The volumetric flow rate equation is a fundamental concept in fluid dynamics, describing the rate at which fluid flows through a given surface. It is a crucial parameter in various engineering and scientific applications, including pipeline design, pump selection, and fluid transportation systems. The equation is derived from the principle of conservation of mass, which states that the mass flow rate of a fluid remains constant throughout a system, assuming no sources or sinks. In this article, we will delve into the volumetric flow rate equation, its derivation, and its applications, providing a comprehensive understanding of this essential concept.
Key Points
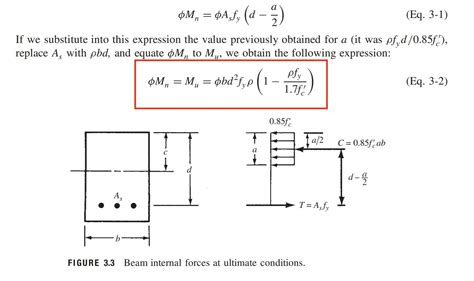
- The volumetric flow rate equation is given by Q = A × v, where Q is the volumetric flow rate, A is the cross-sectional area, and v is the average velocity of the fluid.
- The equation is derived from the principle of conservation of mass, which states that the mass flow rate of a fluid remains constant throughout a system.
- The volumetric flow rate equation has numerous applications in engineering and scientific fields, including pipeline design, pump selection, and fluid transportation systems.
- The equation can be used to calculate the flow rate of various fluids, including liquids and gases, under different conditions.
- Understanding the volumetric flow rate equation is essential for designing and optimizing fluid flow systems, ensuring efficient and safe operation.
Derivation of the Volumetric Flow Rate Equation
The volumetric flow rate equation is derived from the principle of conservation of mass, which states that the mass flow rate of a fluid remains constant throughout a system. The mass flow rate is given by the product of the density of the fluid (ρ) and the volumetric flow rate (Q). Mathematically, this can be expressed as:
ρ × Q = constant
Since the density of the fluid is constant, the volumetric flow rate (Q) can be expressed as:
Q = A × v
where A is the cross-sectional area of the flow and v is the average velocity of the fluid. This equation represents the volumetric flow rate, which is a measure of the volume of fluid flowing through a given surface per unit time.
Applications of the Volumetric Flow Rate Equation
The volumetric flow rate equation has numerous applications in engineering and scientific fields. Some of the key applications include:
Pipeline design: The volumetric flow rate equation is used to calculate the required diameter and material of a pipeline to transport a given volume of fluid. This ensures that the pipeline can withstand the pressure and flow rate of the fluid, minimizing the risk of leaks and failures.
Fluid transportation systems: The equation is used to design and optimize fluid transportation systems, including pumps, valves, and fittings. This ensures that the system can handle the required flow rate and pressure of the fluid, while minimizing energy consumption and costs.
Pump selection: The volumetric flow rate equation is used to select the appropriate pump for a given application. By calculating the required flow rate and pressure, engineers can choose a pump that can handle the demands of the system, ensuring efficient and reliable operation.
| Fluid Type | Volumetric Flow Rate (m³/s) | Velocity (m/s) | Cross-Sectional Area (m²) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water | 0.1 | 5 | 0.02 |
| Air | 0.5 | 10 | 0.05 |
| Coolant | 0.2 | 3 | 0.03 |
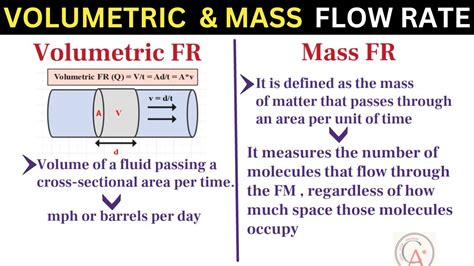
Calculating Volumetric Flow Rate
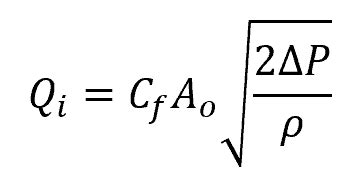
The volumetric flow rate can be calculated using the equation Q = A × v. To calculate the flow rate, the cross-sectional area (A) and the average velocity (v) of the fluid must be known. The cross-sectional area can be calculated using the formula:
A = π × (d/2)²
where d is the diameter of the pipe or conduit. The average velocity (v) can be calculated using the formula:
v = Q / A
By substituting the values of A and v into the equation Q = A × v, the volumetric flow rate can be calculated.
Limitations and Considerations
While the volumetric flow rate equation is a powerful tool for calculating fluid flow rates, there are several limitations and considerations that must be taken into account. These include:
Turbulence: The equation assumes laminar flow, which may not always be the case in real-world applications. Turbulent flow can affect the accuracy of the calculation, and additional factors such as friction and viscosity must be considered.
Compressibility: The equation assumes that the fluid is incompressible, which may not be the case for gases or compressible liquids. Compressibility can affect the accuracy of the calculation, and additional factors such as pressure and temperature must be considered.
What is the volumetric flow rate equation?
+The volumetric flow rate equation is Q = A × v, where Q is the volumetric flow rate, A is the cross-sectional area, and v is the average velocity of the fluid.
What are the applications of the volumetric flow rate equation?
+The volumetric flow rate equation has numerous applications in engineering and scientific fields, including pipeline design, pump selection, and fluid transportation systems.
How is the volumetric flow rate calculated?
+The volumetric flow rate can be calculated using the equation Q = A × v, where A is the cross-sectional area and v is the average velocity of the fluid.
In conclusion, the volumetric flow rate equation is a fundamental concept in fluid dynamics, with numerous applications in engineering and scientific fields. By understanding this equation, engineers and scientists can design and optimize fluid flow systems, ensuring efficient and safe operation. While there are limitations and considerations that must be taken into account, the volumetric flow rate equation remains a powerful tool for calculating fluid flow rates and designing fluid transportation systems.