Understanding basic numerical relationships is fundamental in both everyday contexts and specialized fields like finance, data analysis, and education. When asked what twenty percent of 500,000 is, it might seem like a straightforward calculation, yet the underlying concepts of percentages and proportionality are rich with historical evolution, mathematical principles, and practical significance. Mastering these fundamental computations not only empowers individuals to handle various real-world scenarios—such as budgeting, investing, or interpreting statistical data—but also deepens their appreciation of how numerical relationships underpin many facets of modern life. This article aims to unpack the concept of finding a percentage of a large number with clarity, precision, and authoritative insight, drawing on proven educational methodologies and mathematical rigor.
Fundamentals of Percentage Calculations in Numerical Contexts

At its core, the calculation of a percentage involves translating a part-whole relationship into a proportion out of 100. For instance, to find what 20% of 500,000 is, you align with the general formula:
Part = (Percentage / 100) × Total.This process, rooted in centuries of mathematical tradition, allows for straightforward conversion between ratios and their decimal equivalents, facilitating easy computational application across numerous domains. Historically, the notion of percentage derives from the Latin ‘per centum,’ meaning ‘by the hundred,’ a concept that gained prominence during medieval European trade practices, where rapid calculation of tariffs, interest, and taxes became essential. Today, understanding and applying this principle underpins daily financial decisions, corporate planning, and statistical analyses.
Step-by-Step Calculation of 20% of 500,000
Applying the formula directly: Part = (20 / 100) × 500,000. Breaking it down, 20 divided by 100 simplifies to 0.2, transforming the calculation into:
Part = 0.2 × 500,000.Multiplying 0.2 by 500,000 yields 100,000, which is exactly twenty percent of five hundred thousand. This straightforward example exemplifies the computational clarity brought about through understanding decimal equivalents and proportional reasoning. Such basic operations serve as building blocks for more complex financial models—like compound interest calculations and valuation assessments—highlighting their comprehensive utility.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Percentage | 20% |
| Original Number | 500,000 |
| Result | 100,000 (exactly 20% of 500,000) |

Broader Implications: Percentages in Economic and Professional Spheres
Percentages are more than mere numbers; they are practical tools with a vast array of applications. For example, in finance, understanding how to compute percentages is vital for accurately assessing interest rates, evaluating profit margins, or determining tax liabilities. Similarly, in economics, percentage changes serve as indicators of growth or decline—examples include GDP growth rates, unemployment rate reductions, or inflation metrics. By mastering these computations, professionals can better interpret data, formulate strategies, and communicate insights effectively.
Practical Applications in Business and Personal Finance
Consider a small business owner analyzing sales performance. If the total sales amount to 500,000 and they want to evaluate a 20% increase, understanding these core calculations becomes critical. The increase equates to 100,000, which can then inform inventory decisions, marketing campaigns, or investment needs. On a personal level, individuals calculating discounts, tax obligations, or savings growth rely heavily on percentage operations. The simplicity of such calculations often conceals their significance in financial literacy and decision-making.
| Application Domain | Example Metric |
|---|---|
| Business Growth | 20% increase on 500,000 = 100,000 |
| Personal Savings | With 20% interest on savings |
| Tax Calculation | Tax rate applied to income |
Limitations and Nuances in Percentage Calculations
While the computation of 20% of 500,000 is straightforward, it’s essential to consider contextual nuances that can complicate or modify simple calculations. Variations such as compounded percentages, incremental adjustments, or non-linear scaling introduce additional layers of complexity. For example, calculating the cumulative effect of multiple percentage changes over time—like compound interest—requires iterative processes or formulas that extend beyond the basic multiplication. Similarly, real-world scenarios often demand adjustments for inflation, taxation, or regional factors, which necessitate an understanding of underlying assumptions and contextual variables.
Advanced Considerations and Error Sources
One common challenge arises in ensuring precision amid rounding conventions or when dealing with large financial figures. Rounding billion-dollar values to the nearest thousand can lead to slightly different results, potentially impacting critical decisions. Furthermore, misinterpretations can occur when percentages are applied to incorrect bases, especially in complex multi-step calculations. Knowledge of these pitfalls is a hallmark of advanced financial literacy and analytical sophistication.
| Potential Issue | Impact |
|---|---|
| Rounding Errors | Minor discrepancies in high-stakes calculations |
| Incorrect Base Application | Misestimation of percentages on wrong figures |
| Compound Calculations | Requires iterative or exponential formulas |
The Evolution and Future of Percentage-based Computation in Data-Driven Fields
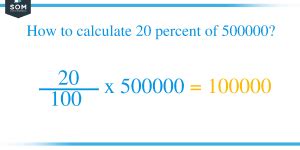
As data-driven decision-making accelerates across industries, the role of percentages extends even further, transforming traditional numerical skills into foundational literacy for 21st-century professionals. The advent of machine learning models, real-time analytics, and big data platforms all hinge on accurate, rapid calculations of ratios, proportions, and percentages. Understanding the history of percentage use—its origins during economic trade and evolving through digital automation—illustrates the enduring importance of these concepts. Future developments may include AI-driven tools that automatically detect and correct percentage misapplications, further empowering users to make precise judgments without extensive manual calculation.
Emerging Trends and Technological Integration
Intelligent systems now incorporate percentage calculations seamlessly, often providing intuitive visualizations like progress bars, financial dashboards, and predictive models. Such integrations not only enhance comprehension but also reduce computational errors—an essential factor as the complexity of data continues to grow. As professionals adapt to these technological advances, a deep foundational understanding of percentages remains indispensable, ensuring that automatic tools serve as support rather than crutches.
| Future Outlook | Implication |
|---|---|
| Automation of Percentage Calculations | Increases efficiency in data analysis and reporting |
| Enhanced Visualization Tools | Improves interpretability of percentage-based insights |
| AI-assisted Error Checks | Reduces human error and enhances accuracy |
Frequently Asked Questions about Calculating Percentages
How do I calculate 20% of any number manually?
+To manually calculate 20% of any number, convert the percentage to a decimal by dividing by 100 (20 ÷ 100 = 0.2), then multiply this decimal by the number. For example, 0.2 × 500,000 equals 100,000. This method applies universally for all percentage calculations.
What are common mistakes when calculating percentages?
+Common errors include incorrect conversion of percentages to decimals, applying percentages to the wrong base or total, and rounding errors, especially with large numbers. Ensuring accuracy in each step and understanding the context prevents these pitfalls.
Why is understanding percentages important in real-world decision-making?
+Percentages are crucial for interpreting financial data, evaluating investment opportunities, analyzing economic indicators, and making everyday personal decisions. They enable quick, meaningful insights into proportional relationships, supporting sound judgment and strategy.
Can percentages be used for non-mathematical purposes?
+Absolutely. Percentages are often used in contexts like survey results, opinion polls, or percentages of completion in projects. They help communicate data succinctly, making complex information accessible and comparable across different domains.