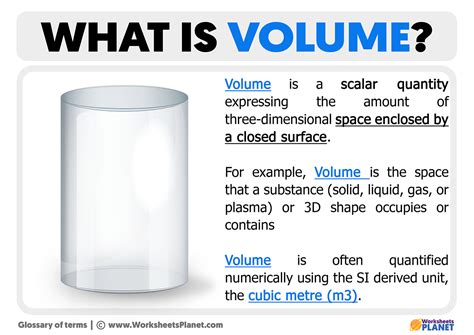
The concept of volume is a fundamental aspect of science, particularly in physics, chemistry, and engineering. Volume refers to the amount of three-dimensional space occupied by an object or a substance. It is a measure of the size of an object or the amount of material it contains. In science, volume is typically measured in units such as cubic meters (m³), cubic centimeters (cm³), or liters (L). Understanding volume is crucial in various scientific fields, as it helps researchers and scientists to calculate and analyze the properties and behaviors of different substances and objects.
In physics, volume is an essential concept in the study of mechanics, thermodynamics, and fluid dynamics. For instance, the volume of a gas is directly related to its pressure and temperature, as described by the ideal gas law. In chemistry, volume is used to calculate the amount of a substance present in a given sample, which is critical in chemical reactions and stoichiometry. In engineering, volume is used to design and optimize systems, such as pipelines, containers, and buildings, to ensure efficient and safe operation.
Key Points
- Volume is a measure of the three-dimensional space occupied by an object or substance.
- It is typically measured in units such as cubic meters, cubic centimeters, or liters.
- Understanding volume is crucial in various scientific fields, including physics, chemistry, and engineering.
- Volume is used to calculate and analyze the properties and behaviors of different substances and objects.
- It is an essential concept in the study of mechanics, thermodynamics, fluid dynamics, and chemical reactions.
Types of Volume

There are several types of volume, each with its own specific definition and application. One of the most common types of volume is the volume of a solid object, which is the amount of space occupied by the object. The volume of a solid object can be calculated using various formulas, such as the formula for the volume of a sphere (V = (4⁄3)πr³) or the formula for the volume of a cube (V = s³), where r is the radius of the sphere and s is the side length of the cube.
Another type of volume is the volume of a fluid, which is the amount of space occupied by the fluid. The volume of a fluid can be calculated using the formula V = m/ρ, where m is the mass of the fluid and ρ is its density. This type of volume is essential in the study of fluid dynamics and is used to calculate the flow rate and pressure of fluids in various systems.
Volume of a Gas
The volume of a gas is a critical concept in physics and chemistry, particularly in the study of thermodynamics. The volume of a gas is directly related to its pressure and temperature, as described by the ideal gas law (PV = nRT), where P is the pressure of the gas, V is its volume, n is the number of moles of gas, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature of the gas. Understanding the volume of a gas is essential in various applications, such as the design of engines, refrigeration systems, and air conditioning systems.
| Gas Constant (R) | Value |
|---|---|
| in J/(mol·K) | 8.3145 |
| in L·atm/(mol·K) | 0.082057 |
| in L·kPa/(mol·K) | 8.3145 |

Measurement of Volume

Measuring volume is a critical aspect of scientific research and engineering applications. There are various methods for measuring volume, depending on the type of object or substance being measured. For solid objects, volume can be measured using a ruler or caliper to calculate the dimensions of the object. For fluids, volume can be measured using a graduated cylinder or a pipette. For gases, volume can be measured using a gas meter or a manometer.
One of the most common methods for measuring volume is the displacement method, which involves measuring the volume of a fluid displaced by an object. This method is based on the principle of Archimedes, which states that the buoyancy force on an object is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. By measuring the volume of the displaced fluid, researchers and scientists can calculate the volume of the object.
Applications of Volume
Understanding volume is essential in various scientific and engineering applications. In physics, volume is used to calculate the density of an object, which is critical in understanding its behavior under different conditions. In chemistry, volume is used to calculate the amount of a substance present in a given sample, which is crucial in chemical reactions and stoichiometry. In engineering, volume is used to design and optimize systems, such as pipelines, containers, and buildings, to ensure efficient and safe operation.
Volume is also used in various medical applications, such as calculating the volume of blood in the body or the volume of a tumor. In environmental science, volume is used to calculate the amount of pollutants in a given area or the volume of a body of water. Understanding volume is essential in various fields, and its applications are diverse and widespread.
What is the difference between volume and density?
+Volume and density are two related but distinct concepts in physics. Volume refers to the amount of space occupied by an object or substance, while density refers to the mass per unit volume of an object or substance. In other words, density is a measure of how much mass is packed into a given volume.
How is volume measured in a laboratory setting?
+Volume is typically measured in a laboratory setting using a graduated cylinder or a pipette. For solid objects, volume can be measured using a ruler or caliper to calculate the dimensions of the object. For gases, volume can be measured using a gas meter or a manometer.
What are some common units of volume?
+Common units of volume include cubic meters (m³), cubic centimeters (cm³), liters (L), and milliliters (mL). The choice of unit depends on the specific application and the size of the object or substance being measured.
In conclusion, volume is a fundamental concept in science, and understanding its definition, types, and measurement is essential in various fields, including physics, chemistry, and engineering. By recognizing the importance of volume and its applications, researchers and scientists can design and optimize systems to achieve specific goals, such as maximizing efficiency or minimizing energy consumption. As science continues to evolve, the concept of volume will remain a critical aspect of scientific research and engineering applications.