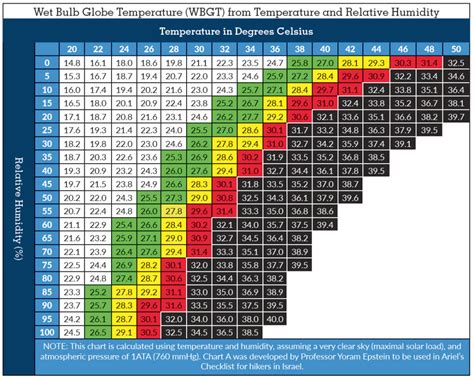
The concept of wet bulb temperature has gained significant attention in recent years, particularly in the context of climate change and its impact on human health. Essentially, the wet bulb temperature (WBT) is a measure of the heat stress caused by a combination of temperature and humidity. It is defined as the lowest temperature that can be reached by wrapping a thermometer in a wet cloth and placing it in the air stream. When the air is fully saturated with water vapor, the WBT equals the air temperature. Understanding and managing wet bulb temperatures is crucial, especially in outdoor and industrial settings, to prevent heat-related illnesses. Here are five key tips related to wet bulb temperatures, focusing on their measurement, implications, and management.
Key Points
- Understanding the concept of wet bulb temperature and its significance in heat stress management.
- Accurate measurement of wet bulb temperatures using appropriate instruments.
- Implementing strategies to mitigate the effects of high wet bulb temperatures in various settings.
- Recognizing the health risks associated with extreme wet bulb temperatures.
- Developing policies and guidelines for work and outdoor activities based on wet bulb temperature readings.
Understanding Wet Bulb Temperature

The wet bulb temperature is a critical metric for assessing the thermal environment, especially in conditions of high heat and humidity. It provides a more accurate representation of how hot it feels to the human body compared to the air temperature alone, as it takes into account the body’s ability to cool itself through sweating. In environments where the wet bulb temperature is high, the body’s cooling mechanisms are less effective, leading to a higher risk of heat-related illnesses. It is essential to understand that the wet bulb temperature can be significantly higher than the air temperature in humid conditions, even if the air temperature itself does not seem excessively high.
Measurement of Wet Bulb Temperature
Measuring the wet bulb temperature requires a psychrometer, which is an instrument specifically designed for this purpose. A psychrometer typically consists of two thermometers, one wrapped in a wet cloth and the other exposed to the air. The difference in readings between the two thermometers, when air is blown over them, gives the wet bulb depression, from which the wet bulb temperature can be calculated. In modern times, digital psychrometers and heat stress monitors have made the measurement process more efficient and accurate. These devices can provide immediate readings and often include alarms for when the wet bulb temperature exceeds safe limits.
| Wet Bulb Temperature Range | Heat Stress Level |
|---|---|
| Up to 28°C (82°F) | Low risk |
| 28-30°C (82-86°F) | Caution, moderate risk |
| 30-32°C (86-90°F) | High risk, heat stress possible |
| Above 32°C (90°F) | Very high to extreme risk |

Health Risks and Mitigation Strategies
High wet bulb temperatures pose significant health risks, including heat exhaustion and heat stroke, which can be life-threatening if not recognized and treated promptly. Symptoms of heat-related illnesses include heavy sweating, pale skin, fast and weak pulse, nausea or vomiting, and dizziness or fainting. In severe cases, the body temperature can rise rapidly, leading to brain damage or even death. Mitigation strategies include providing cool rest areas, ensuring adequate hydration, reducing physical exertion during the hottest parts of the day, and using cooling packs or cool clothing. In industrial settings, workers should be trained to recognize the signs of heat stress and have protocols in place for emergency situations.
Policies and Guidelines
Developing and implementing policies based on wet bulb temperatures is essential for preventing heat-related illnesses. This includes setting thresholds for work and outdoor activities, providing guidelines for hydration and rest, and mandating the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) designed to keep workers cool. In addition, public health campaigns can raise awareness about the risks of heat stress and how to protect oneself, especially during heatwaves. Schools and community centers can serve as cooling centers, offering a safe refuge from extreme heat. By taking a proactive approach, communities can significantly reduce the incidence of heat-related illnesses and ensure a safer, healthier environment for everyone.
What is the significance of wet bulb temperature in heat stress management?
+The wet bulb temperature is significant because it provides a measure of the heat stress caused by both temperature and humidity, offering a more accurate assessment of how hot it feels to the human body compared to air temperature alone.
How can wet bulb temperatures be measured accurately?
+Wet bulb temperatures can be measured accurately using a psychrometer or digital heat stress monitors. These instruments provide immediate readings and can include alarms for when the wet bulb temperature exceeds safe limits.
What are the health risks associated with high wet bulb temperatures?
+High wet bulb temperatures are associated with significant health risks, including heat exhaustion and heat stroke. These conditions can lead to serious health issues, including brain damage and death, if not recognized and treated promptly.