The Wet Bulb Temperature (WBT) is a crucial metric in understanding the heat stress caused by a combination of temperature and humidity in various environments. It is defined as the lowest temperature that can be reached by wrapping a thermometer in a wet cloth and placing it in the air stream. The evaporation of water from the cloth causes the thermometer to show a lower temperature than the actual air temperature, which is the wet bulb temperature. This metric is vital for assessing the heat stress risks in outdoor and indoor environments, especially in industries such as construction, mining, and manufacturing, where workers are exposed to high temperatures and humidity levels for extended periods.
The importance of calculating the WBT lies in its ability to provide a more accurate representation of the perceived temperature by the human body compared to the dry bulb temperature alone. High WBT values indicate a higher risk of heat-related illnesses, making it essential for employers and safety professionals to monitor and manage workplace conditions to prevent heat stress. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) and the American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH) provide guidelines and recommendations for heat stress management based on WBT calculations.
Key Points
- The Wet Bulb Temperature (WBT) is a measure of heat stress caused by temperature and humidity.
- WBT is crucial for assessing heat stress risks in various environments, especially in industries with high temperatures and humidity.
- The calculation of WBT is essential for preventing heat-related illnesses and managing workplace conditions.
- Guidelines from NIOSH and ACGIH provide recommendations for heat stress management based on WBT calculations.
- A WBT calculator tool can help in quickly and accurately determining the WBT based on air temperature and relative humidity.
Understanding Wet Bulb Temperature Calculator Tools
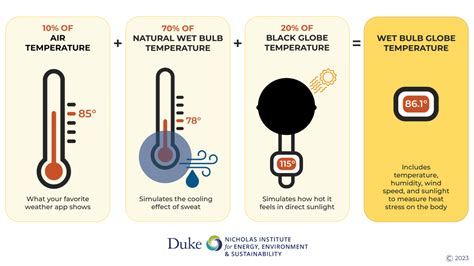
A Wet Bulb Temperature calculator tool is designed to simplify the process of calculating the WBT based on the air temperature and relative humidity. These tools can be in the form of online calculators, mobile applications, or even spreadsheet templates. The basic principle behind these calculators is to use the psychrometric chart or a mathematical model that relates the air temperature, relative humidity, and WBT. The most commonly used method is the Stull formula, which provides a simplified way to estimate the WBT from the air temperature and relative humidity.
Components of a Wet Bulb Temperature Calculator Tool
A typical WBT calculator tool requires the user to input the air temperature and relative humidity. Some advanced tools may also consider other factors such as wind speed, which can affect the evaporation rate and thus the WBT. The output of the calculator is the calculated WBT, which can then be used to assess the heat stress risk according to established guidelines. For instance, the ACGIH recommends different levels of heat stress management based on the WBT, ranging from caution to extreme danger.
| Air Temperature (°C) | Relative Humidity (%) | Wet Bulb Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| 25 | 60 | 20.5 |
| 30 | 80 | 26.2 |
| 35 | 90 | 31.8 |

Applications and Limitations of Wet Bulb Temperature Calculator Tools
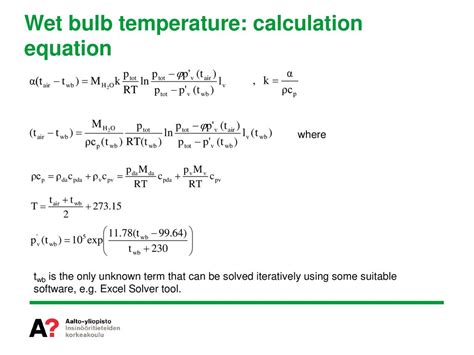
WBT calculator tools have a wide range of applications, from occupational health and safety to climate research and urban planning. They provide a quick and easy way to estimate the WBT, which is crucial for making informed decisions about heat stress management and mitigation strategies. However, it’s also important to consider the limitations of these tools. For example, the accuracy of the calculated WBT can be affected by the quality of the input data and the assumptions of the underlying model. Additionally, WBT calculator tools may not account for all the factors that can influence the WBT, such as clothing, activity level, and air movement.
Future Developments in Wet Bulb Temperature Calculator Tools
As technology advances, we can expect to see more sophisticated WBT calculator tools that incorporate additional factors and provide more accurate estimates of the WBT. For instance, the integration of machine learning algorithms and real-time weather data could enable the development of more precise and location-specific WBT calculations. Furthermore, the increasing availability of wearable sensors and IoT devices could provide more accurate and personalized measurements of heat stress, enabling more effective heat stress management strategies.
What is the Wet Bulb Temperature, and why is it important?
+The Wet Bulb Temperature is a measure of the heat stress caused by a combination of temperature and humidity. It is important because it provides a more accurate representation of the perceived temperature by the human body, helping to assess the risk of heat-related illnesses.
How do Wet Bulb Temperature calculator tools work?
+Wet Bulb Temperature calculator tools use a mathematical model or formula, such as the Stull formula, to estimate the WBT based on the air temperature and relative humidity. The user inputs the air temperature and relative humidity, and the tool calculates and outputs the WBT.
What are the limitations of Wet Bulb Temperature calculator tools?
+The limitations of Wet Bulb Temperature calculator tools include the accuracy of the input data, the assumptions of the underlying model, and the lack of consideration of all factors that can influence the WBT, such as clothing, activity level, and air movement.
In conclusion, Wet Bulb Temperature calculator tools are essential for assessing heat stress risks and managing workplace conditions to prevent heat-related illnesses. While these tools have limitations, they provide a quick and easy way to estimate the WBT, which is crucial for making informed decisions about heat stress management and mitigation strategies. As technology advances, we can expect to see more sophisticated WBT calculator tools that incorporate additional factors and provide more accurate estimates of the WBT, enabling more effective heat stress management strategies.



