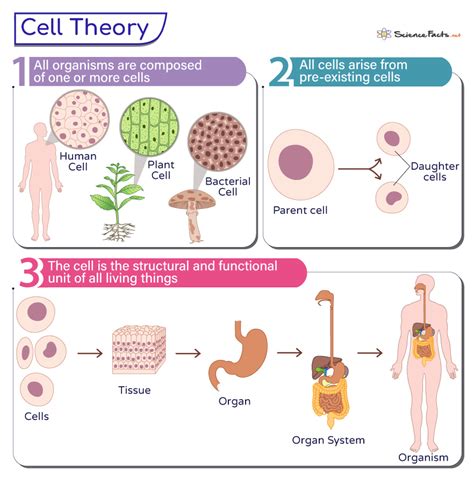
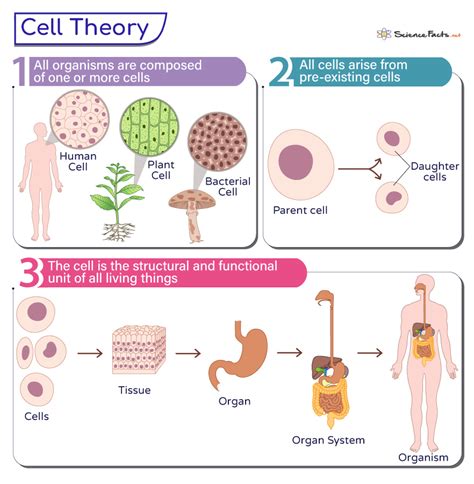
The cell theory is a fundamental concept in biology that explains the structure and function of living organisms. It is based on the idea that all living things are composed of cells, which are the basic units of life. The cell theory has three main components, which are: all living organisms are composed of one or more cells, cells are the basic units of life, and all cells arise from pre-existing cells.
Key Points
- The cell theory consists of three main components that explain the nature of living organisms.
- All living organisms are composed of one or more cells, which can be unicellular or multicellular.
- Cells are the basic units of life, meaning that they are the smallest structures that can function independently and maintain the characteristics of life.
- All cells arise from pre-existing cells, which means that new cells are formed through the division of existing cells.
- The cell theory has been widely accepted and has had a significant impact on our understanding of biology and medicine.
First Component: All Living Organisms Are Composed Of One Or More Cells
This component of the cell theory states that all living organisms, from bacteria to humans, are composed of one or more cells. This means that cells are the basic building blocks of life, and that all living things are made up of cells. This component was first proposed by Matthias Jakob Schleiden and Theodor Schwann in the 19th century, based on their observations of plant and animal tissues.
For example, bacteria are single-celled organisms that consist of a single cell, while humans are multicellular organisms that consist of trillions of cells. The fact that all living organisms are composed of cells provides evidence for the cell theory and highlights the importance of cells in understanding the biology of living organisms.
Types Of Cells
There are two main types of cells: prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria, lack a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells, such as plant and animal cells, have a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. This difference in cell structure reflects the different levels of complexity and organization of living organisms.
| Cell Type | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Prokaryotic Cells | Lack a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles |
| Eukaryotic Cells | Have a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles |
Second Component: Cells Are The Basic Units Of Life
This component of the cell theory states that cells are the smallest structures that can function independently and maintain the characteristics of life. This means that cells are capable of carrying out all the necessary functions of life, such as growth, reproduction, and metabolism, without the need for other cells or organisms.
For example, a single bacterial cell can grow and divide to form a new cell, without the need for any other cells or organisms. This ability of cells to function independently is a key characteristic of life and provides evidence for the cell theory.
Characteristics Of Living Cells
Living cells have a number of characteristics that distinguish them from non-living things. These characteristics include the ability to grow and reproduce, the ability to metabolize and respond to stimuli, and the ability to maintain homeostasis and adapt to changes in the environment.
These characteristics are essential for the survival and function of living organisms and provide evidence for the cell theory. The fact that cells are the basic units of life highlights the importance of understanding cell biology in order to understand the biology of living organisms.
Third Component: All Cells Arise From Pre-Existing Cells
This component of the cell theory states that all cells arise from pre-existing cells, through a process called cell division. This means that new cells are formed through the division of existing cells, rather than through the spontaneous generation of new cells from non-living matter.
For example, when a cell divides, it forms two new cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. This process of cell division is essential for the growth and reproduction of living organisms and provides evidence for the cell theory.
Process Of Cell Division
Cell division is a complex process that involves the replication of DNA, the separation of chromosomes, and the division of the cell into two daughter cells. This process is essential for the growth and reproduction of living organisms and provides evidence for the cell theory.
What is the main idea of the cell theory?
+The main idea of the cell theory is that all living organisms are composed of one or more cells, cells are the basic units of life, and all cells arise from pre-existing cells.
What are the two main types of cells?
+The two main types of cells are prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells lack a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells have a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
What is the process by which new cells are formed?
+New cells are formed through the process of cell division, in which a parent cell divides to form two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell.