Wildfires, also known as wildland fires, are uncontrolled fires that occur in wildland areas, such as forests, grasslands, and brushlands. These fires can be devastating, causing damage to the environment, wildlife, and human communities. Understanding the causes of wildfires is crucial for prevention, mitigation, and management. In this article, we will explore the various factors that contribute to the occurrence of wildfires.
Wildfires can be caused by a combination of natural and human factors. Natural causes include lightning, volcanic eruptions, and spontaneous combustion of organic matter. However, human activities are responsible for the majority of wildfires. Human-caused wildfires can be intentional, such as arson, or unintentional, such as unattended campfires, discarded cigarettes, or equipment malfunctions. According to the National Interagency Coordination Center, human activities account for approximately 90% of all wildfires in the United States.
Natural Causes of Wildfires

Natural causes of wildfires include lightning, which is a major contributor to wildfires, especially in remote areas. Lightning can ignite fires in areas with dry vegetation, and strong winds can spread the fire quickly. Volcanic eruptions can also cause wildfires, as the heat and sparks from the eruption can ignite surrounding vegetation. Spontaneous combustion of organic matter, such as peat or coal, can also occur, especially in areas with high temperatures and low humidity.
Lightning-Induced Wildfires
Lightning is a significant cause of wildfires, particularly in areas with frequent thunderstorms. According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), lightning causes an average of 200,000 wildfires per year in the United States. Lightning-induced wildfires can be challenging to predict and prevent, as they often occur in remote areas with limited access. However, fire management agencies use advanced technologies, such as lightning detection systems and satellite imaging, to monitor and respond to lightning-induced wildfires.
| Year | Number of Wildfires | Acreage Burned |
|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 58,083 | 4,672,307 |
| 2018 | 58,083 | 8,767,492 |
| 2017 | 71,499 | 10,125,110 |
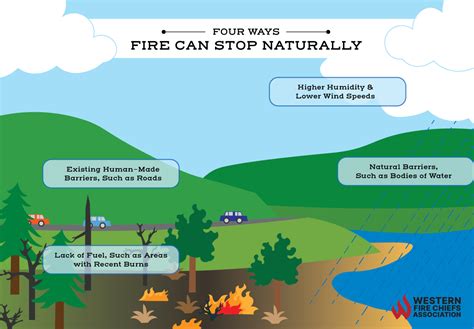
Human-Caused Wildfires

Human activities are responsible for the majority of wildfires. Unattended campfires, discarded cigarettes, and equipment malfunctions are common causes of human-caused wildfires. Arson, or intentionally set fires, is also a significant concern, as it can be challenging to detect and prevent. According to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), human-caused wildfires account for approximately 90% of all wildfires in the United States.
Unattended Campfires
Unattended campfires are a leading cause of human-caused wildfires. Campfires can be extinguished, but they require careful attention to ensure that they are fully extinguished. According to the USDA, campfires are responsible for an average of 10,000 wildfires per year in the United States. To prevent campfire-induced wildfires, it is essential to follow safe campfire practices, such as using fire rings, keeping a bucket of water nearby, and fully extinguishing the fire before leaving the campsite.
Key Points
- Wildfires can be caused by a combination of natural and human factors.
- Human activities account for approximately 90% of all wildfires in the United States.
- Lightning is a significant cause of wildfires, particularly in areas with frequent thunderstorms.
- Unattended campfires are a leading cause of human-caused wildfires.
- Arson, or intentionally set fires, is a significant concern, as it can be challenging to detect and prevent.
Climate Change and Wildfires
Climate change is also a significant factor in the increasing trend of wildfires. Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and increased drought frequency and severity all contribute to an increased risk of wildfires. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), the frequency and severity of wildfires are expected to increase by 50% by 2100 due to climate change.
Impacts of Climate Change on Wildfires
The impacts of climate change on wildfires are far-reaching. Warmer temperatures and changing precipitation patterns can lead to an increase in the frequency and severity of wildfires. Droughts, in particular, can create conditions that are conducive to wildfires, as dry vegetation is more susceptible to ignition. According to the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), the 2019-2020 Australian bushfires, which burned over 10 million hectares of land, were exacerbated by climate change.
What is the main cause of wildfires?
+Human activities, such as unattended campfires, discarded cigarettes, and equipment malfunctions, are the main cause of wildfires, accounting for approximately 90% of all wildfires in the United States.
How can climate change contribute to wildfires?
+Climate change can contribute to wildfires by increasing temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and increasing drought frequency and severity, creating conditions that are conducive to wildfires.
What can be done to prevent wildfires?
+To prevent wildfires, it is essential to follow safe practices, such as fully extinguishing campfires, disposing of cigarettes properly, and maintaining equipment regularly. Additionally, prescribed burning, forest thinning, and public education campaigns can help reduce the risk of wildfires.
Meta description suggestion: “Learn about the causes of wildfires, including natural and human factors, and how climate change contributes to the increasing trend of wildfires. Discover ways to prevent and mitigate wildfires.” (149 characters)