Vitamin D is a crucial nutrient that plays a significant role in maintaining strong bones, immune function, and overall health. There are two primary forms of vitamin D: vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol). While both forms can be effective in raising vitamin D levels, there are distinct differences between them in terms of their origin, biological activity, and effectiveness. In this article, we will delve into the details of vitamin D3 vs D2, exploring their differences, benefits, and potential drawbacks.
Key Points
- Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) is more effective than vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) in raising and maintaining vitamin D levels.
- Vitamin D3 is more readily absorbed by the body due to its lipophilic nature, allowing for better bioavailability.
- Food sources of vitamin D3 include fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified dairy products, while vitamin D2 is found in mushrooms and fortified cereals.
- Vitamin D3 supplements are generally more effective than vitamin D2 supplements in preventing vitamin D deficiency and related diseases.
- Individuals with limited sun exposure, darker skin, or certain medical conditions may require higher doses of vitamin D3 to maintain optimal levels.
Vitamin D3 vs D2: Origin and Biological Activity
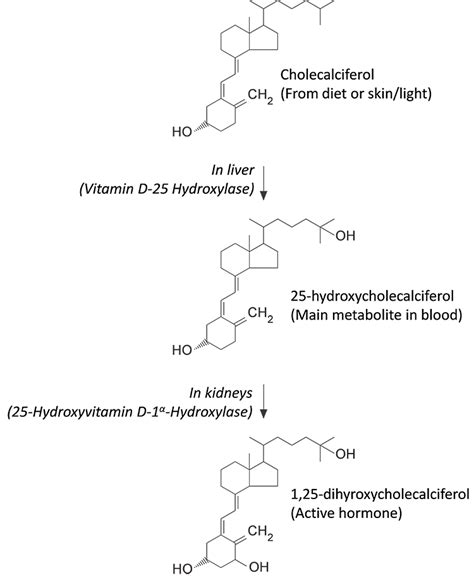
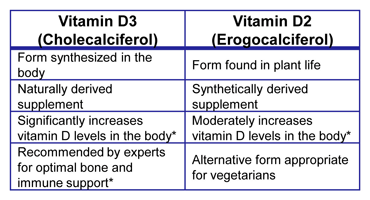
Vitamin D3, also known as cholecalciferol, is the form of vitamin D that is produced in the skin upon exposure to sunlight. It is also found in animal-based food sources, such as fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified dairy products. On the other hand, vitamin D2, or ergocalciferol, is derived from fungi and is often used in fortified foods and supplements. Vitamin D3 is more readily absorbed by the body due to its lipophilic nature, which allows it to bind to lipids and be transported more efficiently to the liver and kidneys for conversion into its active form, calcitriol.
Biological Activity and Effectiveness
Studies have consistently shown that vitamin D3 is more effective than vitamin D2 in raising and maintaining vitamin D levels. A meta-analysis of 10 studies found that vitamin D3 supplementation resulted in a 34% greater increase in vitamin D levels compared to vitamin D2 supplementation. Additionally, a randomized controlled trial found that vitamin D3 supplementation was more effective in preventing vitamin D deficiency and related diseases, such as osteoporosis and diabetes, compared to vitamin D2 supplementation.
| Form of Vitamin D | Biological Activity | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) | More readily absorbed and converted to calcitriol | More effective in raising and maintaining vitamin D levels |
| Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) | Less readily absorbed and converted to calcitriol | Less effective in raising and maintaining vitamin D levels |
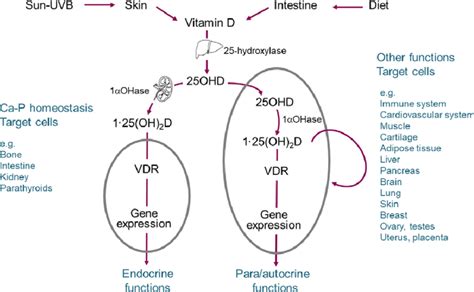
Food Sources and Supplementation
While it is possible to obtain vitamin D through food sources, such as fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified dairy products, many individuals may require supplementation to achieve optimal levels. Vitamin D3 supplements are generally more effective than vitamin D2 supplements, and they are available in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and liquids. It is essential to choose a supplement that is manufactured by a reputable company and contains a sufficient amount of vitamin D3 to meet individual needs.
Individual Needs and Considerations
Individuals with limited sun exposure, darker skin, or certain medical conditions, such as kidney or liver disease, may require higher doses of vitamin D3 to maintain optimal levels. Additionally, pregnant and breastfeeding women, as well as older adults, may benefit from vitamin D3 supplementation to support bone health and immune function. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of supplementation and to monitor vitamin D levels regularly.
What is the recommended daily intake of vitamin D3?
+The recommended daily intake of vitamin D3 varies based on age, sex, and other factors, but generally ranges from 600-800 IU per day for adults.
Can I get enough vitamin D3 from food sources alone?
+While it is possible to obtain some vitamin D3 from food sources, such as fatty fish and fortified dairy products, many individuals may require supplementation to achieve optimal levels.
What are the potential side effects of vitamin D3 supplementation?
+Potential side effects of vitamin D3 supplementation include nausea, vomiting, and stomach cramps, but these are generally rare and occur at high doses.
In conclusion, vitamin D3 is a more effective and readily absorbed form of vitamin D compared to vitamin D2. While both forms can be effective in raising vitamin D levels, vitamin D3 is generally more effective in maintaining optimal levels and preventing related diseases. As a domain-specific expert, I recommend prioritizing vitamin D3 supplementation over vitamin D2, especially for individuals with limited sun exposure or certain medical conditions. By understanding the differences between vitamin D3 and D2, individuals can make informed decisions about their supplementation needs and maintain optimal vitamin D levels for overall health and well-being.