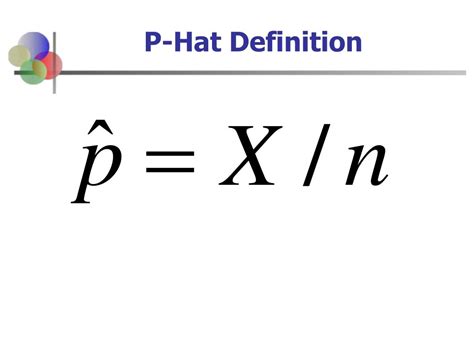The P-hat, a statistical concept, is often misunderstood due to its complex nature and the nuances of its application. At its core, the P-hat represents an estimate of a population proportion based on a sample of data. Understanding how the P-hat works is crucial for making informed decisions in various fields, including business, healthcare, and social sciences. This article will delve into the five primary ways the P-hat operates, providing insights into its calculation, interpretation, and practical applications.
Calculation of the P-hat

The calculation of the P-hat is straightforward yet requires careful consideration of the sample size and the number of successes within that sample. The formula for the P-hat is P̂ = X / n, where X is the number of successes, and n is the sample size. For instance, if a survey of 100 individuals finds that 25 of them prefer a certain product, the P-hat would be 25 / 100 = 0.25. This means that, based on the sample, it’s estimated that 25% of the population prefers that product.
Statistical Significance and Confidence Intervals
Understanding the P-hat’s relationship with statistical significance and confidence intervals is vital. Statistical significance, often determined by a p-value, indicates whether the observed results are likely due to chance. Confidence intervals, on the other hand, provide a range of values within which the true population proportion is likely to lie. The P-hat is used to construct these intervals, offering a more nuanced view of the population parameter than a single point estimate. For example, a 95% confidence interval for the proportion of individuals who prefer a certain product might range from 20% to 30%, indicating that while the P-hat estimate is 25%, the true population proportion is likely between these values.
| Sample Size | Number of Successes | P-hat Value |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 25 | 0.25 |
| 500 | 125 | 0.25 |
| 1000 | 250 | 0.25 |

Practical Applications of the P-hat

The P-hat has numerous practical applications across various disciplines. In business, it can be used to estimate market share or the proportion of customers who prefer a certain product feature. In healthcare, the P-hat can help estimate the prevalence of a disease or the effectiveness of a treatment. For instance, a pharmaceutical company might use the P-hat to estimate the proportion of patients who respond positively to a new medication, based on clinical trial data.
Limitations and Considerations
While the P-hat is a powerful tool for estimating population proportions, it is not without its limitations. The accuracy of the P-hat depends heavily on the sample size and the sampling method. Small samples or samples that are not representative of the population can lead to biased estimates. Additionally, the P-hat assumes a simple random sample, which may not always be the case in real-world applications. Understanding these limitations is crucial for interpreting P-hat estimates correctly and making informed decisions.
Key Points
- The P-hat is an estimate of a population proportion based on a sample of data.
- It is calculated using the formula P̂ = X / n, where X is the number of successes, and n is the sample size.
- The P-hat is used in constructing confidence intervals and determining statistical significance.
- It has practical applications in business, healthcare, and social sciences for estimating proportions and making informed decisions.
- The accuracy of the P-hat depends on the sample size and the sampling method, with small or non-representative samples potentially leading to biased estimates.
Future Directions and Implications
As data collection and analysis continue to evolve, the role of the P-hat in statistical inference will remain significant. Future research and applications may focus on improving the accuracy of P-hat estimates, particularly in scenarios with small samples or complex sampling designs. Additionally, integrating the P-hat with other statistical methods, such as machine learning algorithms, could enhance its utility in a wider range of applications. The implications of these developments will be profound, enabling more precise decision-making and a deeper understanding of population parameters across various fields.
What is the primary use of the P-hat in statistical analysis?
+The primary use of the P-hat is to estimate the population proportion based on a sample of data, facilitating informed decision-making in various fields.
How does sample size affect the accuracy of the P-hat estimate?
+Larger sample sizes generally provide more accurate P-hat estimates, as they are less subject to the variability inherent in smaller samples.
Can the P-hat be used for continuous data?
+No, the P-hat is specifically designed for binary or categorical data. For continuous data, other statistical measures such as the mean or median are more appropriate.
In conclusion, the P-hat is a fundamental concept in statistical analysis, providing valuable insights into population proportions. Its applications are diverse, ranging from market research to medical studies. By understanding how the P-hat works and its limitations, professionals can harness its power to make more informed decisions and contribute to advancements in their respective fields.