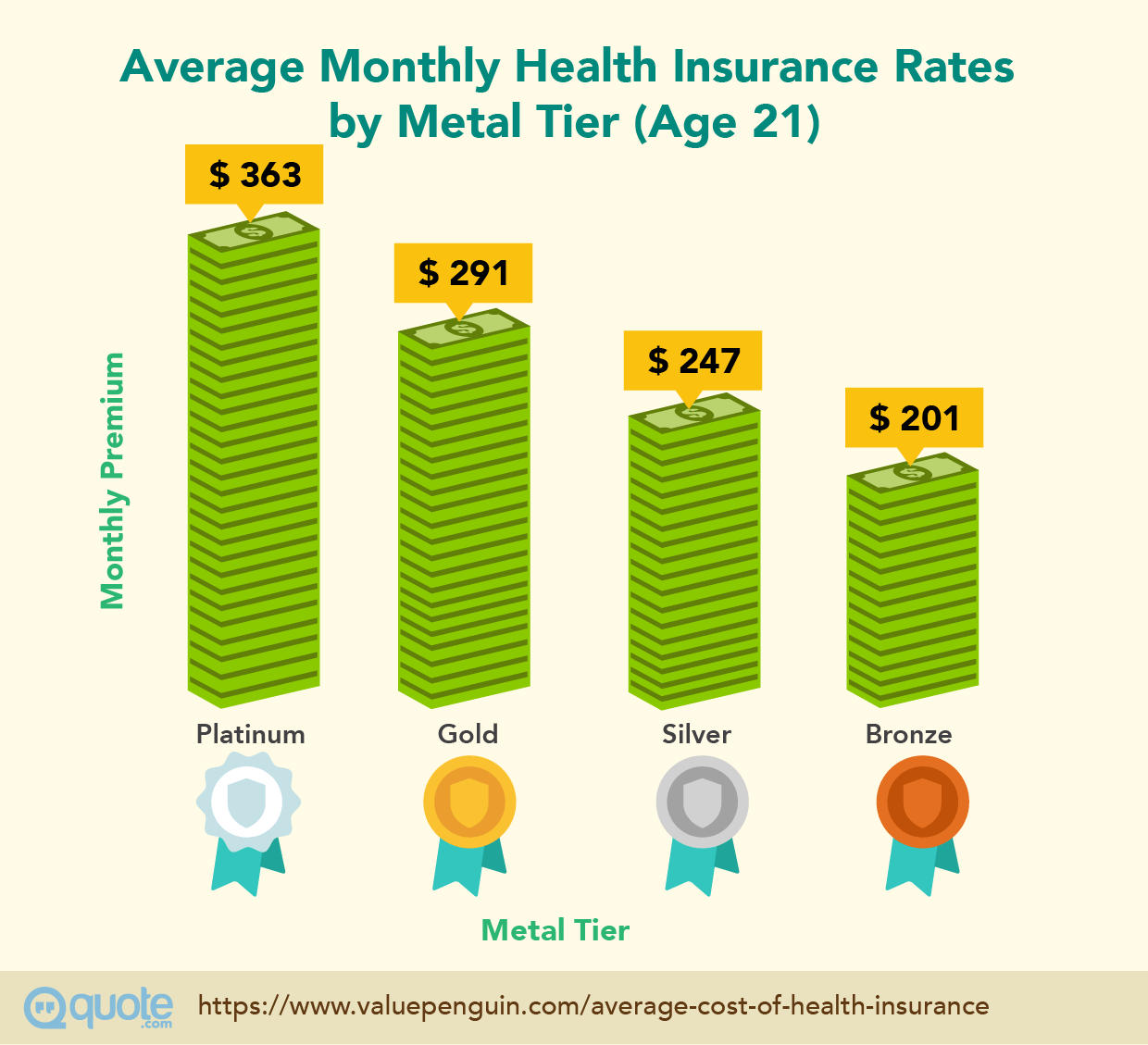
Several factors contribute to the determination of medical insurance premiums. These include the policyholder’s age, with older individuals typically facing higher premiums due to the increased likelihood of health issues. Health status is another critical factor, as pre-existing conditions or a history of certain illnesses can lead to higher premiums. Location also plays a role, as the cost of living and healthcare varies significantly across different regions. The type of coverage selected, including the level of deductible, copayment, and coinsurance, also impacts the premium amount. Lastly, lifestyle factors such as smoking status and occupation can influence premiums, as they are associated with varying levels of health risk.
Calculating Medical Insurance Premiums
The calculation of medical insurance premiums involves a multifaceted approach that takes into account various actuarial and statistical models. Insurance companies employ actuaries to analyze data on healthcare costs, utilization patterns, and demographic trends to estimate the expected costs of providing coverage. This information is then used to determine the premium amount required to ensure the insurance company’s financial stability and profitability. Regulatory requirements, such as those related to minimum coverage levels and rate setting, also influence the premium calculation process. Furthermore, market forces, including competition among insurance providers and consumer demand, can impact premium prices.
| Factor | Influence on Premium |
|---|---|
| Age | Generally increases with age |
| Health Status | Pre-existing conditions or poor health history increase premiums |
| Location | Varies by region due to differences in cost of living and healthcare |
| Coverage Type | Higher deductibles and copayments can lower premiums |
| Lifestyle Factors | Smoking and high-risk occupations can increase premiums |
Implications of Medical Insurance Premiums
The implications of medical insurance premiums are far-reaching and can have significant effects on individuals, families, and the broader healthcare system. High premiums can lead to decreased accessibility of health insurance, particularly for low-income individuals or those with pre-existing conditions. This, in turn, can result in delayed or foregone medical care, exacerbating health disparities and worsening health outcomes. On the other hand, affordable premiums can increase health insurance enrollment, leading to better health outcomes, reduced financial burdens, and a more equitable distribution of healthcare resources.
In conclusion, medical insurance premiums are a complex and multifaceted aspect of health insurance that requires a nuanced understanding of the underlying factors and their interplay. By recognizing the role of premiums in the broader healthcare landscape, individuals can make more informed decisions about their coverage and advocate for policies that promote accessibility, affordability, and equity in healthcare.
What is the primary purpose of a medical insurance premium?
+The primary purpose of a medical insurance premium is to provide financial protection against healthcare costs by transferring the risk from the individual to the insurance provider.
How are medical insurance premiums calculated?
+Medical insurance premiums are calculated based on factors such as age, health status, location, and coverage type, using actuarial models and statistical analysis to estimate expected healthcare costs.
What are the implications of high medical insurance premiums?
+High medical insurance premiums can lead to decreased accessibility of health insurance, delayed or foregone medical care, and worsening health outcomes, particularly for low-income individuals or those with pre-existing conditions.